Theory of Operation B-11
If a soft X-ray Neutralizer (Model 3088) is installed in the Classifier 3082,
the same equations (B-2 and B-3) are used to calculate the charge
fractions. The coefficients and the ion mobility ratio differ in this case (see
above and Table B-3).
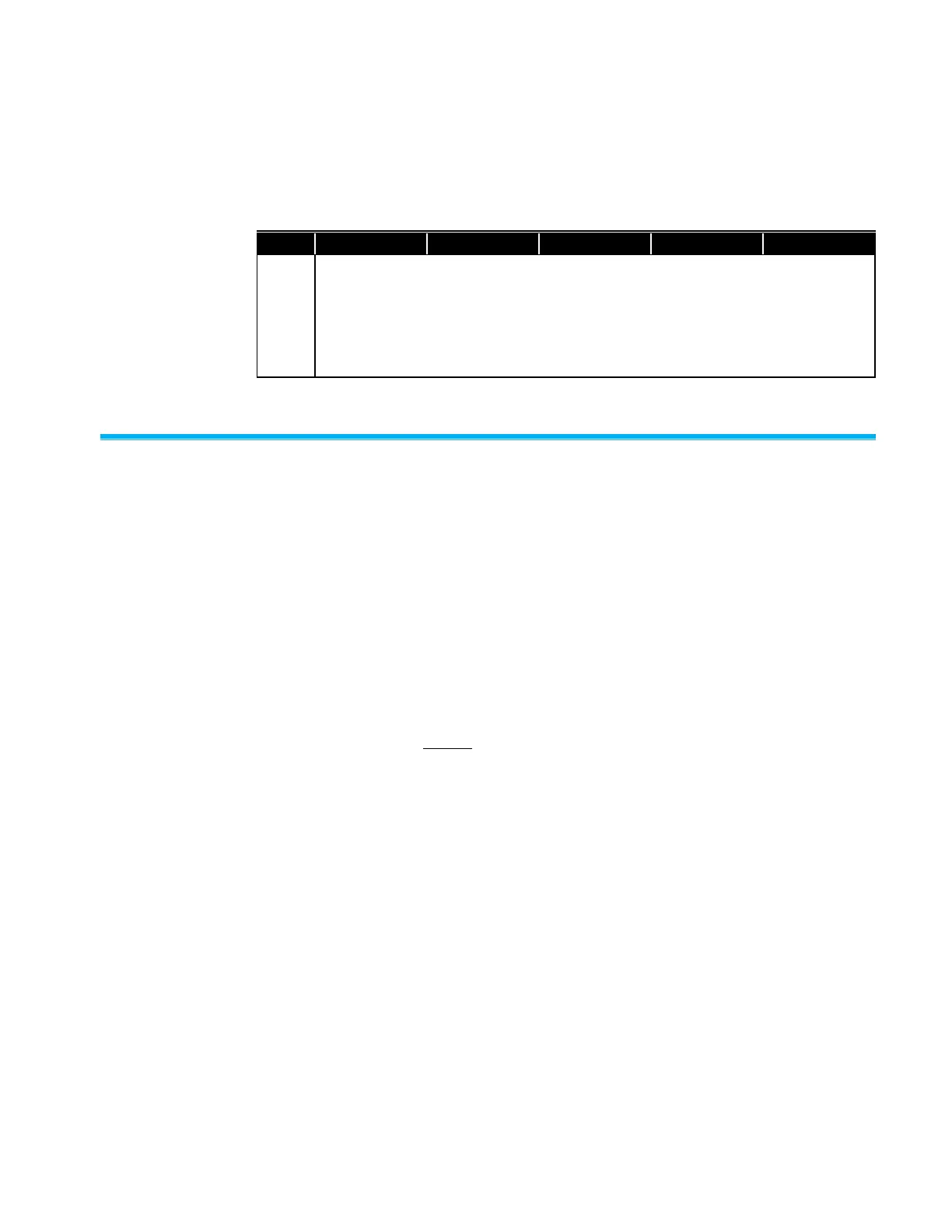
Table B-3
Coefficients for Equation B-2 used for soft X-ray Neutralizer (Model 3088), from Knobel et al. (2013)
Partic l e M obility Th e o ry
As mentioned previously, only particles with a narrow range of electrical
mobilities are extracted by the DMA to be measured by a particle sensor.
To determine the particle size associated with this range of mobilities, the
definition of particle electrical mobility must be examined.
An aerosol particle in an electric field, E, carrying n electric charges
experiences an electrical force, causing it to move through the gas in which
it is suspended. It very quickly reaches its terminal velocity, v. The resulting
drag force on the particle is given by Stokes law and can be equated to the
electrical force to determine the electrical mobility of a particle. The
electrical mobility, then, is a measure of the particle's ability to move in an
electric field. The electrical mobility, Z
p
, is defined by the equation B-4:
Equation B-4

 Loading...
Loading...