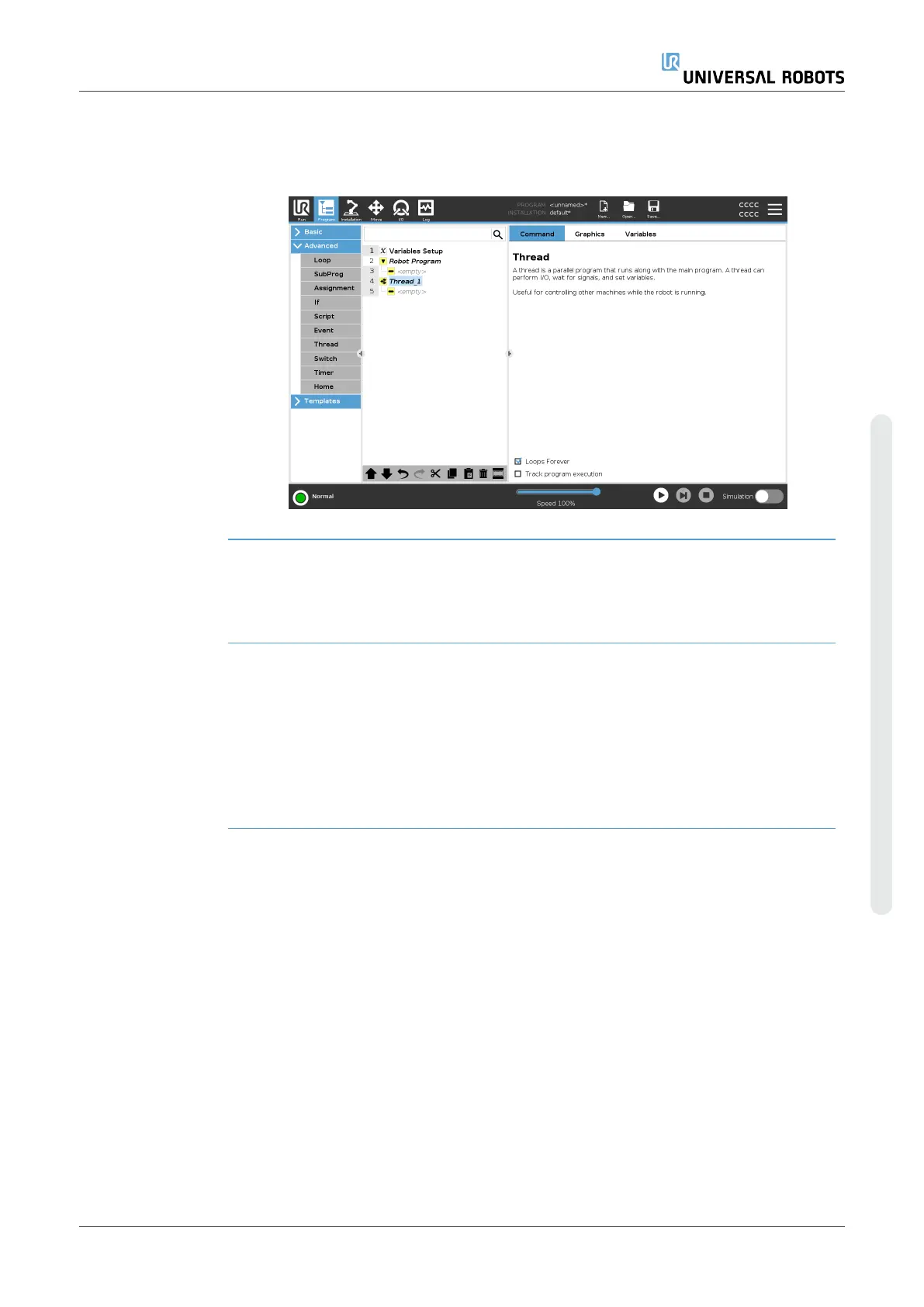
Description A thread is a parallel process to the robot program. A thread can be used to
control an external machine independently of the robot arm. A thread can
communicate with the robot program with variables and output signals.
7.8.8. Switch
Description A Switch Case construction can make the robot change behavior based on
sensor inputs or variable values.
Use the Expression Editor to describe the base condition and define the
cases under which the robot should proceed to the sub-commands of this
Switch.
If the condition is evaluated to match one of the cases, the lines inside the
Case are executed. If a Default Case has been specified, then the lines
will be executed only if no other matching cases were found.
User Manual 245 UR16e
Copyright © 2009–2024 by UniversalRobotsA/S. All rights reserved.
 Loading...
Loading...