Speed Control Speed Mode Speed Regulation 2-139
Speed Control
Speed Mode
Speed Regulation
The purpose of speed regulation is to allow the drive to adjust certain
operating conditions, such as output frequency, to compensate for actual
motor speed losses in an attempt to maintain motor shaft speed within the
specified regulation percentage.
The [Speed Mode] parameter selects the speed regulation method for the
drive, and can be set to one of 3 choices on the PowerFlex 70. Additional
choices are available on the PowerFlex 700 (see
page 2-142):
• Open Loop - No speed control is offered
• Slip Comp - Slip Compensation is active – approximately 5% regulation
• Process PI – The PI Loop sets the actual speed based on process
variables
Open Loop
As the load on an induction motor increases, the rotor speed or shaft speed
of the motor decreases, creating additional slip (and therefore torque) to
drive the larger load. This decrease in motor speed may have adverse effects
on the process. If the [Speed Mode] parameter is set to “Open Loop,” no
speed control will be exercised. Motor speed will be dependent on load
changes and the drive will make no attempt to correct for increasing or
decreasing output frequency due to load.
Slip Compensation
As the load on an induction motor increases, the rotor speed or shaft speed
of the motor decreases, creating additional slip (and therefore torque) to
drive the larger load. This decrease in motor speed may have adverse effects
on the process. If speed control is required to maintain proper process
control, the slip compensation feature of the PowerFlex drives can be
enabled by the user to more accurately regulate the speed of the motor
without additional speed transducers.
When the slip compensation mode is selected, the drive calculates an
amount to increase the output frequency to maintain a consistent motor
speed independent of load. The amount of slip compensation to provide is
selected in [Slip RPM @ FLA]. During drive commissioning this parameter
is set to the RPM that the motor will slip when operating with Full Load
Amps. The user may adjust this parameter to provide more or less slip.
As mentioned above, induction motors exhibit slip which is the difference
between the stator electrical frequency, or output frequency of the drive, and
the induced rotor frequency.
The slip frequency translates into a slip speed resulting in a reduction in
rotor speed as the load increases on the motor. This can be easily seen by
examining
Figure 2.16.
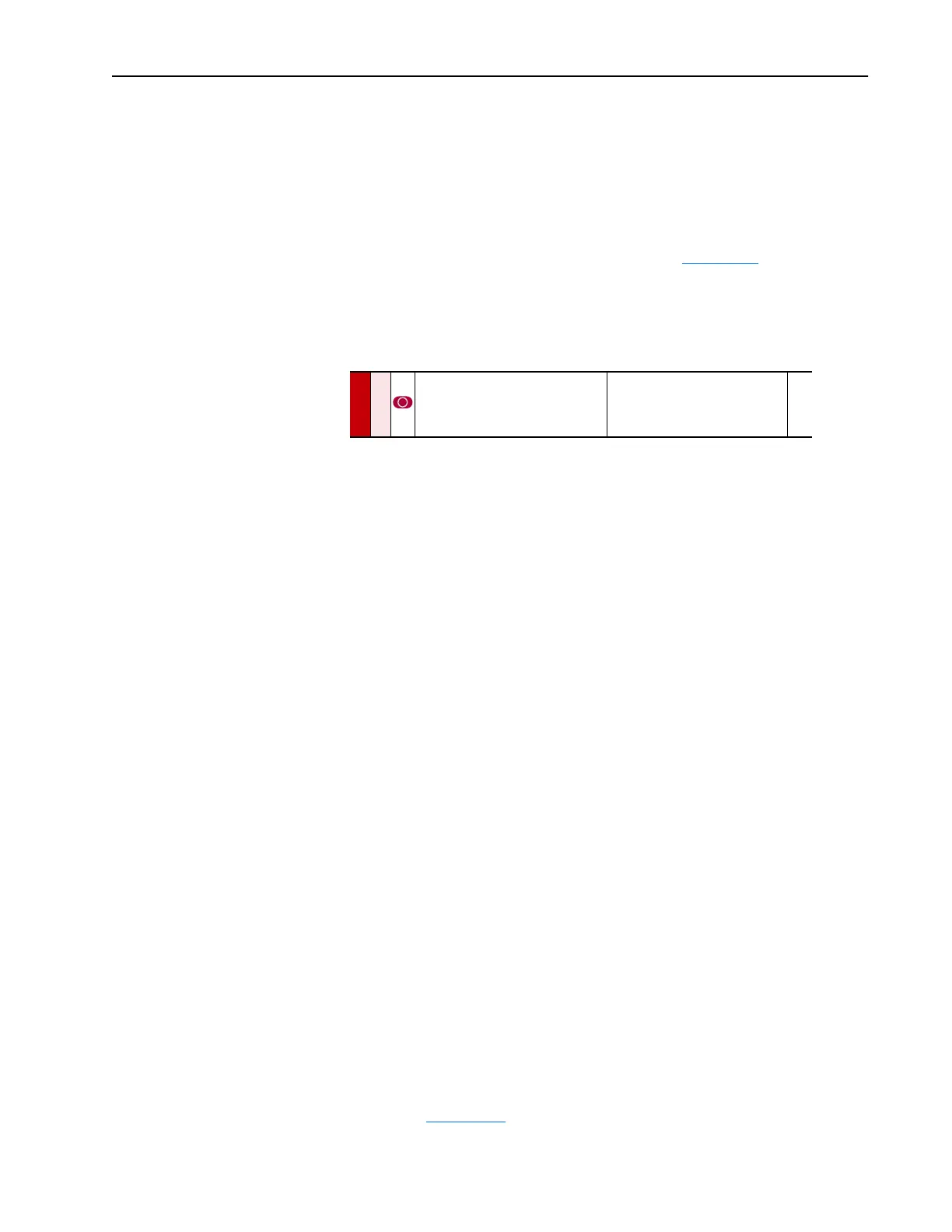
080 [Speed Mode]
Sets the method of speed regulation.
Default:
Options:
0
0
1
2
“Open Loop”
“Open Loop”
“Slip Comp”
“Process PI”
121
thru
138

 Loading...
Loading...











