Chapter 7 Counters
© National Instruments 7-13 X Series User Manual
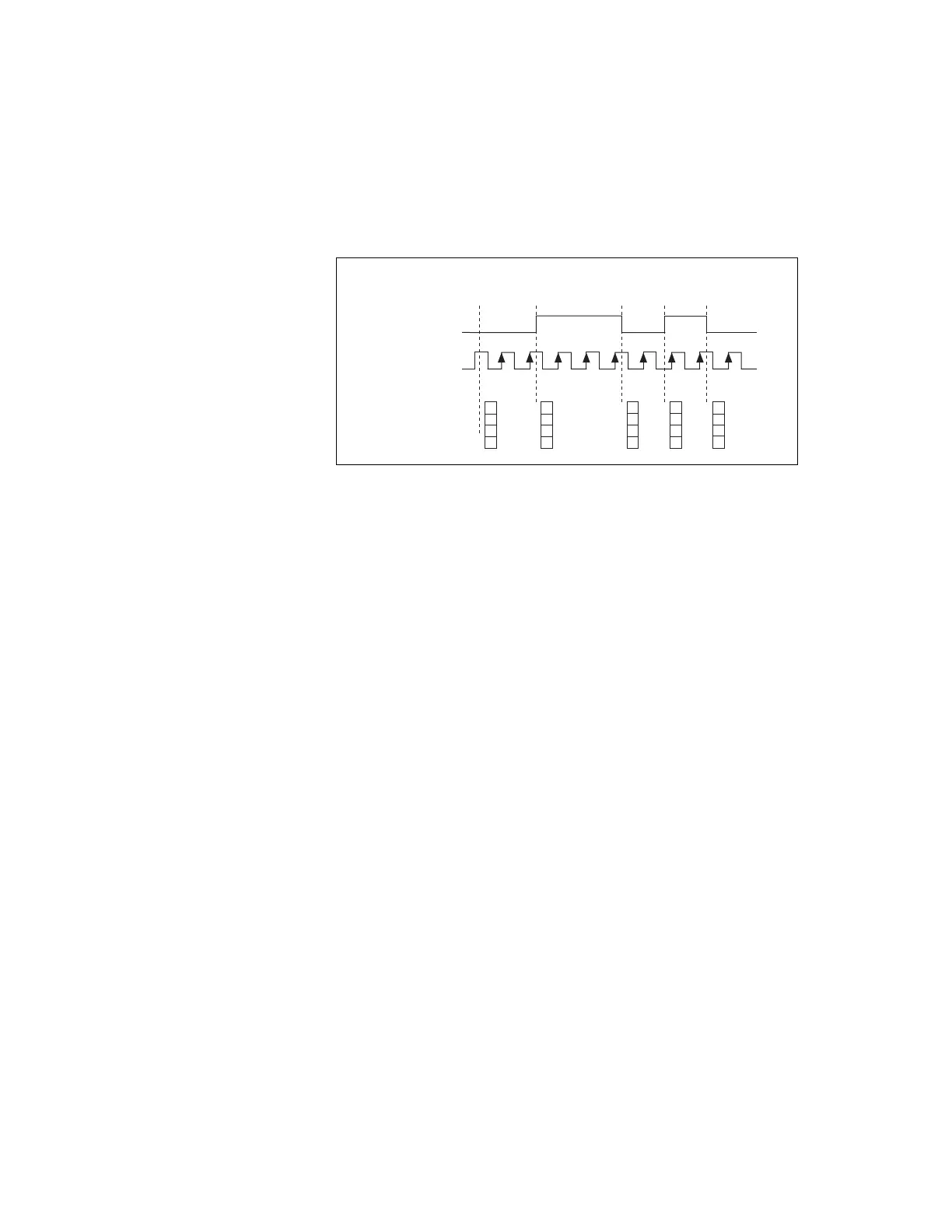
Figure 7-11 shows an example of an implicit buffered semi-period
measurement.
Figure 7-11. Implicit Buffered Semi-Period Measurement
For information about connecting counter signals, refer to the Default
Counter/Timer Pinouts section.
Frequency Measurement
You can use the counters to measure frequency in several different ways.
Refer to the following sections for information about X Series frequency
measurement options:
• Low Frequency with One Counter
• High Frequency with Two Counters
• Large Range of Frequencies with Two Counters
• Sample Clocked Buffered Frequency Measurement
• Hardware-Timed Single Point Frequency Measurement
Low Frequency with One Counter
For low frequency measurements with one counter, you measure one
period of your signal using a known timebase.
You can route the signal to measure (fx) to the Gate of a counter. You can
route a known timebase (fk) to the Source of the counter. The known
timebase can be an onboard timebase, such as 100 MHz Timebase, 20 MHz
Timebase, or 100 kHz Timebase, or any other signal with a known rate.
1
2
3
1
3
3
Source
Gate
Counter Value
Buffer
1 3
2
2
1 1
13
1 2
0
Counter
Armed
Starting
Edge
Artisan Technology Group - Quality Instrumentation ... Guaranteed | (888) 88-SOURCE | www.artisantg.com

 Loading...
Loading...











