21
Interrupt Functions Section 1-4
1-4-2 Processing the Same Memory Locations with the Main Program
and Interrupt Subroutines
If a memory location is manipulated both by the main program and an inter-
rupt subroutine, an interrupt mask must be set to disable interrupts.
When an interrupt occurs, execution of the main program will be interrupted
immediately, even during execution of an instruction. The intermediate pro-
cessing results is saved for use after completing the interrupt subroutine, i.e.,
when the interrupt subroutine has been executed, execution of the main pro-
gram is started from the same position with data restored to the previous con-
dition. If any of the memory locations being used by the main program are
changed in the interrupt subroutine, the changes will be lost when data is
restored to the previous state when restarting execution of the main program.
It is thus necessary to disable interrupts before and enable interrupts after any
instructions that should be executed to completion even if an interrupt occurs.
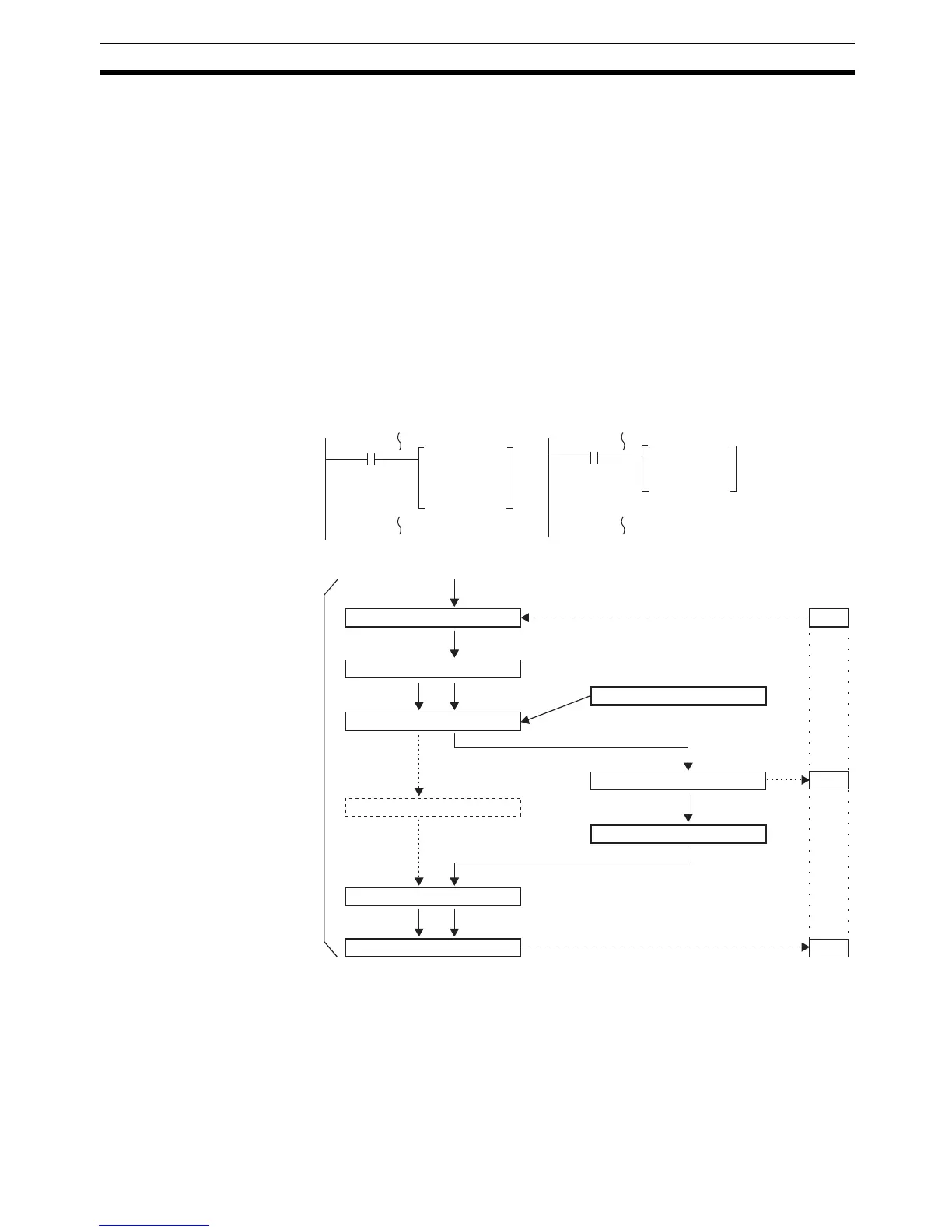
Processing Interrupted
between 1st and 3rd
Operands
Flow of Processing
When the interrupt occurs while processing ADD, the addition result, 1235, is
saved temporarily in memory and not stored in DM 0000. Although #0010 is
moved to DM 0000 in the interrupt program, the addition result that was saved
is written to DM 0000 as soon as processing returns to the main program,
effectively undoing the results of the interrupt program.
ADD
DM0000
#0001
DM0000
MOV
#0010
DM0000
Interrupt SubroutineMain Program
Status of DM 0000 read. 1234) 1234
DM0000
0010
1235
BCD addition performed. 1234+1=1235
Processing interrupted.
#0010 moved to DM 0000.
Addition results (1235) written.
Addition results data (1235)
Processing continued.
Interrupt processing completed.
Data saved.
Processing of ADD
Data restored.
MOV executed.
Interrupt occurs

 Loading...
Loading...