Routing
The routing pages provide options for firewall, port forwarding, port triggering, DMZ, packet filtering, MAC filtering, domain filtering,
static routing, RIP and URL blocking.
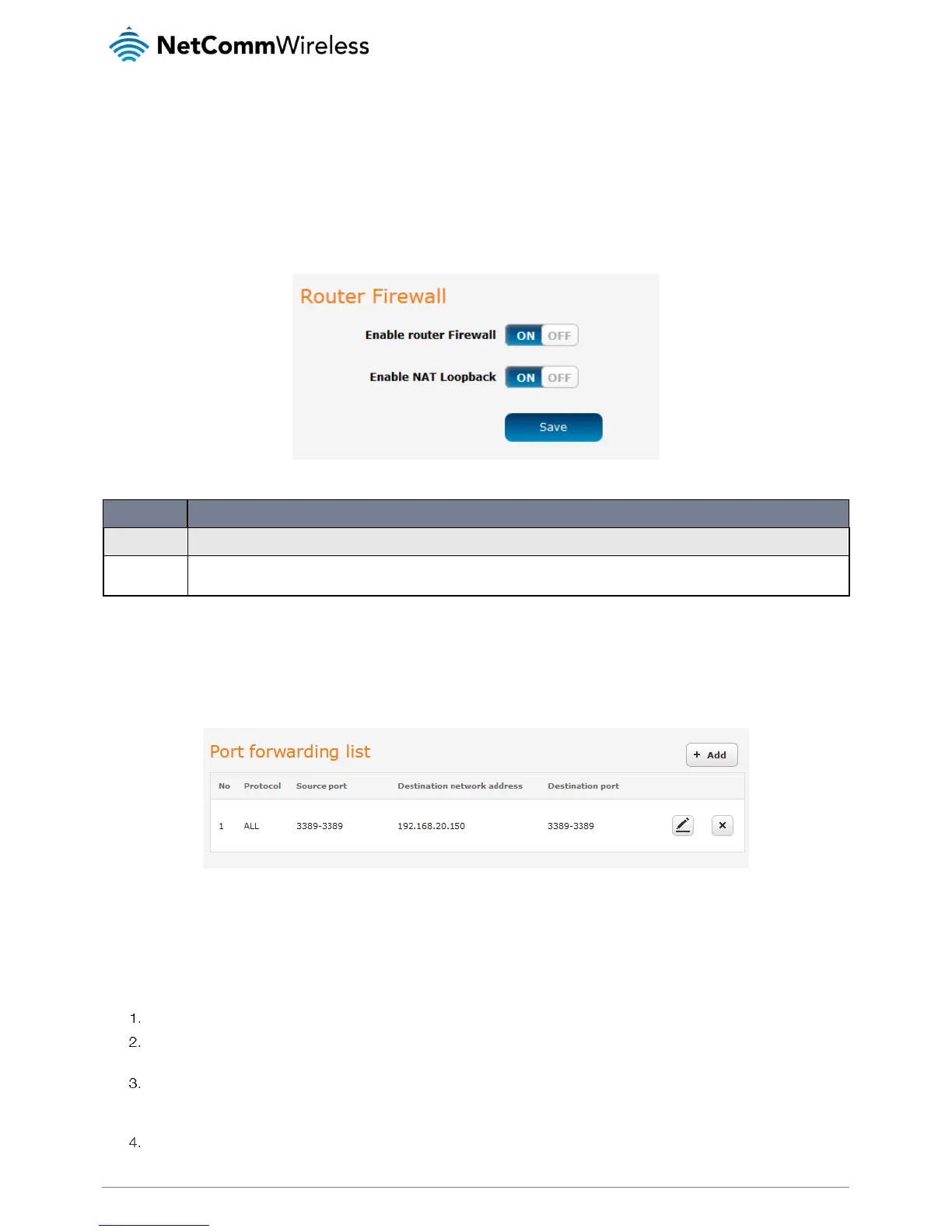
Router firewall
This page provides options for the built-in firewall of the router. To access the Router firewall page, click on Networking, Routing
and then Router firewall.
Figure 17 - Router firewall
Enables or disables the NAT loopback feature. NAT loopback allows a local machine to access a service via the public IP address from inside the
network. For example, a web server operated on a machine inside the network can be access locally by another machine via the use of NAT
loopback using the public address.
Table 11 - Router firewall
Port forwarding
The Port forwarding list is used to configure the Network Address Translation (NAT) rules currently in effect on the router. To access
the Port forwarding page, click on the Networking menu at the top of the screen, click on the Routing menu on the left, then click
on the Port forwarding menu item.
Figure 18 – Port forwarding list
The purpose of the port forwarding feature is to allow mapping of inbound requests to a specific port on the WAN IP address to a
device connected on the Ethernet interface.
Adding a port forwarding rule
To create a new port forwarding rule:
Click the +Add button. The port forwarding settings screen is displayed.
Use the Protocol drop down list to select the type of protocol you want to use for the rule. The protocols selections
available are TCP, UDP and All.
The Source port range (From) and (To) fields are used to specify the port(s) on the source side that are to be forwarded.
This allows you to send a range of consecutive port numbers by entering the first in the range in the (From) field and the
last in the range in the (To) field. To forward a single port, enter the port in the (From) field and repeat it in the (To) field.
In the Destination network address field, enter the IP address of the client to which the traffic should be forwarded.

 Loading...
Loading...