.1
20 / 93
6. Supported Work Flow
6.1 Communication methods
cobas c 111 instruments support real-time communication and batch communication for
test ordering and analytical data upload.
6.1.1 Automated Real-Time Communication (REAL)
Real-time communication refers to a communication model where the reception of a
sample on the system triggers an inquiry for test orders from cobas c 111 instrument to
host. The host may now download the known orders for this specific sample order (also
known as Host Query Mode).
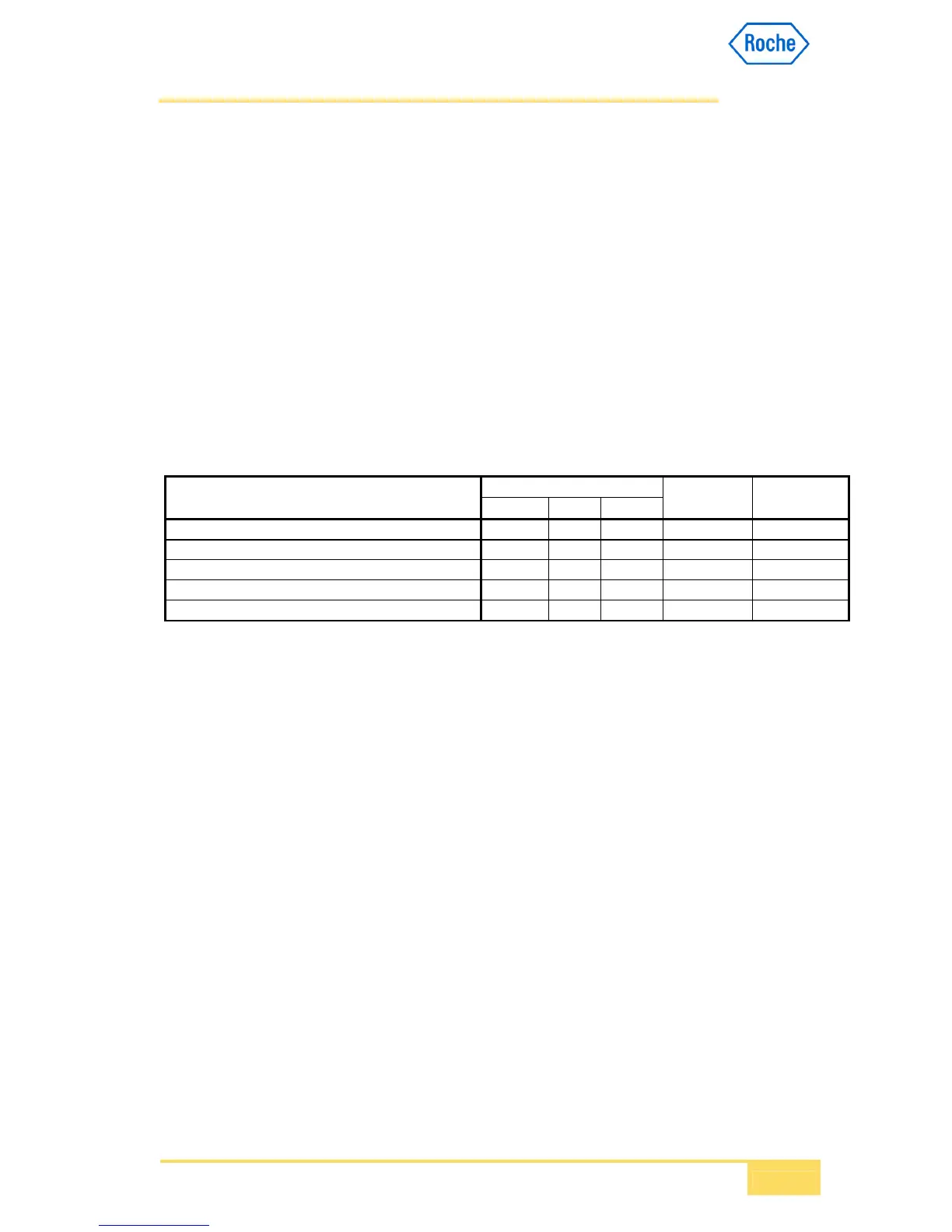
The relationships between real-time communication functions and types of samples are
shown in Table 1. The following are the details regarding communication procedures and
communication functions.
Communication Functions Patient Samples Control
Sample
Calibration
Sample
Routine Stat Rerun
Test order inquiry (host query)
× ×
Analytical data transmission (result upload)
Rerun test order reception
× 1) × ×
Rerun test order inquiry
× 1) × ×
Rerun analytical data transmission
× 1) × ×
( = Possible; × = not possible) 1) Rerun of a rerun is not supported
Table 1: Real time Communication Functions
6.1.1.1 Sample Introduction
Samples (tubes and cups) are placed directly into one of the sample carrier slots of the
cobas c 111 instrument. (Sample Area)
6.1.1.2 Sample Identification and Test Ordering
A sample is identified by the sample ID either read via barcode reader or the number given
by the operator. On cobas c 111 instruments a sample is never referred to by a position.
The system looks for test orders for each sample, depending on configuration settings. Test
orders can come from:
• The host prior to testing
• The host as a result of a ‘Test order inquiry’ initiated by the analyzer
• Manually programmed test orders on the analyzer by the operator
6.1.1.3 Sample Aspiration
The aspiration of sample will take place at the position in the Sample Area. Once all sample
aspirations have been done, the sample can be removed without disturbing the perfor-
mance of the system.

 Loading...
Loading...