10–19
FFT Setup
Setting Up FFT Span and Resolution
The FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) converts a time domain
waveform into frequency domain spectra similar to those of
an RF spectrum analyzer display. But unlike the analyzer,
which has controls for span and resolution bandwidth, FFT
span is determined by sampling rate, while resolution
bandwidth is inversely proportional to record length.
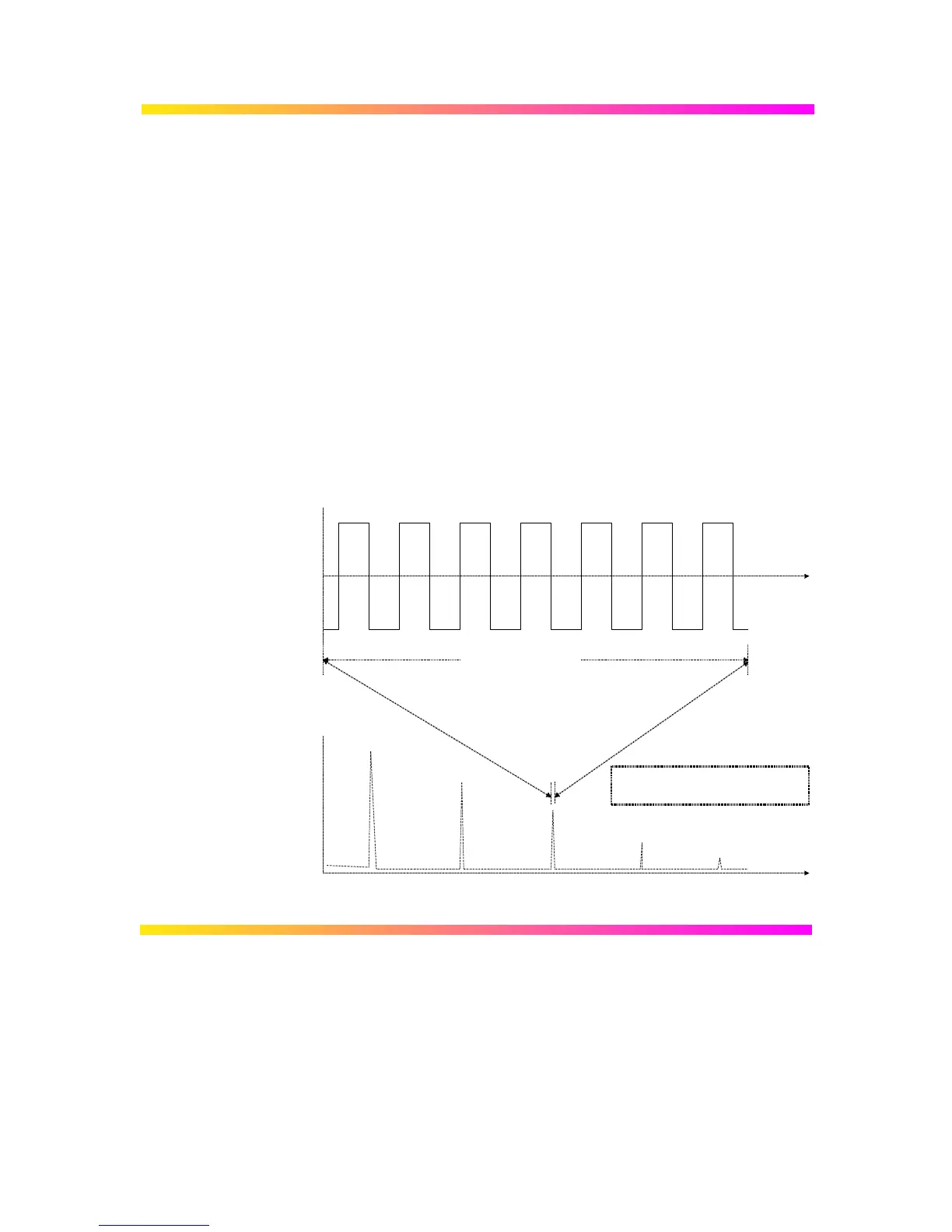
Frequency Resolution ∆f Correctly setting up an FFT starts with the frequency resolution,
or ∆f. This parameter is the spacing of samples in the frequency
domain display. The ∆f is set by inputting the time duration of
the time domain signal to the FFT. If an acquisition channel
(Channel 1 or 2, or 3 or 4) is the source, then the waveform
duration is the capture time: the TIME/DIV setting multiplied by
ten. The relationship between capture time and frequency
resolution is illustrated here.
TIME
CAPTURE TIME
= 10 X TIME / DIV
FREQUENCY
AMPLITUDEAMPLITUDE
∆
f
FREQUENCY
RESOLUTION
ACQUIRED WAVEFORM
FAST FOURIER TRANSFORM (FFT)
∆
f = 1/ CAPTURE TIME

 Loading...
Loading...





