then forwards the NTDP topology-collection request after its prior port forwards the NTDP
topology-collection request.
Cluster management maintenance
1. Adding a candidate switch to a cluster
You should specify the management switch before creating a cluster. The management switch discovers
and defines a candidate switch through NDP and NTDP protocols. The candidate switch can be
automatically or manually added to the cluster.
After the candidate switch is added to the cluster, it can obtain the member number assigned by the
management switch and the private IP address used for cluster management.
2. Communication within a cluster
In a cluster the management switch communicates with its member switches by sending handshake
packets to maintain connection between them.
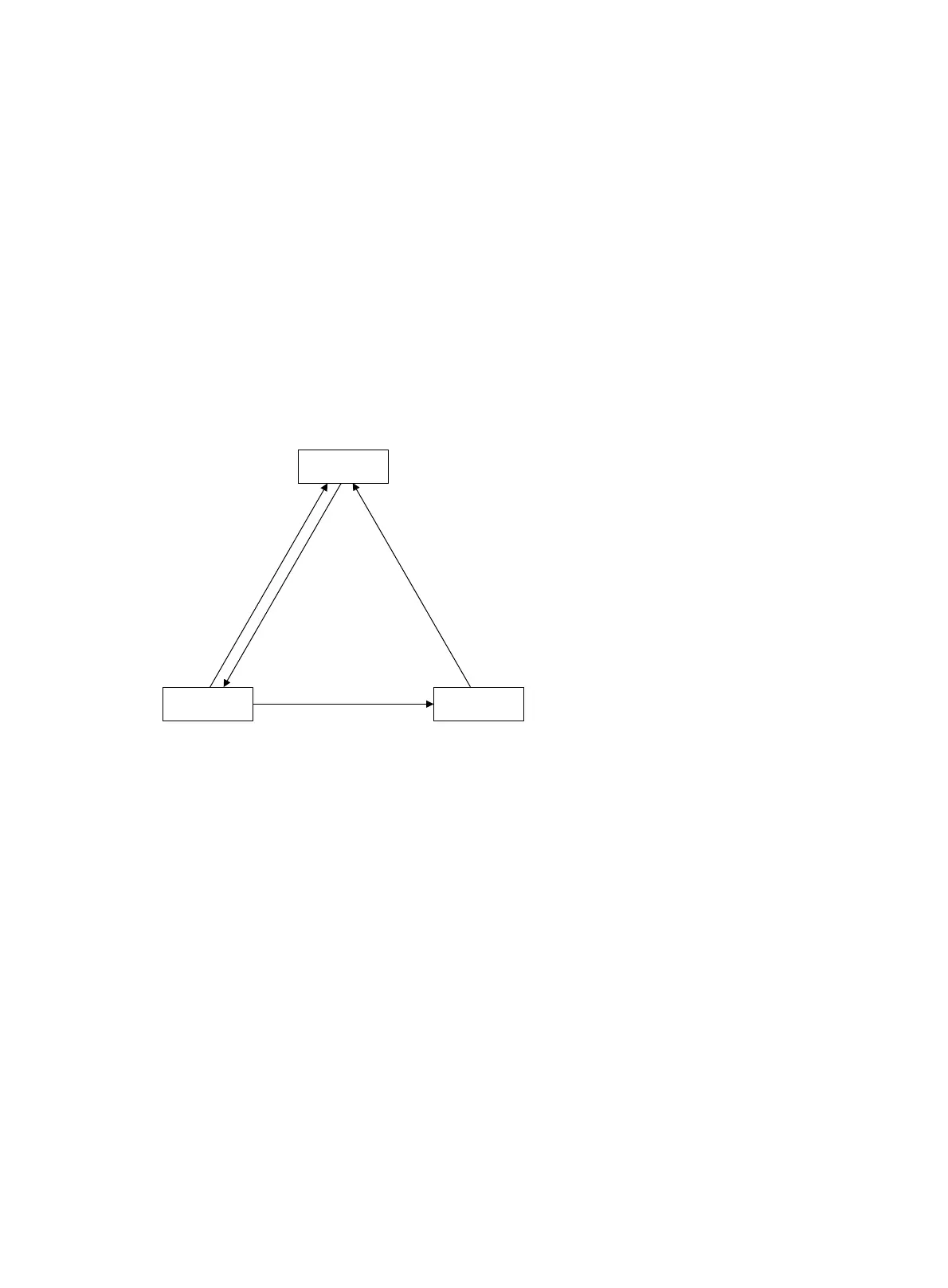
Figure 43 Management/member switch state change
R
ec
e
i
v
e
s
t
he
h
ands
ha
k
e
or
m
an
age
m
e
nt
pac
k
et
s
F
a
i
ls
t
o
r
e
c
eiv
e
han
ds
hak
e
p
ac
k
et
s
in
t
hr
e
e
c
o
ns
ec
ut
iv
e
int
e
r
v
al
s
State holdtime exceeds
the specified value
D
i
s
c
on
n
ec
t
s
t
at
e
i
s
r
ec
ov
ere
d
Active
DisconnectConnect
• After a cluster is created and a candidate switch is added to the cluster and becomes a member
switch, the management switch saves the state information of the member switch and identifies it as
Active. The member switch also saves its state information and identifies itself as Active.
• After a cluster is created, its management switch and member switches begin to send handshake
packets. Upon receiving the handshake packets from the other, the management switch or a
member switch simply maintains its state as Active, without sending a response.
• If the management switch does not receive handshake packets from a member switch in an interval
three times the interval to send handshake packets, it changes the status of the member switch from
Active to Connect. Likewise, if a member switch fails to receive handshake packets from the
management switch in an interval three times of the interval to send handshake packets, the
member switch changes its own status from Active to Connect.
• During information holdtime, if the management switch receives handshake or management
packets from a member switch that is in Connect state, it changes the state of the member switch to
Active. Otherwise, it considers the member switch to be disconnected, and changes the state of the
member switch to Disconnect.
• During information holdtime, if a member switch in Connect state changes its state to Active if it
receives handshake or management packets from the management switch; otherwise, it changes its
state to Disconnect.
108
 Loading...
Loading...