Note:
If you set the service port of the virtual server as 80, you must set the Web management port on
System Tools > Remote Management page to be any other value except 80 such as 8080.
Otherwise there will be a conflict to disable the virtual server.
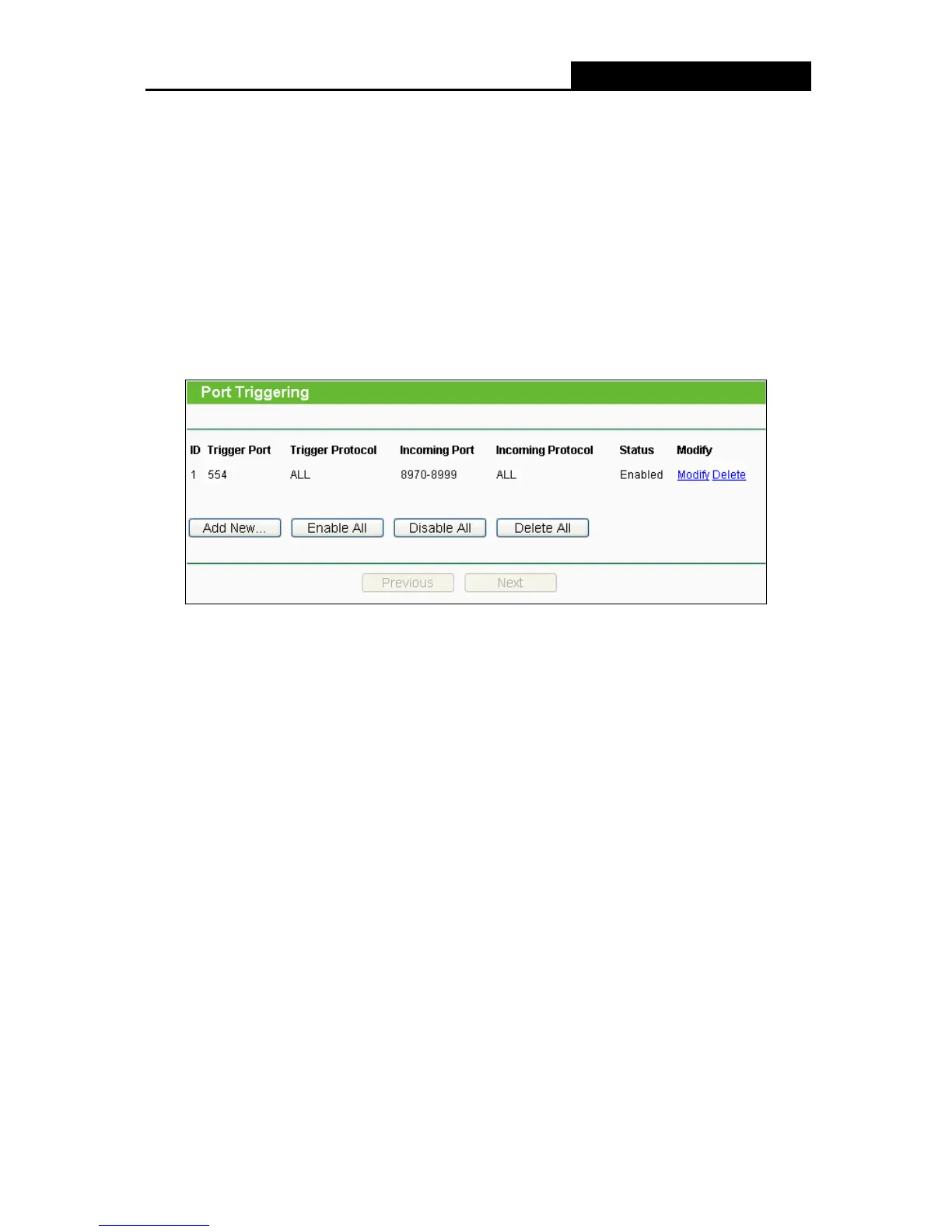
4.9.2 Port Triggering
Choose menu “Forwarding > Port Triggering”, you can view and add port triggering in the next
screen. Some applications require multiple connections, like Internet games, video conferencing,
Internet calling and so on. These applications cannot work with a pure NAT router. Port Triggering
is used for some of these applications that can work with an NAT router.
Once the router is configured, the operation is as follows:
1. A local host makes an outgoing connection using a destination port number defined in the
Trigger Port field.
2. The router records this connection, opens the incoming port or ports associated with this
entry in the Port Triggering table, and associates them with the local host.
3. When necessary the external host will be able to connect to the local host using one of the
ports defined in the Incoming Ports field.
Trigger Port - The port for outgoing traffic. An outgoing connection using this port will
"Trigger" this rule.
Trigger Protocol - The protocol used for Trigger Ports, either TCP, UDP, or All (all
protocols supported by the router).
Incoming Port - The port or port range used by the remote system when it responds to the
outgoing request. A response using one of these ports will be forwarded to the PC that
triggered this rule. You can input at most 5 groups of ports (or port section). Every group of
ports must be set apart with ",". For example, 2000-2038, 2050-2051, 2085, 3010-3030.
Incoming Protocol - The protocol used for Incoming Ports Range, either TCP or UDP, or
ALL (all protocols supported by the router).
Status - The status of this entry either Enabled or Disabled.
-49-

 Loading...
Loading...











