5-14 Delta, Pulse Delta, and Differential Conductance Model 6220/6221 User’s Manual
Return to Section 5 topics
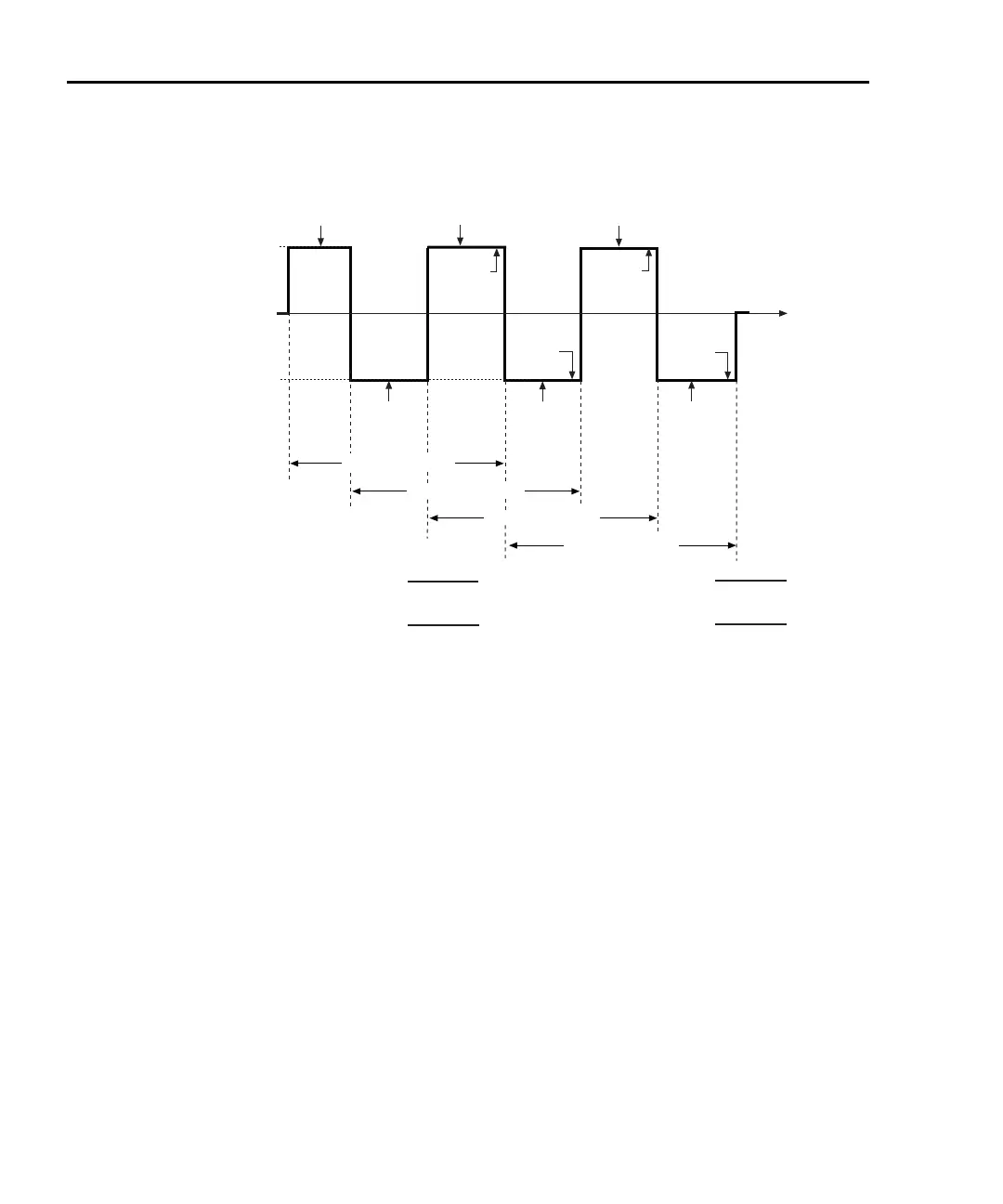
Figure 5-6
Delta measurement technique
The following equation can be used to calculate any Delta reading:
Where: X, Y, and Z are the three A/D measurements for a Delta reading.
n = Delta Cycle Number – 1
Example – Calculate the 21st Delta reading:
X, Y, and Z are the three A/D measurements for the 21st Delta reading.
n = Delta Cycle Number – 1
= 21 – 1
= 20
Therefore;
The (-1)
n
term in the Delta calculation is used for polarity reversal of every other
calculated Delta reading. This makes all calculated Delta readings in the test the
same polarity.
DELTA
Reading
1st
622x
I-Source
0
time
1st Delta Cycle
2nd Delta Cycle
I-High
I-Low
3rd Delta Cycle
4th Delta Cycle
A - 2B + C
DELTA
Reading
2nd
(
1st Delta Reading =
4
)
·
(-1)
0
B - 2C + D
(
2nd Delta Reading =
4
)
·
(-1)
1
C - 2D + E
(
3rd Delta Reading =
4
)
·
(-1)
2
D - 2E + F
(
4th Delta Reading =
4
)
·
(-1)
3
DELTA
Reading
4th
DELTA
Reading
3rd
2182/
2182A
A/D B
2182/2182A
A/D A
2182/2182A
A/D C
2182/2182A
A/D E
2182/
2182A
A/D D
2182/
2182A
A/D F
Delta
X2Y– Z+
4
---------------------------
⎝⎠
⎛⎞
1–()
n
•=
Delta
X2Y– Z+
4
---------------------------
⎝⎠
⎛⎞
1–()
20
•=
X2Y– Z+
4
---------------------------=

 Loading...
Loading...