Planning wireless systems
105542_en_05 PHOENIX CONTACT 129 / 198
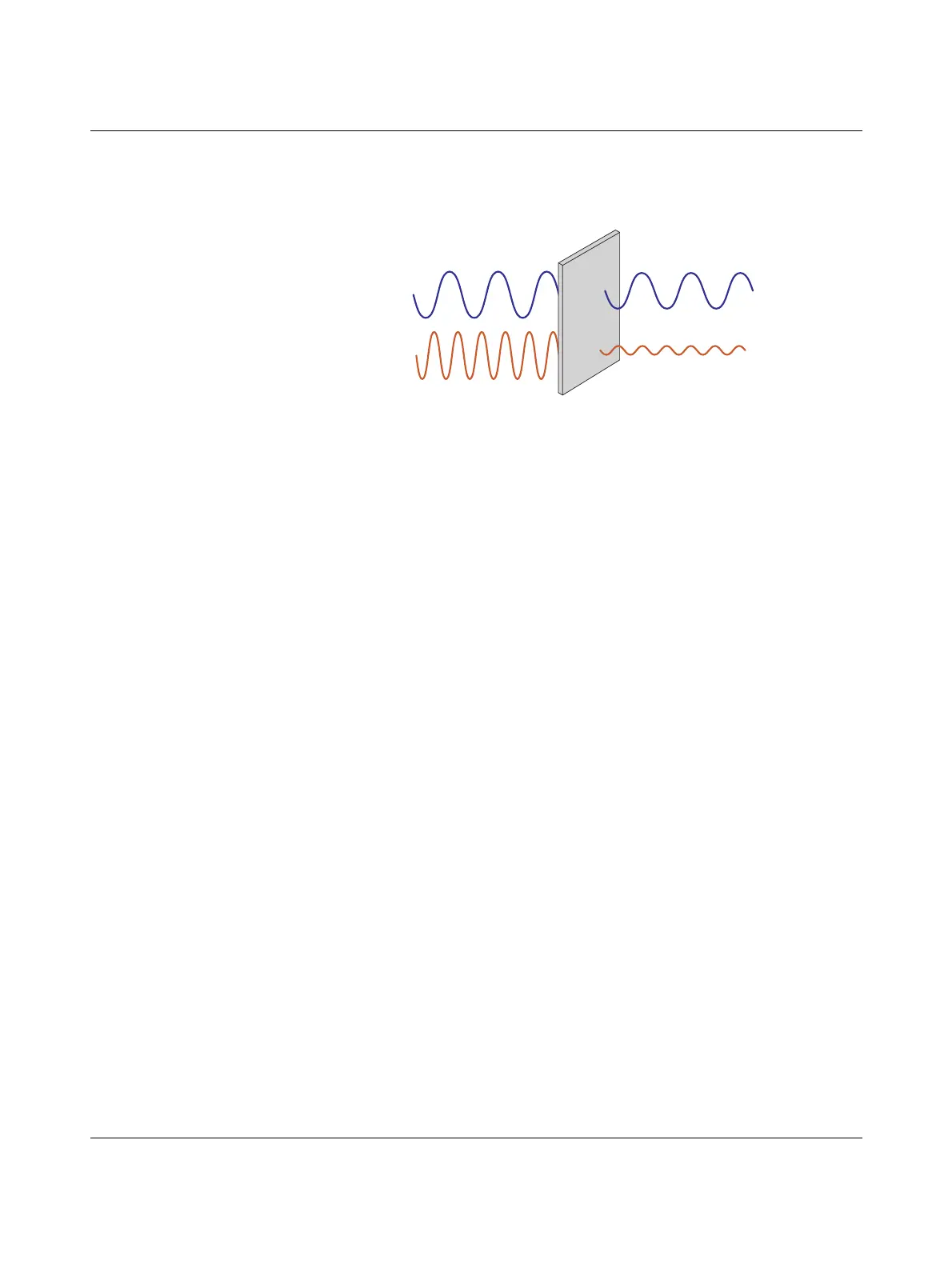
2.4 GHz and 868 MHz wireless systems have different characteristics due to the wave-
length. Lower frequencies can overcome obstacles more easily. They also support longer
ranges.
Figure 8-1 Penetration of obstacles at different frequencies
The 2.4 GHz and 868 MHz frequency bands are subject to various directives. 20 dBm
(100 mW) maximum may be transmitted in the 2.4 GHz frequency band. In the 868 MHz fre-
quency band, the transmission power may reach 27 dBm (500 mW). Due to the higher
transmission power in the 868 MHz frequency band, longer ranges can also be achieved.
Duty cycle in the 868 MHz band
The duty cycle or holding period refers to the legally regulated period of use for the
869.4 MHz ... 869.65 MHz frequency band. The aim of this regulation is to ensure the func-
tion of all devices operating in this frequency band. The maximum transmission time is 10%
of one hour (6 minutes). Usually, the duty cycle is not reached during operation, since only
low volumes of data are transmitted.

 Loading...
Loading...