100
Port types
To display the port type status, open the View menu and select View Port Types. Table 23 lists the possible
port types and their descriptions. Each port can be configured to self-discover the proper port type to
match the device or switch to which it is connected. The Running Type field on the Port Properties dialog
box indicates the port type that is currently active.
To change the port type:
1. Select one or more ports in the faceplate display.
2. Select Port > Port Properties to open the Port Properties dialog box.
3. Select the Port Type option from the drop-down list.
4. Click OK to write the new port type to the switch.
Port speeds
SFP ports with 8Gb SFPs installed can transmit and receive at 2 Gb/s, 4 Gb/s, or 8 Gb/s. XPAK ports
can transmit and receive at 10 Gb/s or 20 Gb/s. All ports can be configured for either a fixed
transmission speed or to sense (auto-detect) the transmission speed of the device to which it is connected.
To display the speed of each port, open the View menu and select View Port Speeds. See Table 24 for the
possible port speeds.
NOTE: 8 Gb/s SFPs do not support 1 Gb/s speed. You should not set the port speed to 1 Gb/s if an 8
Gb/s SFP is inserted, as the port will be downed if you do.
To change the port transmission speed:
1. Select one or more ports in the faceplate display.
2. Open the Port menu and select Port Properties to open the Port Properties dialog box.
3. Select the Port Speed option from the drop-down list.
4. Click OK to write the new port speed to the switch.
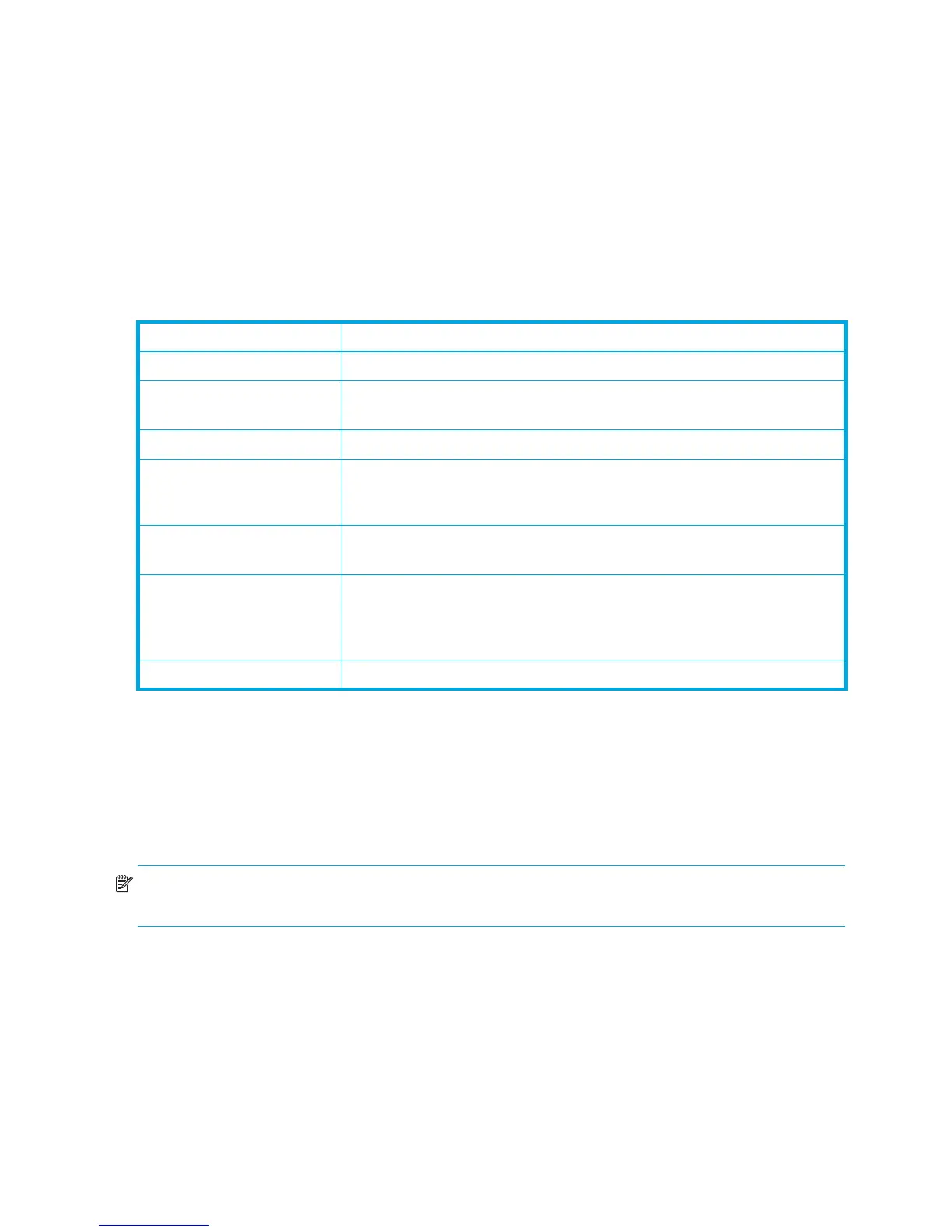
Table 23 Port types
State Description
F_Port Fabric port—Supports a single public device (N_Port).
FL_Port Fabric loop port—Self-discovers a single device (N_Port) or a loop of up
to 126 public devices (NL_Port).
G_Port Generic port—Self-discovers as an F_Port or an E_Port.
GL_Port Generic loop port—Self-discovers as an F_Port, FL_Port, or an E_Port.
GL_Port is the default port type. A single device on a public loop will
attempt to configure as an F_Port first, then if that fails, as an FL_Port.
E_Port Expansion port—The mode that a G_Port or GL_Port is in when attached
by an ISL (inter-switch link) to another fibre channel switch.
TR_Port Transparent Router port—Enables devices on a remote fabric to be
mapped to devices on the local HP SN6000 Fibre Channel Switch fabric.
TR_Ports do not support online port diagnostics. See ”Testing ports”
(page 103).
Donor Donor port—Enables buffer credits to be used by another port.
 Loading...
Loading...











