TP-6714 4/10 81Section 5 Setup
5.12.4 Output Functions
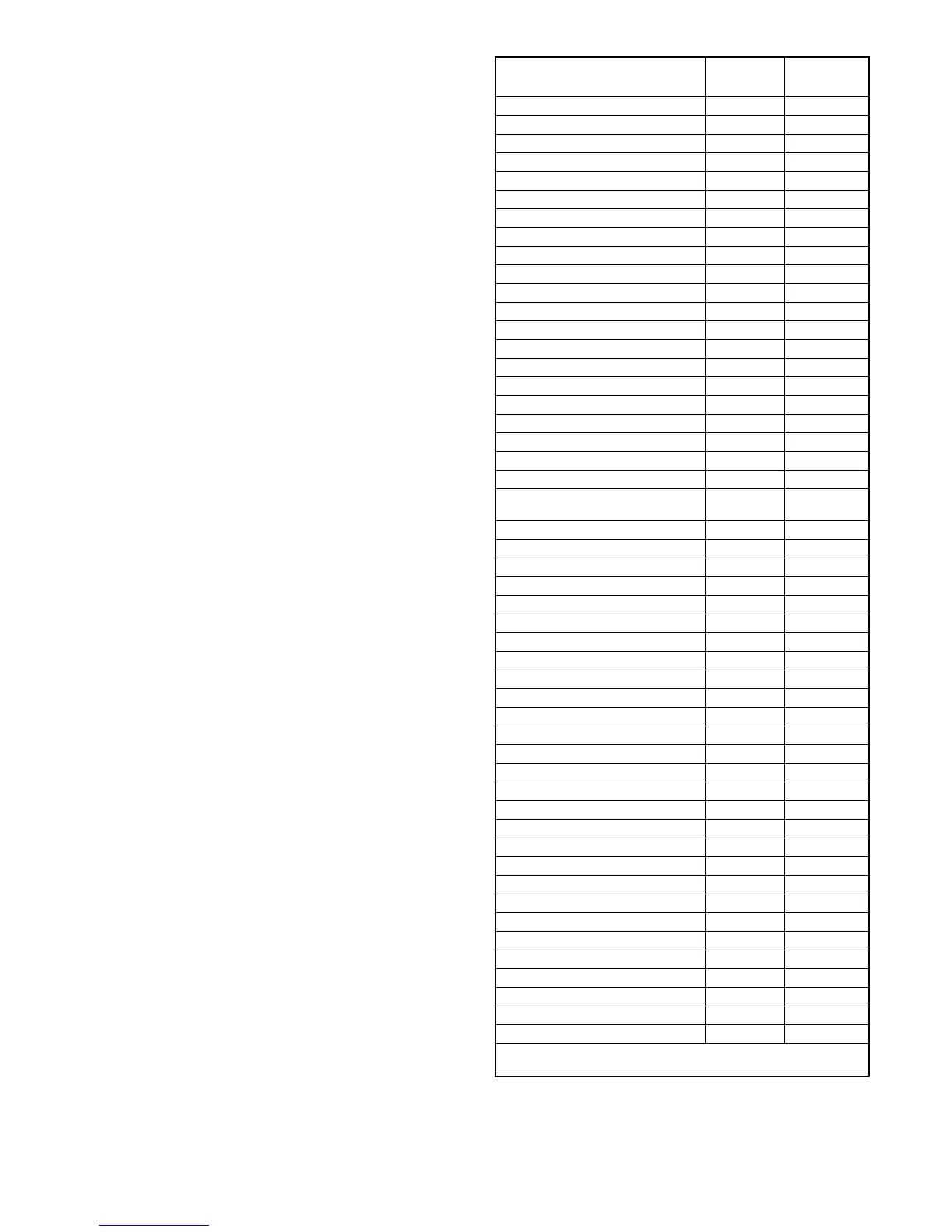
Output functions are shown in Figure 5-19. Information
about selected output functions is shown below. Refer
to the section number shown in Figure 5-19 for more
information about the output function.
In-Phase Monitor Sync Output. Is activated when the
in-phase transfer fail or fail to sync time delays expire,
indicating that the sources did not synchronize in the
allotted time. See Section 5.11.2 for more information
about the in-phase monitor. For closed-transition
models, customer-supplied equipment used to boost
the generator set can be connected to this output. See
Sections 1.1.1 and 8.4 for output connection
information.
Note: The In-phase Transfer Fail and/or Fail to Sync
time delays are set in the Set Sources menu. See
Section 5.11.
Load Control Output, 1--9. Connect up to nine loads
that can be connected or disconnected using either
time-based or current-based load control. Assign load
control outputs 1 through 9 to the corresponding outputs
on the main board or I/O modules, and then go to the
Time Delay setup screen to set up the load control
sequences. See Section 5.9 for the Time Delay setup
menus, and Section 5.10 for more information about
load control.
MBUS-Controlled Outputs. There are four
Modbus-Controlled Output functions. These four
functions can be assigned to any of the outputs on either
the main logic board or the optional I/O boards. The
state of any or all of these four functions can be
controlled and monitored via Modbus messages only.
Source N Engine Start Signal. UseifSourceNisa
generator set, especially for three-source systems or
prime power mode. See Section 5.15 for more on
three-source systems. See Section 5.8 for more about
prime power mode.
Source E Engine Start Signal. An alternative to the
engine start contacts on the transfer switch.
Programmable Output Type
See
Section
3 Src Sys Disabled Control 5.15
Alarm Silenced Monitor 8.5
Audible Alarm Control 8.5
Aux Switch Fault Fault 3.13
Aux Switch Open Fault 3.13
Battery Backup Low (not used) * Monitor *
Common Alarm Active (1 and 2) Fault 5.13
Contactor in OFF position Monitor —
Contactor in Preferred Position Monitor —
Contactor in Source E Position Monitor —
Contactor in Source N Position Monitor —
Contactor in Standby Position Monitor —
Exerciser Active Monitor 5.7, 3.6.2
Fail to Acquire Preferred Fault 3.13
Fail to Acquire Standby Fault 3.13
Fail to Transfer Fault 3.13
Fail to Open Source1 Fault —
Fail to Close Source1 Fault —
Fail to Open Source2 Fault —
Fail to Close Source2 Fault —
I/O Module Lost Comm Fault 3.13
In-Phase Monitor Sync Control 5.12.4,
5.11.2
Load Bank Control Active Control 5.12.4
Load Control Active Monitor 5.10.1
Load Control Out 1--9 Control 5.10.1
Low Battery (external battery) Monitor 8.6
Maintenance Mode Monitor 5.3
Non-Emergency Transfer Monitor —
Not in Auto Monitor 3.2.2
Peak Shave Active Monitor 5.14.8
Preferred Source Available Monitor 5.11.5
MBUS Control RDO #1--4 Control 5.12.4
Source E (Phase) Rotation Error Fault —
Source E Loss of Phase Fault —
Source E Over Frequency Fault 5.11.5
Source E Over Voltage Fault 5.11.5
Source E Start Signal Control 5.12.4
Source E Under Frequency Fault 5.11.5
Source E Under Voltage Fault 5.11.5
Source E Voltage Unbalance Fault 5.11.5
Source N (Phase) Rotation Error Fault —
Source N Loss of Phase Fault —
Source N Over Frequency Fault 5.11.5
Source N Over Voltage Fault 5.11.5
Source N Start Signal Control 5.12.4, 5.15
Source N Under Frequency Fault 5.11.5
Source N Under Voltage Fault 5.11.5
Source N Voltage Unbalance Fault 5.11.5
Standby Source Available Monitor 5.11.5
Test Mode Active Monitor 3.10
* Do not use the Backup Battery Low output. A design
improvement has eliminated the need for a backup battery.
Figure 5-19 Available Programmable Outputs

 Loading...
Loading...











