Cycle and Response Times of the S7-400
9.3 Different cycle times
S7-400 Automation System, CPU Specifications
9-6 Manual, 10/2006, 6ES7498-8AA04-8BA0
9.3 Different cycle times
Fundamentals
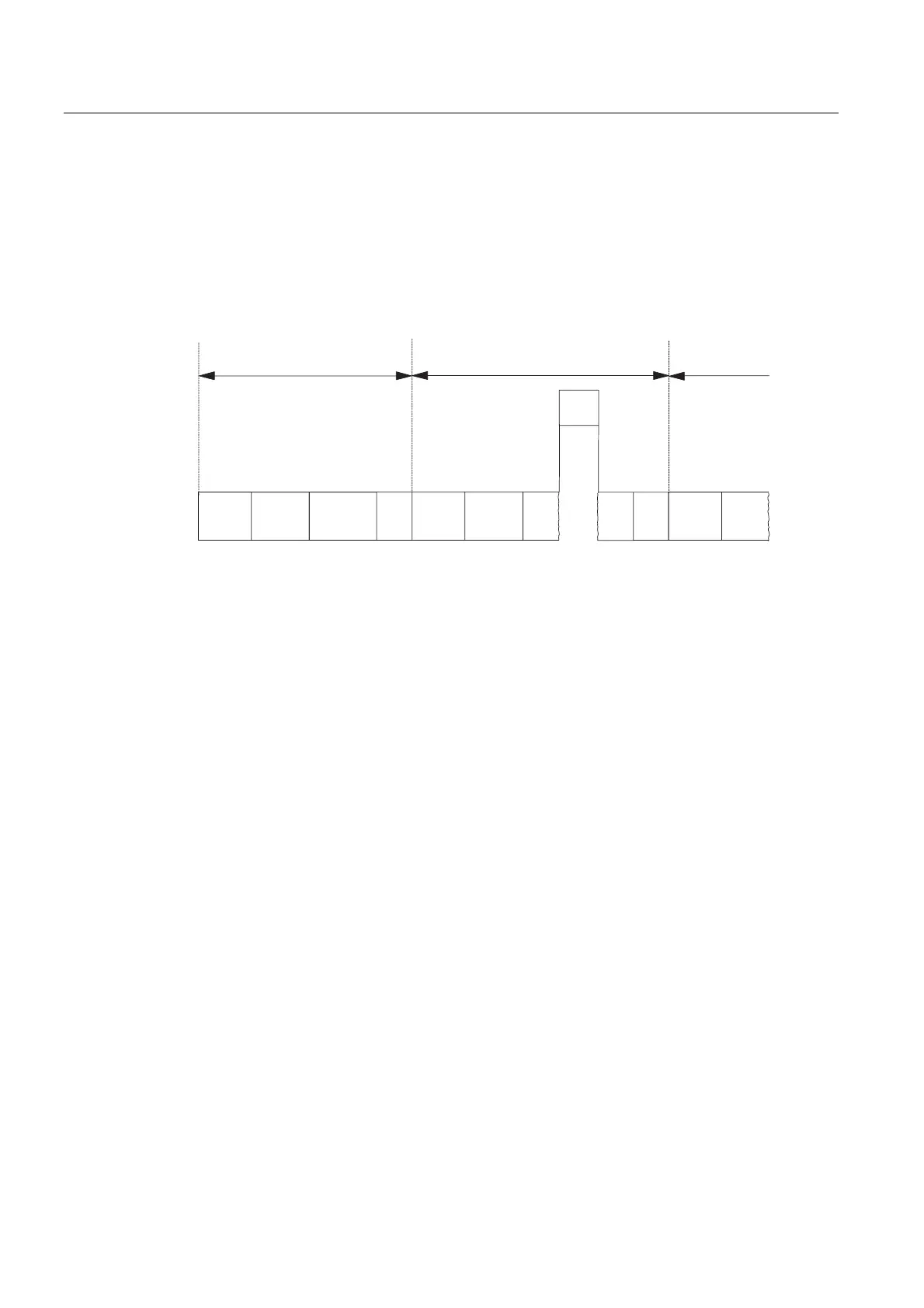
The length of the cycle time (T
cyc
) is not identical in each cycle. The following figure shows
different cycle times, T
cyc1
and T
cyc2
. T
cyc2
is longer than T
cyc1
, because the cyclically scanned
OB 1 is interrupted by a time-of-day interrupt OB (here, OB10).
OB10
T
OB1
PIQ
cyc 1
PII
SCC
OB1
PIQ PII
SCC
OB1
cyc 2
T
PIQ PII
Current cycle Next cycle Next cycle but one
Upda-
ting
Upda-
ting
Upda-
ting
Upda-
ting
Upda-
ting
Upda-
ting
Figure 9-2 Different cycle times
Fluctuation of the block processing time (e.g. OB 1) may also be a factor causing cycle time
fluctuation, due to:
● Conditional commands
● Conditional block calls
● Different program paths,
● Loops, etc.
Maximum Cycle Time
You can modify the default maximum cycle time in STEP 7 (cycle monitoring time). When
this time has expired, OB 80 is called. In OB 80 you can specify how the CPU is to react to
time errors. If you do not retrigger the cycle time with SFC43, OB 80 doubles the cycle time
at the first call. In this case, the CPU goes to STOP at the second call of OB 80.
If there is no OB 80 in the CPU memory, the CPU goes to STOP.

 Loading...
Loading...




















