119
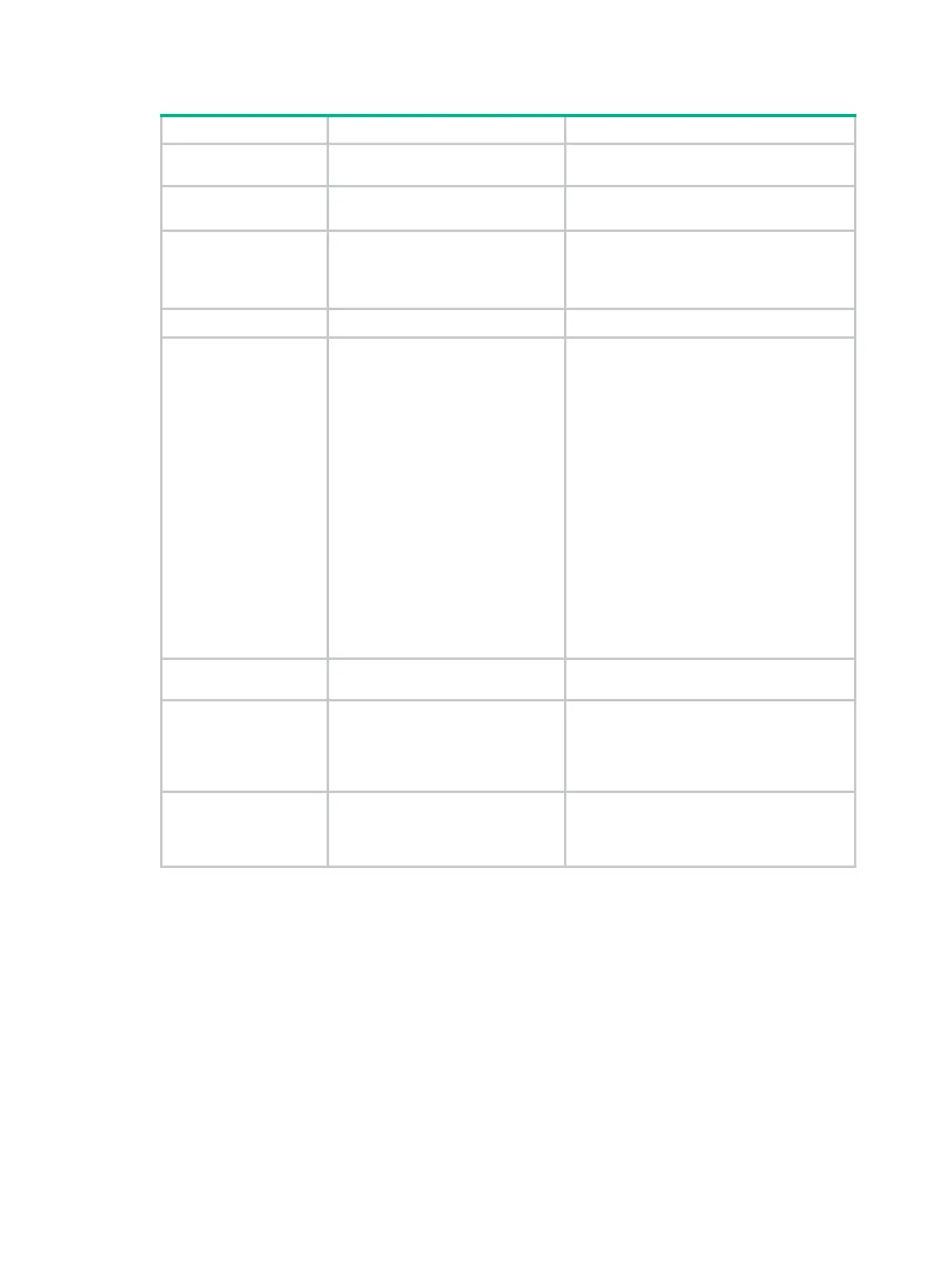
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system
view.
system-view
N/A
2. Enter VLAN view.
vlan
vlan-id
If the specified VLAN does not exist, this
command creates the VLAN first.
3. Create a protocol
template for the
VLAN.
protocol-vlan
[ protocol-index ]
{
at
|
ipv4
|
ipv6
|
ipx ethernetii
|
mode
{
ethernetii
etype
etype-id |
snap
etype
etype-id } }
Not configured by default.
4. Exit VLAN view.
quit
N/A
5. Enter interface
view or port group
view.
• Enter Layer 2 Ethernet
interface view:
interface interface-type
interface-number
• Enter Layer 2 aggregate
interface view:
interface
bridge-aggregation
interface-number
• Enter port group view:
port-group manual
port-group-name
Use any command.
• The configuration made in Ethernet
interface view applies only to the port.
• The configuration made in port group
view applies to all ports in the port
group.
• The configuration made in Layer 2
aggregate interface view applies to
the aggregate interface and its
aggregation member ports. If the
system fails to apply the configuration
to the aggregate interface, it stops
applying the configuration to
aggregation member ports. If the
system fails to apply the configuration
to an aggregation member port, it
skips the port and moves to the next
member port.
6. Configure the port
link type as hybrid.
port link-type
hybrid
By default, all ports are access ports.
7. Assign the hybrid
port to the
specified
protocol-based
VLANs.
port hybrid
vlan
vlan-list {
tagged
|
untagged
}
By default, a hybrid port is only in VLAN 1.
8. Assign the
protocol template
you have created
to the hybrid port.
port hybrid protocol-vlan
vlan
vlan-id { protocol-index [
to
protocol-end ] |
all
}
N/A
Protocol-based VLAN configuration example
Network requirements
In a lab environment, as shown in Figure 37, most hosts run the IPv4 protocol, and the rest of the
hosts run the IPv6 protocol for teaching purposes. To avoid interference, isolate IPv4 traffic and IPv6
traffic at Layer 2.
 Loading...
Loading...











