4.32
9926813 R04 - 2013-2016 RZR 570 Service Manual
© Copyright Polaris Industries Inc.
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR (CPS)
OPERATION OVERVIEW
Mounted on top of the stator cover, the crankshaft
position sensor is essential to engine operation,
constantly monitoring the rotational speed (RPM) and
position of the crankshaft.
A ferromagnetic 35-tooth encoder ring with a missing
tooth is built onto the flywheel. The inductive speed
sensor is mounted 1.0 ± 0.26 mm (0.059 ± 0.010 in.)
away from the encoder ring. During rotation, an AC pulse
is created within the sensor for each passing tooth. The
ECU calculates engine speed from the time interval
between the consecutive pulses.
The encoder ring missing tooth creates an “interrupt”
input signal, corresponding to specific crankshaft
position. This signal serves as a reference for the control
of ignition timing by the ECU. Synchronization of the
CPS and crankshaft position takes place during the first
two revolutions each time the engine is started. This
sensor must be properly connected at all times. If the
sensor fails or becomes disconnected for any reason, the
engine will stop running.
CPS TEST
The CPS is a sealed, non-serviceable assembly. If fault
code diagnosis indicates a problem with this sensor, test
as follows:
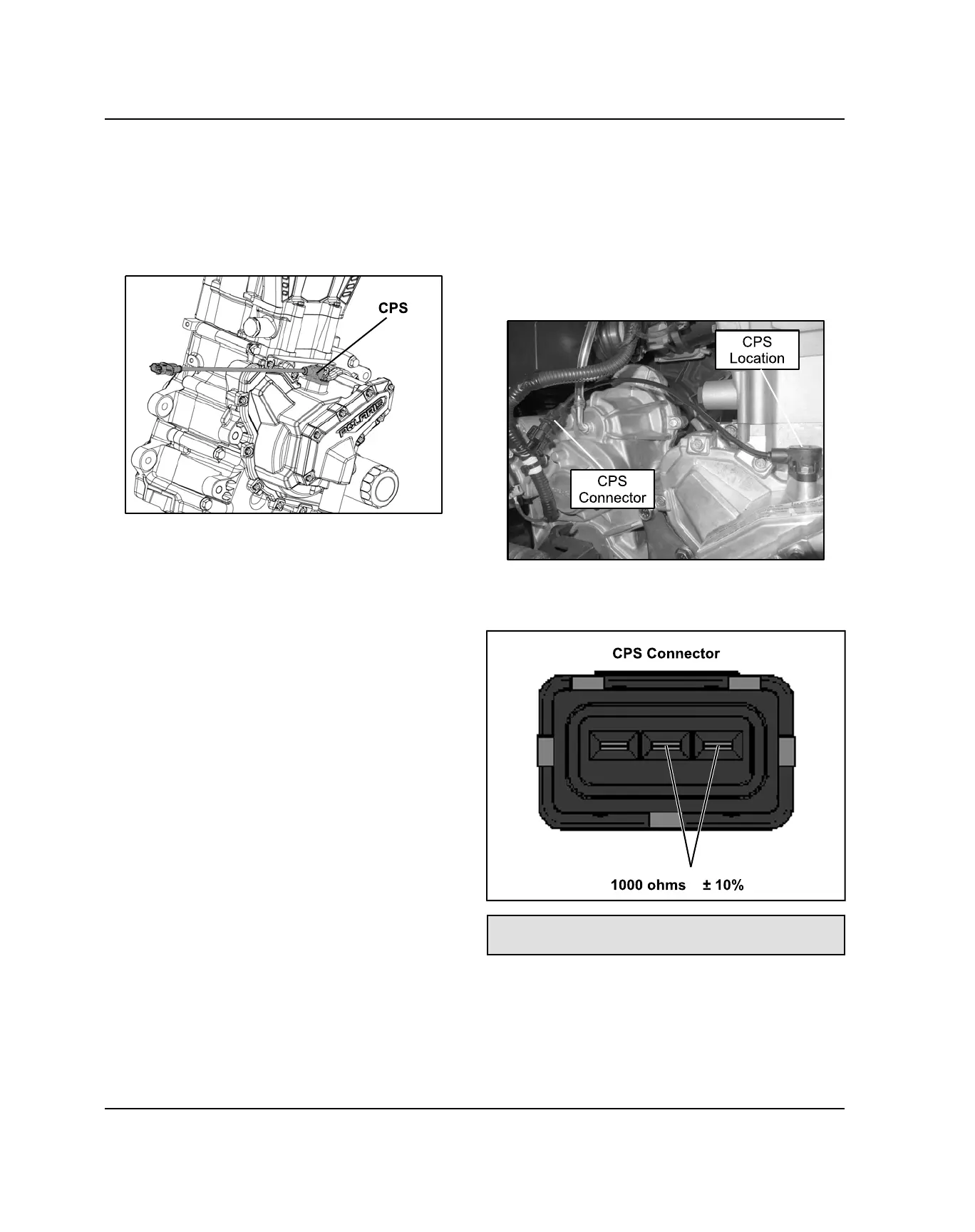
1. The CPS is accessible through the right-hand rear
wheel well area.
2. Disconnect CPS harness connector.
3. Connect an ohmmeter between the CPS pin
terminals shown below. A resistance value of 1000 Ω
± 10% at room temperature should be obtained.
CPS Resistance Specification:
1000 Ω ± 10%
FUEL SYSTEM

 Loading...
Loading...











