Communication
4.2 Communication services
S7-400 Automation System, CPU Specifications
Manual, 10/2006, 6ES7498-8AA04-8BA0
4-11
4.2.6 Global data communication
Properties
Global data communication is used for cyclic exchange of global data via MPI subnets (for
example, I, Q, M) between SIMATIC S7 CPUs. The data communication is unacknowledged.
One CPU broadcasts its data to all other CPUs on the MPI subnet.
The integrated communication functions are called via SFCs in the user program.
SFCs for the Global Data Communication
The following SFCs are integrated in the operating system of the S7-400 CPUs:
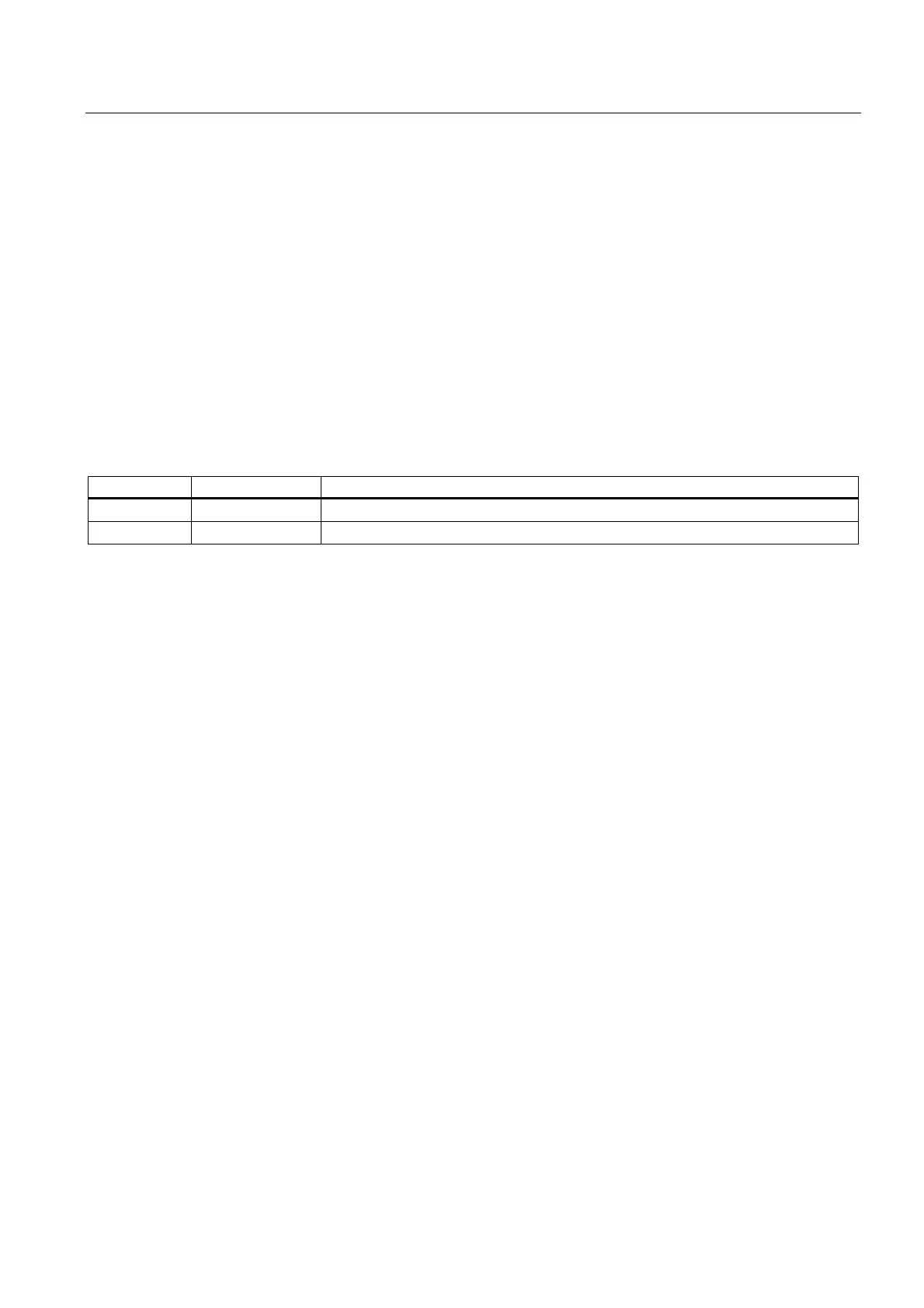
Table 4-4 SFCs for the Global Data Communication
Block Block name Brief description
SFC 60 GD_SEND Collect and send data of a GD packet
SFC 61 GD_REC Fetch data of an arrived GD message frame and enter it in the receive GD packet.
Reduction ratio
The reduction ratio specifies the cyclic intervals for GD communication. You set the
reduction ratio when you configure global data communication in STEP 7. For example, if
you set a reduction ratio of 7, global data communication is performed every 7th cycle. This
reduces the load on the CPU.
Send and Receive Conditions
Meet the following conditions for communication via GD circuits:
● For the transmitter of a GD packet:
Reduction ratio
transmitter
x cycle time
transmitter
≥ 60 ms
● For the receiver of a GD packet:
Reduction ratio
receiver
x cycle time
receiver
< reduction ratio
transmitter
x cycle time
transmitter
A GD packet may be lost if you do not adhere to these conditions. The reasons being:
● The performance of the "smallest" CPU in the GD circuit
● Transmission and reception of global data is performed asynchronously at the stations.
When setting in STEP 7: “Transmit after each CPU cycle“, and the CPU has a scan cycle
time < 60 ms, the operating system might overwrite a GD packet of the CPU before it is
transmitted. The loss of global data is indicated in the status box of a GD circuit, if you set
this function in your STEP 7 configuration.

 Loading...
Loading...




















