RocketIO™ Transceiver User Guide www.xilinx.com 23
UG024 (v3.0) February 22, 2007
RocketIO Transceiver Instantiations
R
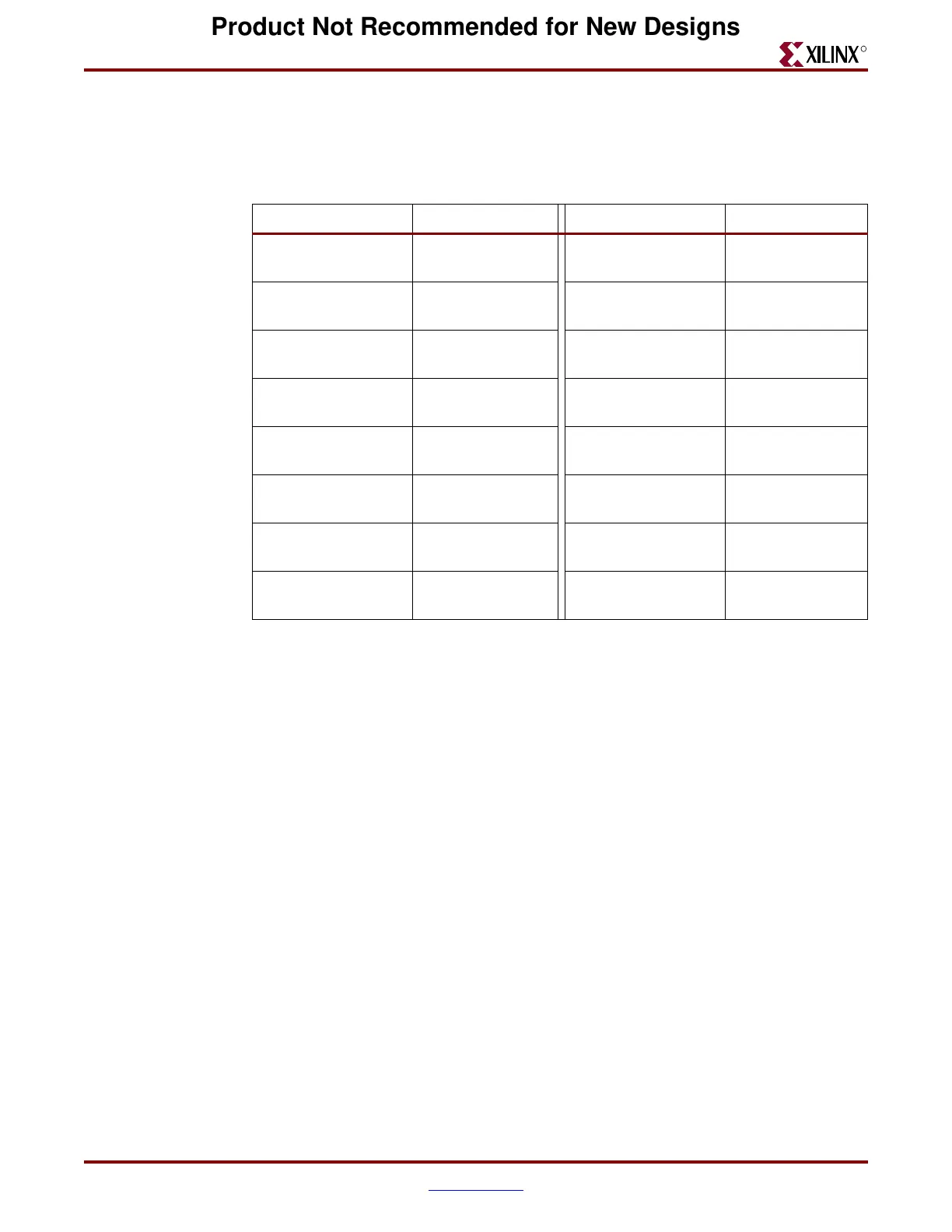
Table 1-4 lists the sixteen gigabit transceiver primitives provided. These primitives carry
attributes set to default values for the communications protocols listed in Table 1-2. Data
widths of one, two, and four bytes are selectable for each protocol.
There are two ways to modify the RocketIO transceiver:
• Static properties can be set through attributes in the HDL code. Use of attributes are
covered in detail in “Primitive Attributes,” page 29.
• Dynamic changes can be made by the ports of the primitives
The RocketIO transceiver consists of the Physical Media Attachment (PMA) and Physical
Coding Sublayer (PCS). The PMA contains the serializer/deserializer (SERDES), TX and
RX buffers, clock generator, and clock recovery circuitry. The PCS contains the 8B/10B
encoder/decoder and the elastic buffer supporting channel bonding and clock correction.
The PCS also handles Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC). Refer again to Figure 1-1, showing
the RocketIO transceiver top-level block diagram and FPGA interface signals.
RocketIO Transceiver Instantiations
For the different clocking schemes, several things must change, including the clock
frequency for USRCLK and USRCLK2 discussed in “Digital Clock Manager (DCM)
Examples” in Chapter 2. The data and control ports for GT_CUSTOM must also reflect this
change in data width by concatenating zeros onto inputs and wires for outputs for Verilog
designs, and by setting outputs to open and concatenating zeros on unused input bits for
VHDL designs.
HDL Code Examples
Please use the Architecture Wizard to create instantiation templates. This wizard creates
code and instantiation templates that define the attributes for a specific application.
Table 1-4: Supported RocketIO Transceiver Primitives
Primitives Description Primitive Description
GT_CUSTOM
Fully customizable
by user
GT_XAUI_2
10-Gb Ethernet,
2-byte data path
GT_FIBRE_CHAN_1
Fibre Channel,
1-byte data path
GT_XAUI_4
10-Gb Ethernet,
4-byte data path
GT_FIBRE_CHAN_2
Fibre Channel,
2-byte data path
GT_INFINIBAND_1
Infiniband, 1-byte
data path
GT_FIBRE_CHAN_4
Fibre Channel,
4-byte data path
GT_INFINIBAND_2
Infiniband, 2-byte
data path
GT_ETHERNET_1
Gigabit Ethernet,
1-byte data path
GT_INFINIBAND_4
Infiniband, 4-byte
data path
GT_ETHERNET_2
Gigabit Ethernet,
2-byte data path
GT_AURORA_1
Xilinx protocol,
1-byte data path
GT_ETHERNET_4
Gigabit Ethernet,
4-byte data path
GT_AURORA_2
Xilinx protocol,
2-byte data path
GT_XAUI_1
10-Gb Ethernet,
1-byte data path
GT_AURORA_4
Xilinx protocol,
4-byte data path
Product Not Recommended for New Designs

 Loading...
Loading...