PACSystems™ RX3i and RSTi-EP CPU Reference Manual Section 4
GFK-2222AK October 2019
CPU Operation 111
4.10.2 I/O System Diagnostic Data Collection
Diagnostic data in a PACSystems I/O system is obtained in either of the following two
ways:
▪ If an I/O module has an associated bus controller, the bus controller provides the
diagnostic data from that module to the CPU. For details on GBC faults, see
PACSystems Handling of GBC Faults.
▪ For I/O modules not interfaced through a bus controller, the CPU’s I/O Scanner
subsystem generates the diagnostic bits based on data provided by the module.
The diagnostic bits are derived from the diagnostic data sent from the I/O modules to
their I/O controllers (CPU or bus controller). Diagnostic bits indicate the current fault
status of the associated module. Bits are set when faults occur and are cleared when
faults are cleared.
Diagnostic data is not maintained for modules from other manufacturers. The application
program must use the BUS Read function blocks to access diagnostic information
provided by those boards.
Note: At least two sweeps must occur to clear the diagnostic bits: one scan to send the
%Q data to the module and one scan to return the %I data to the CPU. Because module
processing is asynchronous to the controller sweep, more than two sweeps may be
needed to clear the bits, depending on the sweep rate and the point at which the data is
made available to the module.
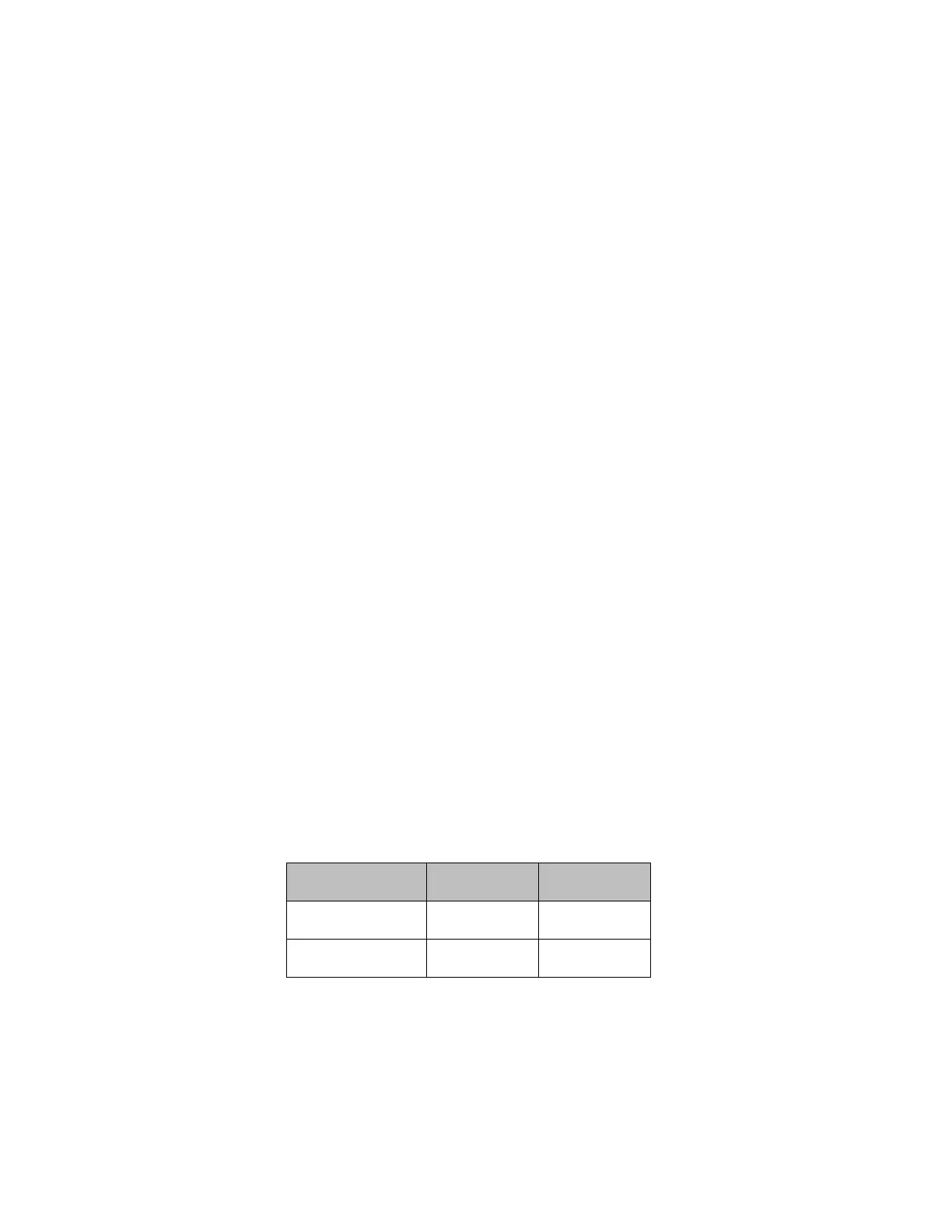
4.10.2.1 Discrete I/O Diagnostic Information
The CPU maintains diagnostic information for each discrete I/O point. Two memory
blocks are allocated in application RAM for discrete diagnostic data, one for %I memory
and one for %Q memory. One bit of diagnostic memory is associated with each I/O point.
This bit indicates the validity of the associated I/O data. Each discrete point has a fault
reference that can be interrogated using two special contacts: a fault contact (-[F]-) and a
no-fault contact (-[NF]-). The CPU collects this fault data if enabled to do so by the
programming software. The following table shows the state of the fault and no-fault
contacts.
4.10.2.2 Analog I/O Diagnostic Data
Diagnostic information is made available by the CPU for each analog channel associated
with analog modules and Genius analog blocks. One byte of diagnostic memory is
allocated to each analog I/O channel. Since each analog I/O channel uses two bytes of %AI
and %AQ memory, the diagnostic memory is half the size of the data memory.

 Loading...
Loading...















