4.6 Holding brake
4.6.1 Types and modes of operation of the holding brakes
Overview
The chapter describes types and modes of operation of the installed holding brakes.
The type of the holding brake installed depends on the motor frame size.
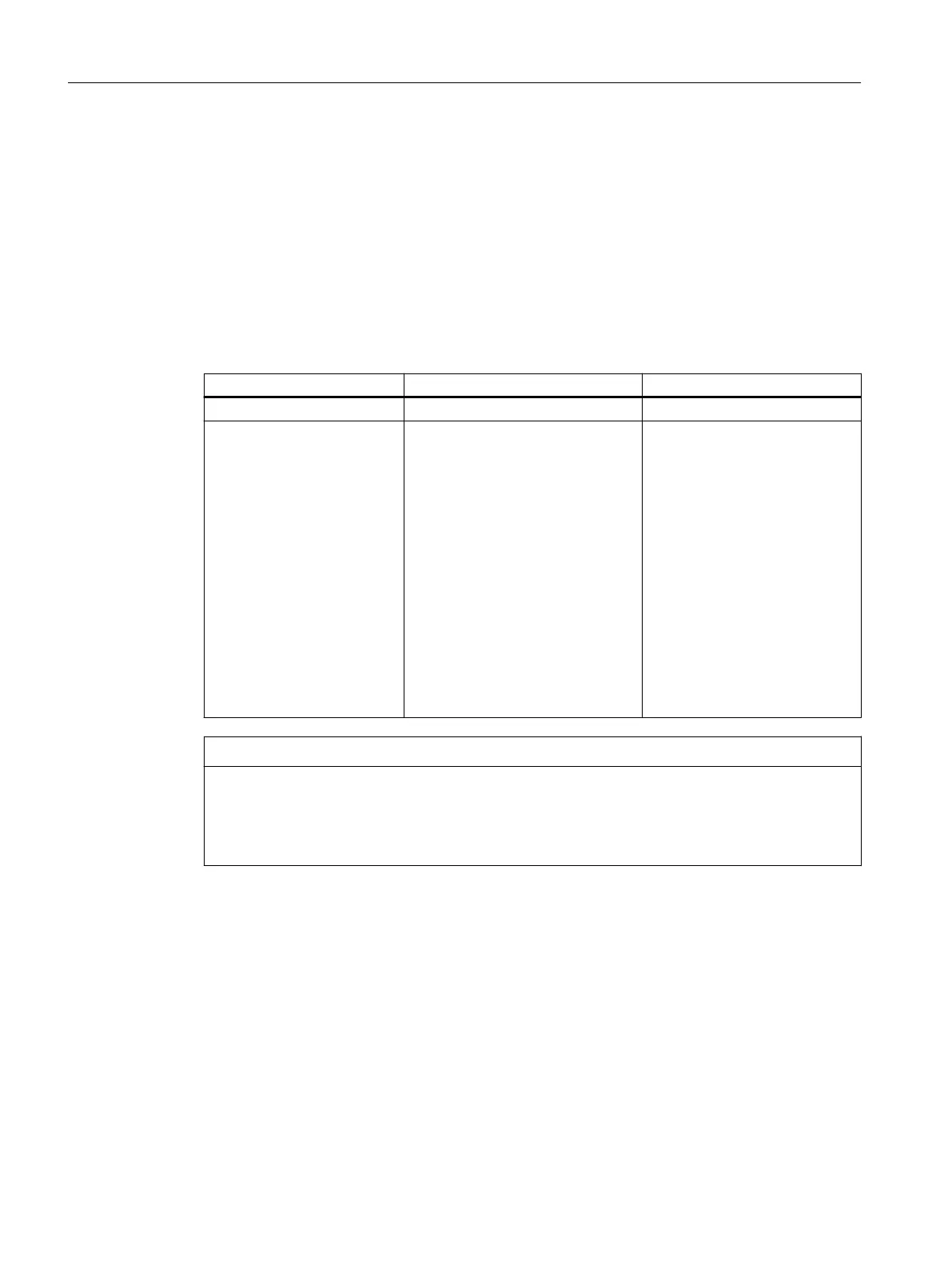
Type of holding brake Spring-loaded brake Permanent-magnet brake
Installed in the motors 1FK2☐03 ... 1FK2☐04 1FK2☐05 ... 1FK2☐10
Method of operation The spring causes a compressive
force on the brake armature disk.
This means that in the no-current
condition, the brake is closed and
the motor shaft is held.
When 24VDC rated voltage is ap‐
plied to the brake, the current-carry‐
ing coil produces an opposing eld.
This neutralizes the force of the
spring and the brake opens without
any residual torque.
The spring-loaded brake has a tor‐
sional backlash less than 1°.
The magnetic eld of the perma‐
nent magnets exerts a pulling
force on the brake armature disk.
This means that in the no-current
condition, the brake is closed and
the motor shaft is held.
When 24VDC rated voltage is
applied to the brake, the current-
carrying coil produces an oppos‐
ing eld. This neutralizes the
force of the permanent magnets
and the brake opens without any
residual torque.
The permanent magnet brake
has a torsionally sti connection
to the motor rotor.
NOTICE
Damage to the motor due to axial forces on the shaft extension
Axial forces on the shaft extension can damage motors with an integrated holding brake.
• Avoid impermissible forces on the shaft extension. The permissible axial forces are listed in
the associated Conguration Manual.
Mounting and options
4.6Holding brake
SIMOTICS S-1FT2 synchronous motors for SINAMICS S120
50 Operating Instructions, 12/2023, A5E50610821B AF
 Loading...
Loading...











