A-21
Appendices
CJ-series PROFIBUS Master Unit Operation Manual for NJ-series CPU Unit (W509)
A-6 I/O Data Type Definitions
App
A-6 I/O Data Type Definitions
Standard PROFIBUS DP defines two types of I/O data.
• 8-bit bytes sized data.
• 16-bit word sized data.
The standard for PROFIBUS extension, also referred to as PROFIBUS DP-V1, defines the following
additional data types:
• 8-bit byte signed / unsigned Integer data.
• 16-bit word signed / unsigned Integer data.
• 32-bit double word signed / unsigned Integer data.
• 32-bit single precision floating point (IEEE754 format).
• ASCII Text strings of indeterminate length (in 8-bit bytes).
• 7 byte Date format.
• 6 byte Time of Day format.
• 6 byte Time Difference format.
The NJ-series controller unit defines similar data types, which however differ in size and/or storage for-
mat in the CPU memory. Since the PROFIBUS Master Units provides an interface between a PROFI-
BUS network and the NJ-series controller unit, the Unit will provide the necessary conversions to
ensure that the I/O data on the PROFIBUS network is transferred to the CPU memory in the correct for-
mat. This Appendix explains the conversions in detail.
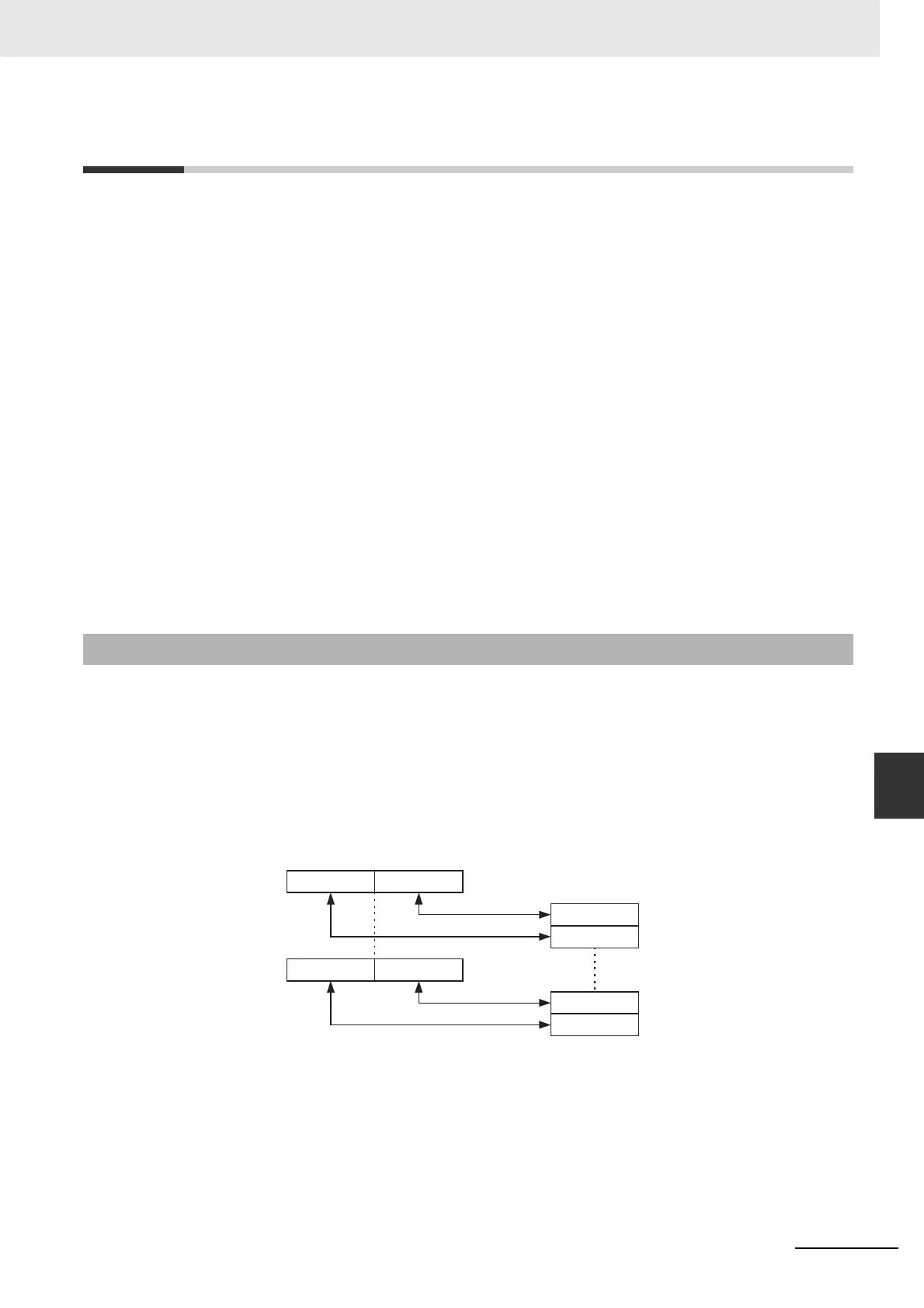
8-bit Byte Data
The NJ-series controller unit memory layout is word oriented. The PROFIBUS Master will therefore
convert a stream consisting of one or more bytes of data into words. The figure below shows the
conversion in graphic format.
Note m = (n-1)/2, rounded to the next lowest integer.
A sequence of bytes transmitted over the PROFIBUS network is copied to the CPU memory in the
following procedure.
• The first two bytes are stored in the lowest word of the destination data block in CPU memory
word. Every consecutive two bytes are stored in the next higher words.
• Odd byte numbers are copied to the Least Significant byte of a CPU memory word.
• Even byte numbers are copied to the Most Significant Byte of a CPU memory word.
A-6-1 Integer Data Conversions
CPU Data area
Byte
sequence
Byte 1
Byte 2
PROFIBUS
Bit 07 Bit 00
Byte n-1Byte nWord m
Bit 15 Bit 00
Byte 1Byte 2Word 0
Byte n-1
Byte n
 Loading...
Loading...











