Q & A
8-20
72. Give basic information on radars.
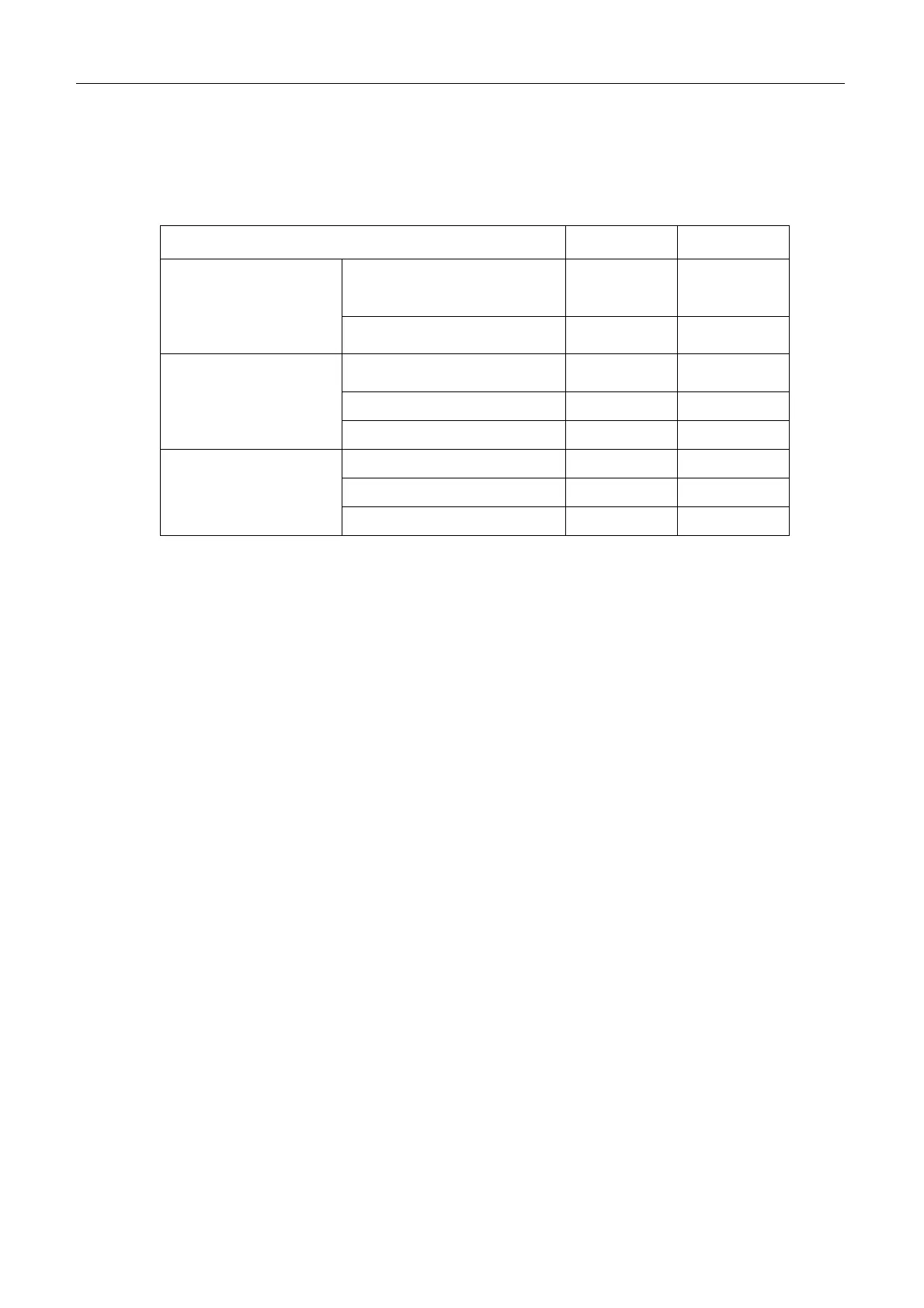
1) Comparison between S-band and X-band
Characteristics X-band S-Band
Loss due to raindrops
Large
4 mm/h:
0.064 dB/km
Small
4 mm/h:
0.017 dB/km
In relation to electric
wave transmission
(Related to
meteorological
phenomena)
Sea returns
Large Small
Size at the same gain and
the same horizontal directivity
Large Small
Loss in waveguide tube
Large Small
In relation to antenna
Size of waveguide tube
Small Large
Detection range
Small Large
Bearing and range resolution
Large Small
Others
Noise index of receiver
Large Small
2) Range resolution:
The distance R is determined by the pulse length: (
τ
).
R (m)=150 x
τ
For instance, if the pulse length is 0.07
s for S1 pulse
R = 150 x 0.07
R = 10.5 m
3) Minimum range:
The pulse length (
τ
) determines the minimum range R.
R (m)=150 x
τ
In the actual situation, the relation between the antenna height and vertical beam
width produce a shadow sector (target is not located within the vertical beam
width). This makes it impossible to detect targets at a close range. If the antenna
height is lowered to make the minimum detection range shorter, this makes the
maximum detection range shorter.
The minimum detection range can be calculated in the following equation:
Rmin = H / tan (
θ
v/2)
where Antenna height (m) and vertical beam width (
θ
v deg.).
Assuming that the antenna height is 30 m and the vertical beam width is 20
degrees (in case of the antenna XN-24AF)
Rmin = 30 / tan (20/2)
Rmin = 170.1 m

 Loading...
Loading...











