Electrical system
89
Instruments
Select a position where the instruments will be unob-
structed and easily readable.
NOTE! The safe distance for the compass location to
avoid magnetic interference from the rev counter is
0.3 m (1 ft). If the compass is placed closer, compen-
sation must be made. Also see installation instruc-
tions for the compass.
Check to make sure that there is sufficient space un-
derneath for the instruments and leads. Attach the
template (if needed) on the selected position.
Make sure the panel is accessible for inspection and
repair.
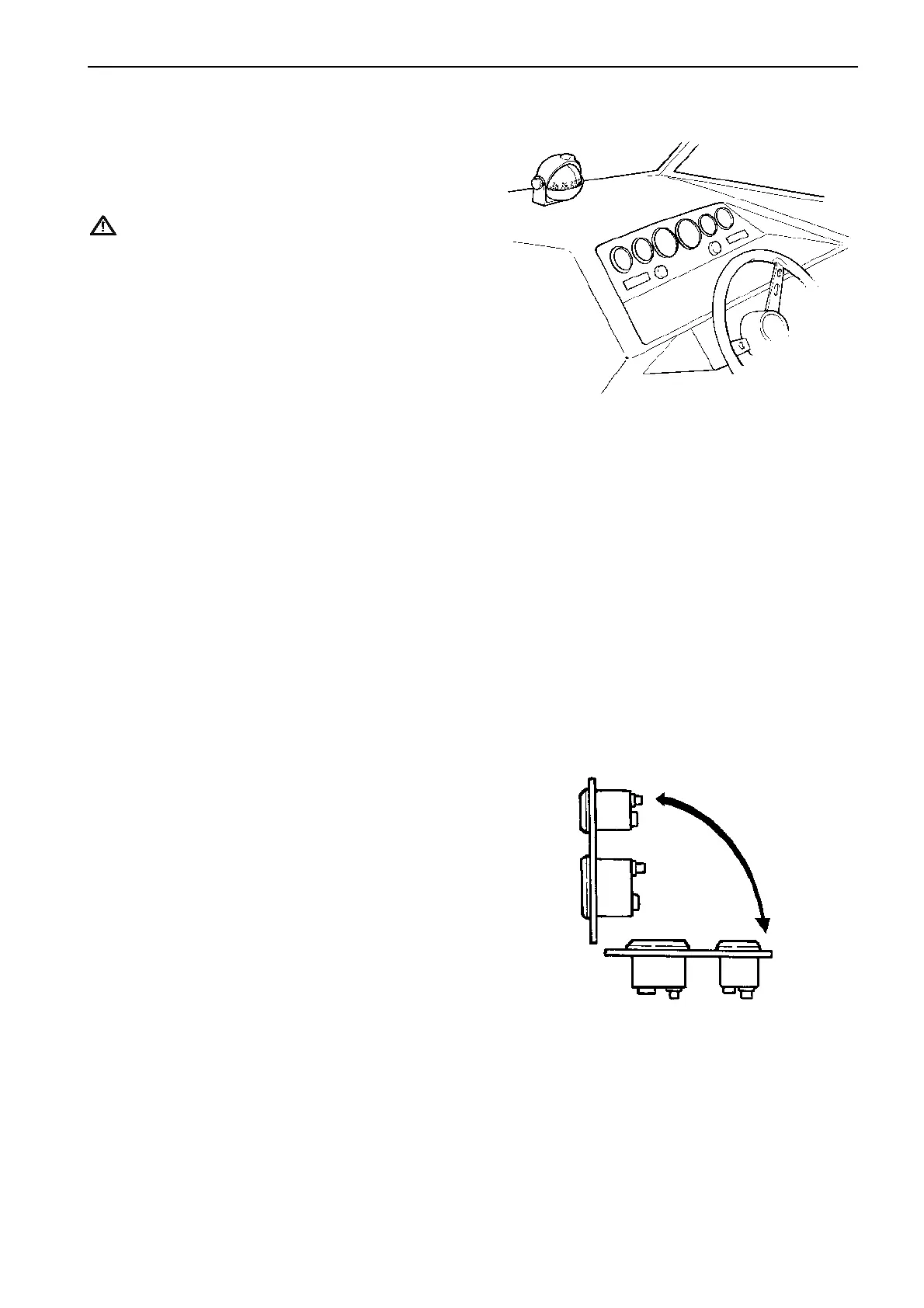
The instruments can be installed from a horizontal
plane (lying) to the vertical plane (standing). Other an-
gles (inclinations) lead to reduced accuracy and risk
of greater wear (shorter life span) of the instruments.
Risk of explosion
Gas is formed in the battery during charging. Short cir-
cuit, naked flames or sparks in the vicinity of the bat-
tery can cause a powerful explosion. Ensure proper
ventilation, especially if the battery is charged in a
closed room.
WARNING! Always disconnect the charge
current before removing the cable clamps.
Charge state
The charge state is the level to which the battery is
charged. This state can be measured either by mea-
suring the battery acid specific gravity in each cell or
by measuring the off-load voltage of the cell. The lat-
ter cannot be done on modern batteries since the
cells’ electrical connections are enclosed and there-
fore not accessible for measurement. Measuring the
off-load voltage across the poles gives entirely wrong
information if any cell(s) should be defective. The bat-
tery acid’s specific gravity is instead measured with a
hydrometer. Specific gravity varies with temperature.
The lower the temperature the higher the specific
gravity.
The battery is fully charged when the acid density is
1.28 g/cm
3
at +25°C (77°F). A battery filled with tropi-
cal acid is fully charged when the acid specific gravity
is 1.24 g/cm
3
at +25°C (77°F).

 Loading...
Loading...











