Cycle and Response Times of the S7-400
9.2 Cycle Time Calculation
S7-400 Automation System, CPU Specifications
Manual, 10/2006, 6ES7498-8AA04-8BA0
9-3
9.2 Cycle Time Calculation
Increasing the Cycle Time
Basically, you should note that the cycle time of a user program is increased by the
following:
● Time-driven interrupt processing
● Hardware interrupt processing
● Diagnostics and error handling
● Communications via the MPI, PROFINET interface and CPs connected automation-
system internally
(for example, Ethernet, PROFIBUS DP); included in the communication load
● Special functions such as control and monitoring of tags or block status
● Transfer and clearance of blocks, compression of the user program memory
● Internal memory test
Influencing factors
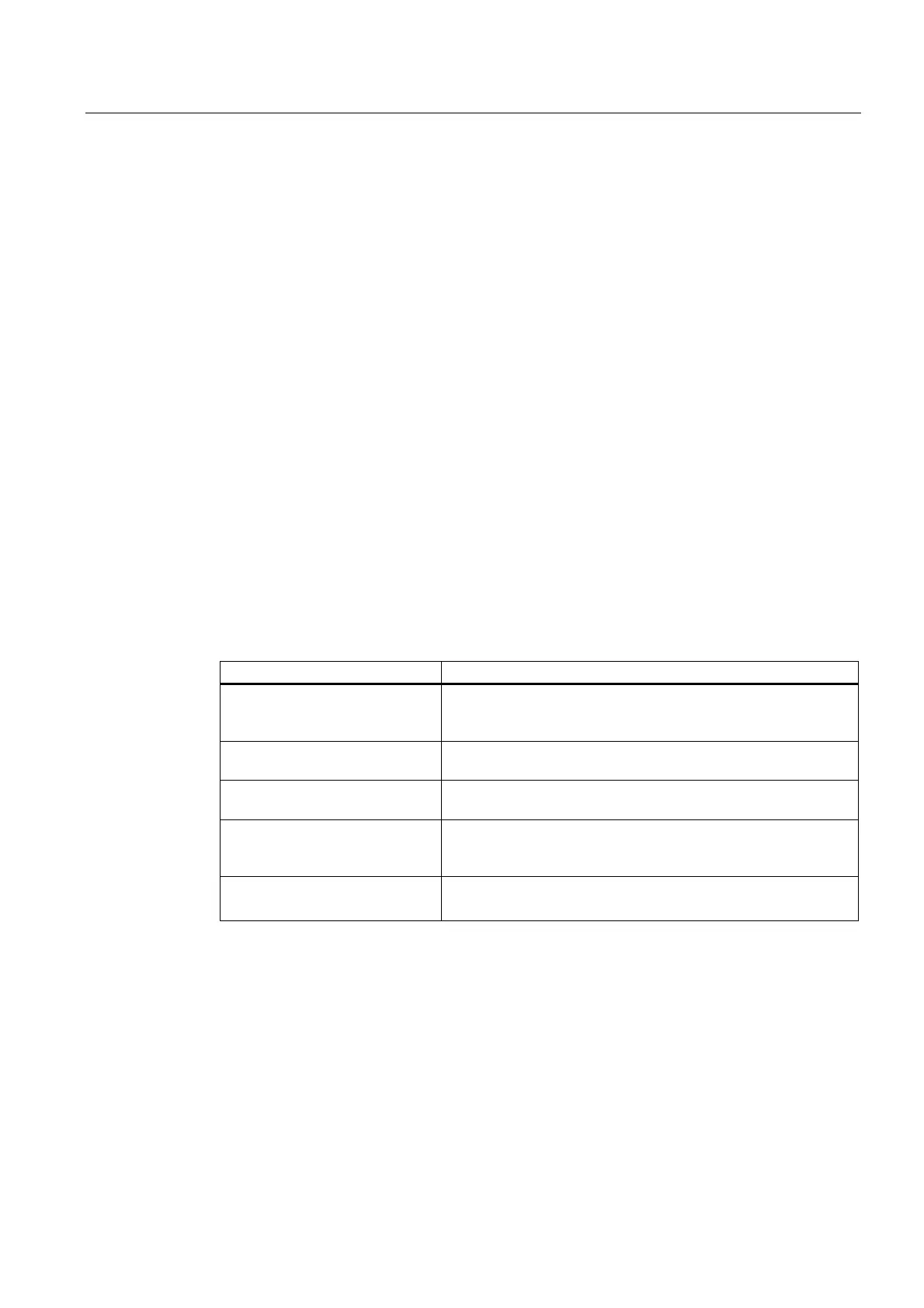
The following table indicates the factors that influence the cycle time.
Table 9-2 Factors that Influence the Cycle Time
Factors Remarks
Transfer time for the process-
image output table (PIQ) and the
process-image input table (PII)
... See table "Portions of the process image transfer time"
User program
execution time
... is calculated from the execution times of the different
instructions, see
S7-400 Instruction List
.
Operating system scan time at
the scan cycle checkpoint
... See table "Operating system scan time at the scan cycle
checkpoint"
Increase in the cycle time through
communications
You set the maximum permissible cycle load expected for
communication in % in
STEP 7
, see manual
Programming with
STEP 7
.
Impact of interrupts on the cycle
time
Interrupt can interrupt the user program at any time.
... See table "Increase in cycle time by nesting interrupts"

 Loading...
Loading...




















