Quality of Service 80
Using DSCP values to provide QoS
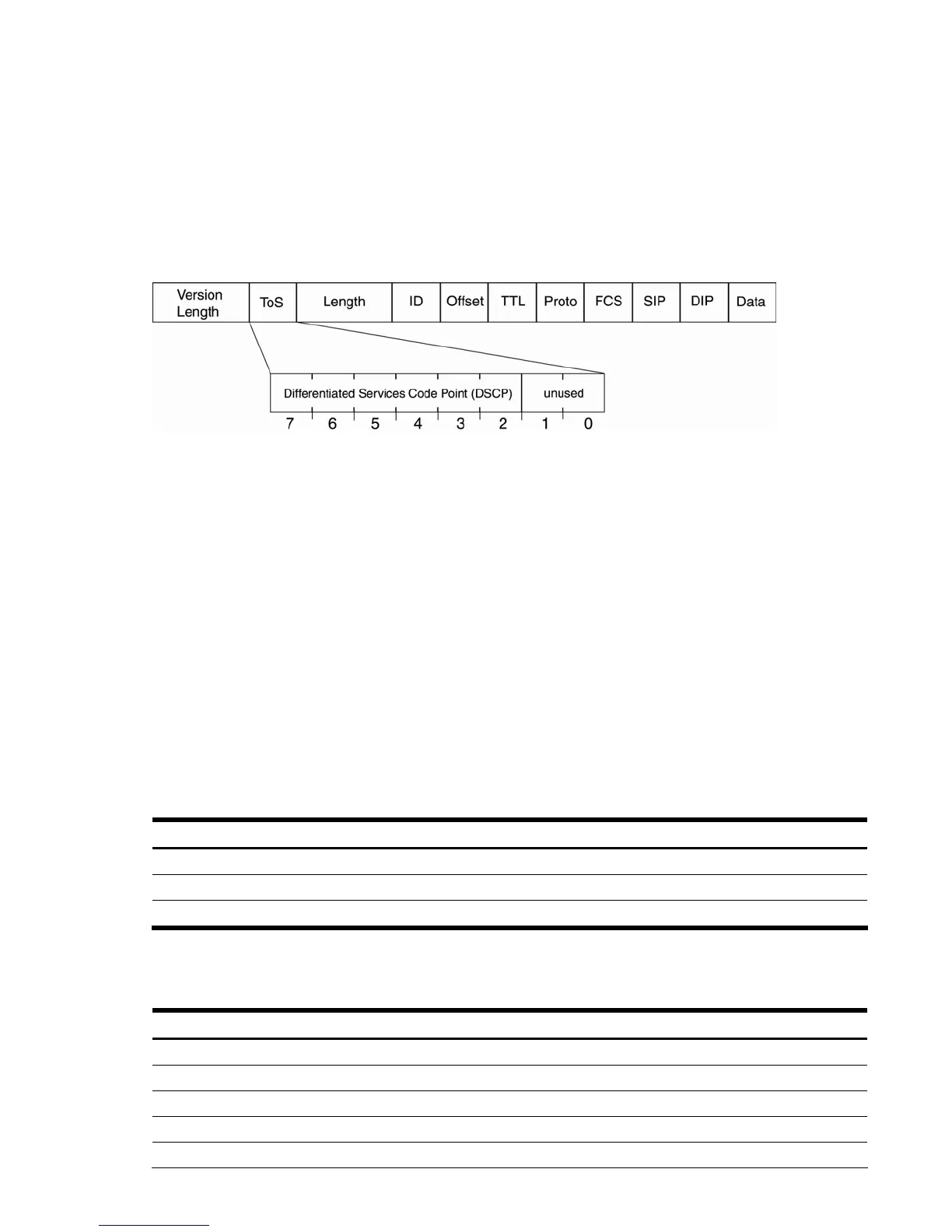
The six most significant bits in the TOS byte of the IP header are defined as DiffServ Code Points (DSCP). Packets are
marked with a certain value depending on the type of treatment the packet must receive in the network device. DSCP
is a measure of the Quality of Service (QoS) level of the packet.
Differentiated Services concepts
To differentiate between traffic flows, packets can be classified by their DSCP value. The Differentiated Services (DS)
field in the IP header is an octet, and the first six bits, called the DS Code Point (DSCP), can provide QoS functions.
Each packet carries its own QoS state in the DSCP. There are 64 possible DSCP values (0-63).
Figure 12 Layer 3 IPv4 packet
The GbE2c can perform the following actions to the DSCP:
• Read the DSCP value of ingress packets
• Re-mark the DSCP value to a new value
• Map the DSCP value to an 802.1p priority
Once the DSCP value is marked, the GbE2c can use it to direct traffic prioritization.
Per Hop Behavior
The DSCP value determines the Per Hop Behavior (PHB) of each packet. The PHB is the forwarding treatment given to
packets at each hop. QoS policies are built by applying a set of rules to packets, based on the DSCP value, as they
hop through the network.
The GbE2c default settings are based on the following standard PHBs, as defined in the IEEE standards:
• Expedited Forwarding (EF)—This PHB has the highest egress priority and lowest drop precedence level. EF
traffic is forwarded ahead of all other traffic. EF PHB is described in RFC 2598.
• Assured Forwarding (AF)—This PHB contains four service levels, each with a different drop precedence, as
shown below. Routers use drop precedence to determine which packets to discard last when the network
becomes congested. AF PHB is described in RFC 2597.
Table 18 Assured forwarding drop-down precedence
Drop Precedence Class 1 Class 2 Class 3 Class 4
Low AF11 (DSCP 10) AF21 (DSCP 18) AF31 (DSCP 26) AF41 (DSCP 34)
Medium AF12 (DSCP 12) AF22 (DSCP 20) AF32 (DSCP 28) AF42 (DSCP 36)
High AF13 (DSCP 14) AF23 (DSCP 22) AF33 (DSCP 30) AF43 (DSCP 38)
• Class Selector (CS)—This PHB has eight priority classes, with CS7 representing the highest priority, and CS0
representing the lowest priority, as shown below. CS PHB is described in RFC 2474.
Table 19 Class selector priority classes
Priority Class Selector DSCP
Highest CS7 56
CS6 48
CS5 40
CS4 32
CS3 24

 Loading...
Loading...















