Chapter 7 Counters
© National Instruments 7-37 X Series User Manual
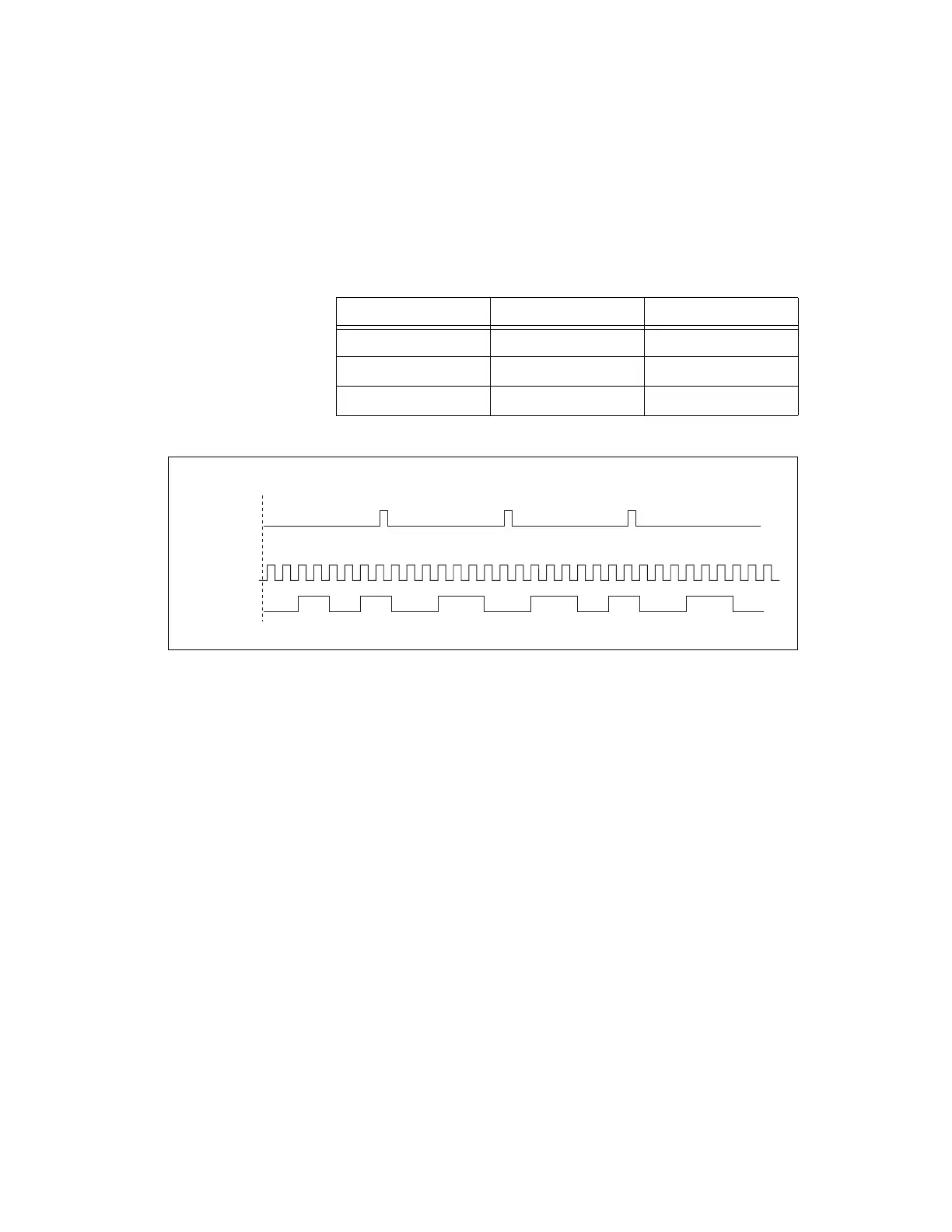
Table 7-7 and Figure 7-35 detail a finite sample clocked generation of
three samples where the pulse specifications from the create channel are
two ticks idle, two ticks active, and three ticks initial delay.
Figure 7-35. Finite Buffered Sample Clocked Pulse Train Generation
There are several different methods of continuous generation that control
what data is written. These methods are regeneration, FIFO regeneration
and non-regeneration modes.
Regeneration is the repetition of the data that is already in the buffer.
Standard regeneration is when data from the PC buffer is continually
downloaded to the FIFO to be written out. New data can be written to
the PC buffer at any time without disrupting the output. With FIFO
regeneration, the entire buffer is downloaded to the FIFO and regenerated
from there. Once the data is downloaded, new data cannot be written to the
FIFO. To use FIFO regeneration, the entire buffer must fit within the FIFO
size. The advantage of using FIFO regeneration is that it does not require
communication with the main host memory once the operation is started,
thereby preventing any problems that may occur due to excessive bus
traffic.
Table 7-7. Finite Buffered Sample Clocked Pulse Train Generation
Sample Idle Ticks Active Ticks
1 3 3
2 2 2
3 3 3
Source
Out
Counter Armed
Sample
Clock
Counter
Load Values
2 101 01 01 2 10 2100 21021010 02102110
3 222 33 332 332
Artisan Technology Group - Quality Instrumentation ... Guaranteed | (888) 88-SOURCE | www.artisantg.com

 Loading...
Loading...











