two different clusters of the disk array, and give each host group access to separate but identical
LUNs. This arrangement minimizes the shared components among the four paths, providing both
mirroring and greater failure protection.
NOTE: For the highest level of availability and fault tolerance, HP recommends the use of two
XP7 disk arrays, one for the Primary disks and one for the Mirror disks.
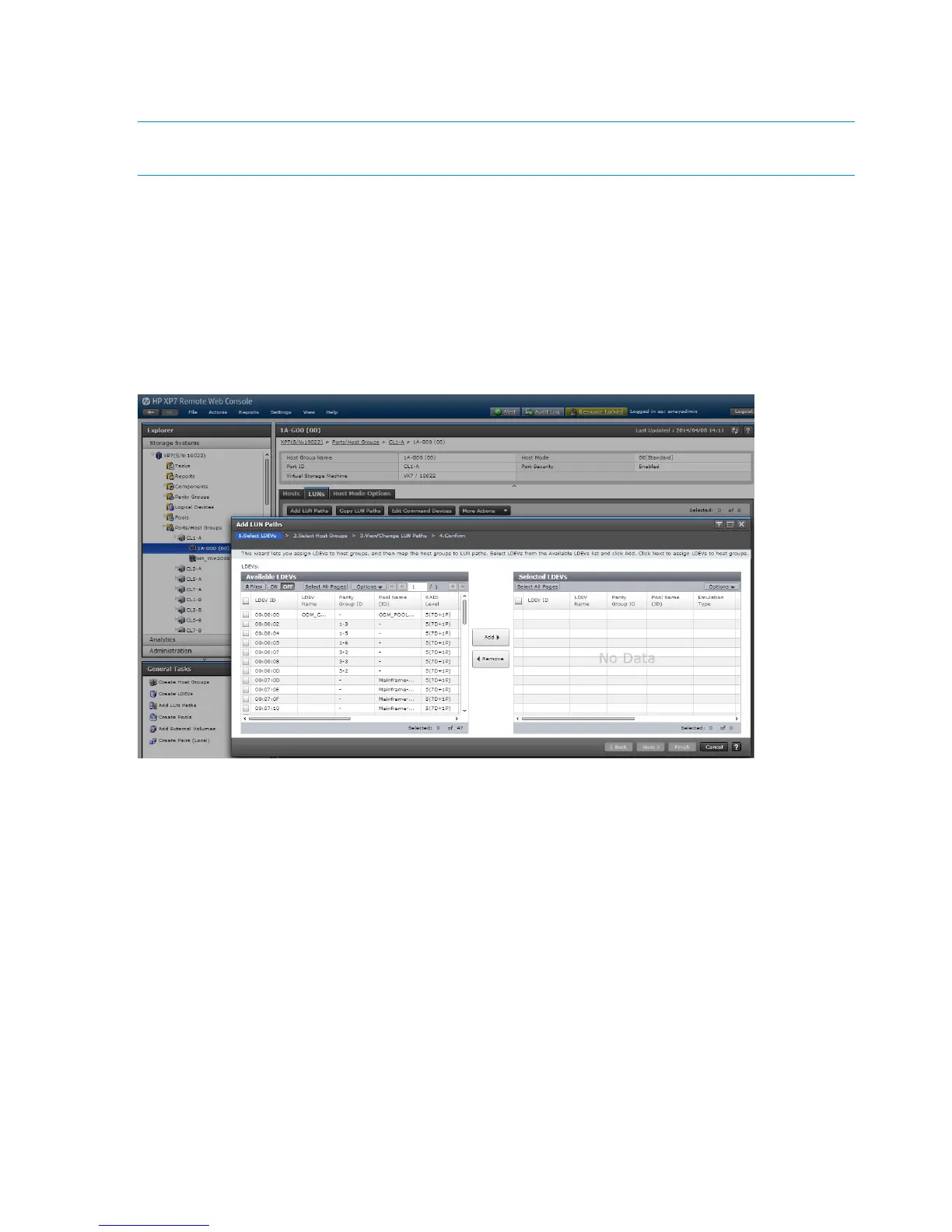
This process is also called “LUN mapping.”
In the XP7 Remote Web Console, LUN mapping includes:
• Configuring ports
• Enabling LUN security on the ports
• Creating host groups
• Assigning Fibre Channel ServerNet adapter WWNs to host groups
• Mapping volumes (LDEVs) to host groups (by assigning LUNs)
In XP7 Command View Advanced Edition, LUN mapping includes:
• Configuring ports
• Creating storage groups
• Mapping volumes and WWN/host access permissions to the storage groups
For details, see HP XP7 Provisioning for Open Systems User Guide.
Record the LUNS and their ports, WWNs, nicknames, and LDEVs. This information will be used
later to verify host and device configuration.
Setting the host mode and host group mode for the disk array ports
After the disk array is installed, you must set the host mode for each host group that is configured
on a disk array port to match the host OS. Set the host mode using LUN Manager in the XP7
Remote Web Console (shown) or XP7Command View Advanced Edition Software. If these are not
available, the HP service representative can set the host mode using the SVP. The host mode for
NonStop is 0C or 2C. Use host mode 2C if you plan to use LUN size expansion (LUSE).
36 NonStop
 Loading...
Loading...