Model 6517A Getting Started Manual Measurement Options 2-17
Figure 2-5
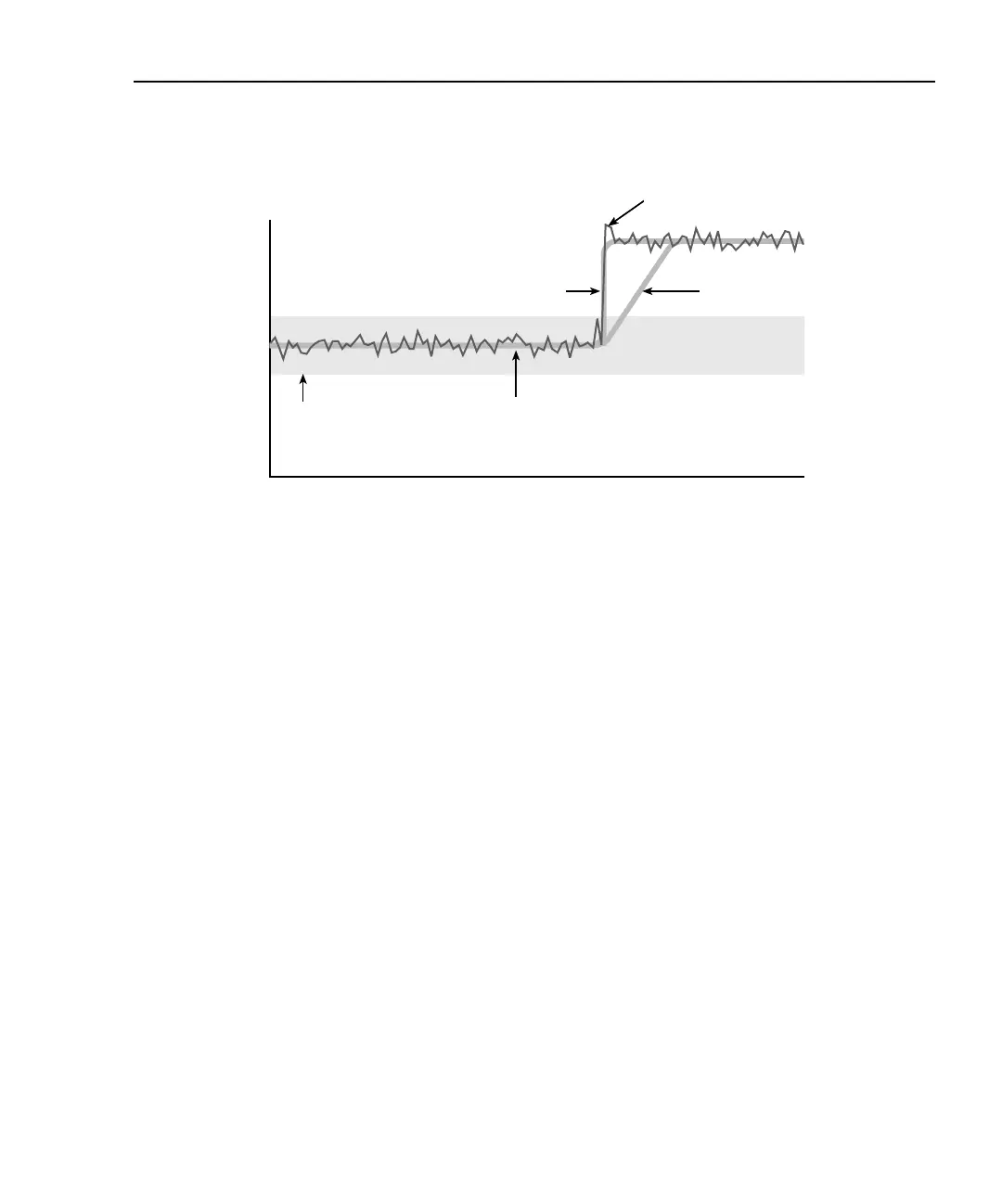
Filter response/noise window
Filter modes
There are two filter modes: moving or repeating. The moving filter uses a first-in, first-out
stack. When the stack becomes full, the measurement conversions are averaged, yielding a
reading. For each subsequent conversion, the new conversion is placed into the stack, the
oldest conversion is discarded, and a new reading is averaged.
For the repeating filter, the stack is filled and the conversions are averaged to yield a read-
ing. The stack is then cleared and the process starts over. See the User’s Manual for com-
plete information on filter modes.
Median filter
Median filtering uses the “middle-most” reading from a group of sample readings
arranged in ascending order. For example, assume the following readings:
20V, 1V, 3V
They are then arranged in ascending order as follows:
1V, 3V, 20V
The median (“middle-most”) reading from the above sample group is 3V.
The number of sample readings is determined by the specified rank as follows:
Sample readings = (2 × R) + 1
where: R is the selected rank (1 to 5)
For example, a rank of 4 will use the last nine readings to determine the median;
(2 × 4) + 1 = 9.
Each new reading replaces the oldest reading, and the median is then determined from the
updated sample group of readings.
Value displayed
with filtering
Response with the noise
window turned “on” shifts
when the input signal moves
beyond the specified range
Response with
no noise window
Limits of the
user-specified
noise window
Input signal

 Loading...
Loading...