39-3
Catalyst 3750 Switch Software Configuration Guide
OL-8550-02
Chapter 39 Configuring HSRP and Enhanced Object Tracking
Understanding HSRP
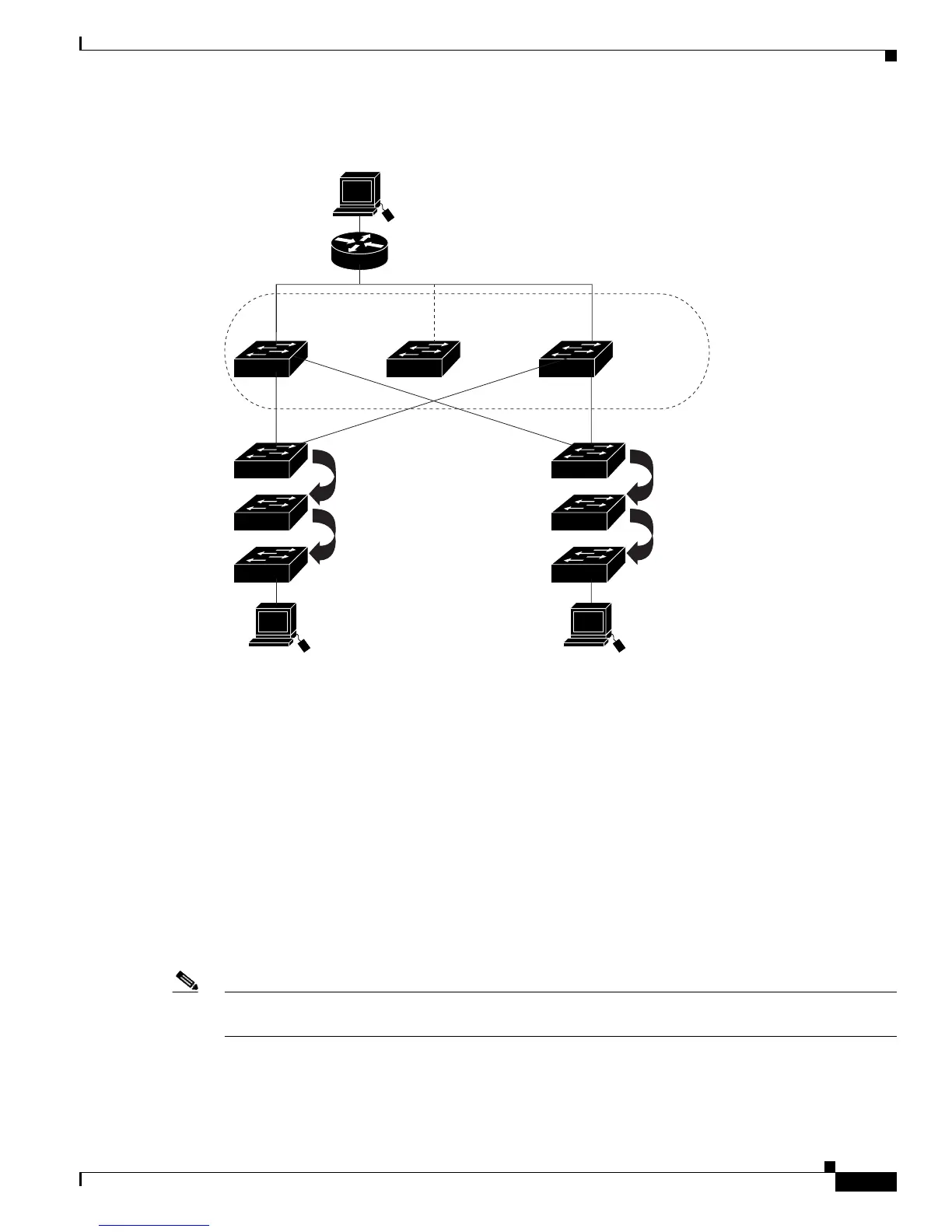
Figure 39-1 Typical HSRP Configuration
Multiple HSRP
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(18)SE and above supports Multiple HSRP (MHSRP), an extension of HSRP that
allows load sharing between two or more HSRP groups. You can configure MHSRP to achieve load
balancing and to use two or more standby groups (and paths) from a host network to a server network.
In Figure 39-2, half of the clients are configured for Router A, and half of the clients are configured for
Router B. Together, the configuration for Routers A and B establish two HSRP groups. For group 1,
Router A is the default active router because it has the assigned highest priority, and Router B is the
standby router. For group 2, Router B is the default active router because it has the assigned highest
priority, and Router A is the standby router. During normal operation, the two routers share the IP traffic
load. When either router becomes unavailable, the other router becomes active and assumes the
packet-transfer functions of the router that is unavailable.
See the “Configuring MHSRP” section on page 39-9 for the example configuration steps.
Note For MHSRP, you need to enter the standby preempt interface configuration command on the HSRP
interfaces so that if a router fails and then comes back up, preemption occurs and restores load sharing
Host B
172.20.130.5
172.20.128.32
Host A
172.20.128.55
172.20.128.1 172.20.128.3 172.20.128.2
Virtual
router
Active
router
Standby
router
Router A Router B
101361
Host C

 Loading...
Loading...











