Click the Next button to go to the next page and Click the Previous button to return the previous
page.
4.9 Forwarding
There are four submenus under the Forwarding menu: Virtual Servers, Port Triggering, DMZ
and UPnP. Click any of them, and you will be able to configure the corresponding function.
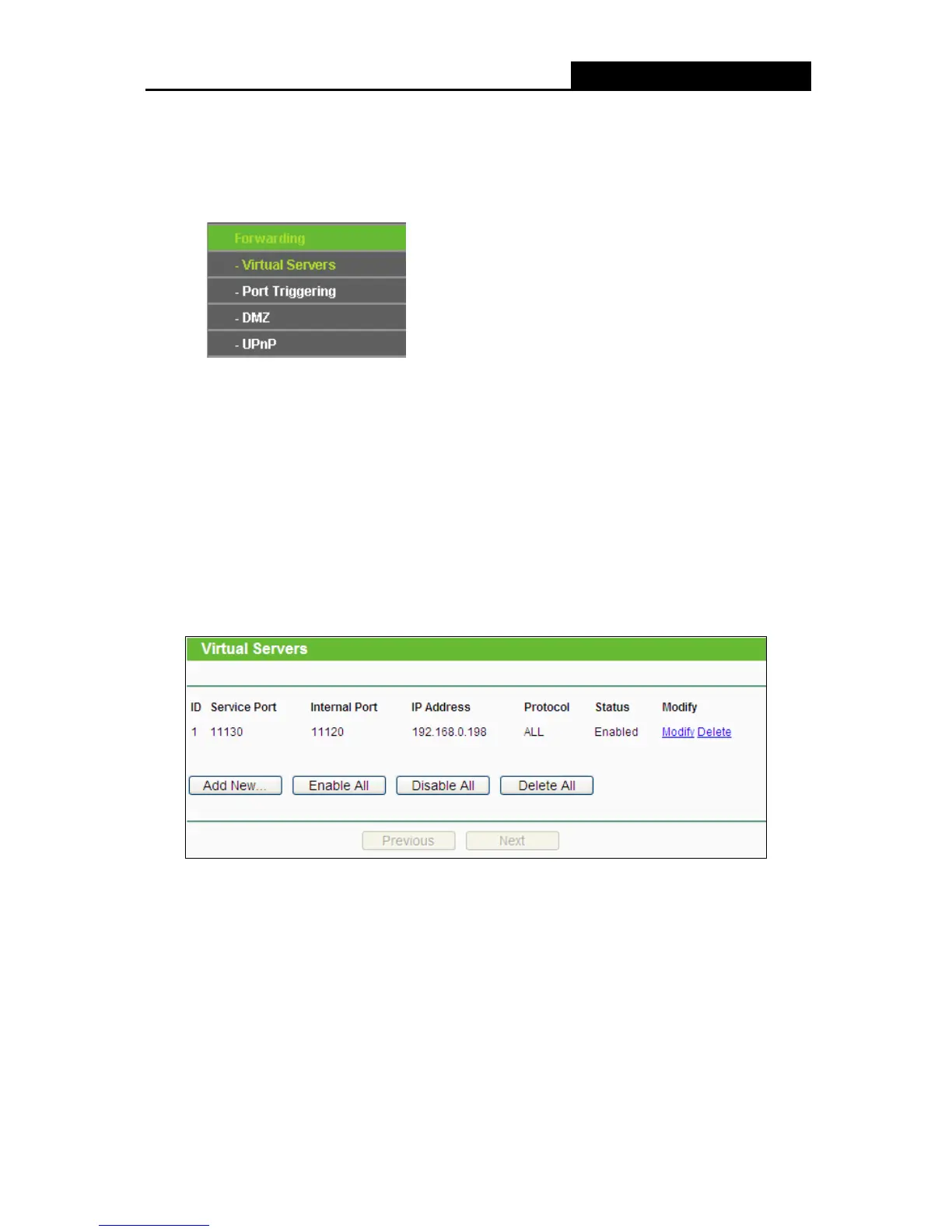
4.9.1 Virtual Servers
Choose menu “Forwarding > Virtual Servers”, you can view and add virtual servers in the next
screen. Virtual servers can be used for setting up public services on your LAN, such as DNS,
Email and FTP. A virtual server is defined as a service port, and all requests from the Internet to
this service port will be redirected to the computer specified by the server IP. Any PC that was
used for a virtual server must have a static or reserved IP Address because its IP Address may
be changed when using the DHCP function.
Service Port - The numbers of External Ports. You can type a service port or a range of
service ports (in XXX – YYY format, XXX is the start port number, YYY is the end port
number).
Internal Port - The Internal Service Port number of the PC running the service application.
You can leave it blank if the Internal Port is the same as the Service Port, or enter a
specific port number when Service Port is a single one.
IP Address - The IP Address of the PC providing the service application.
Protocol - The protocol used for this application, either TCP, UDP, or All (all protocols
supported by the router).
Status - The status of this entry either Enabled or Disabled.
-47-

 Loading...
Loading...











