Structured Text Programming
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-RM006K-EN-P - November 2018 535
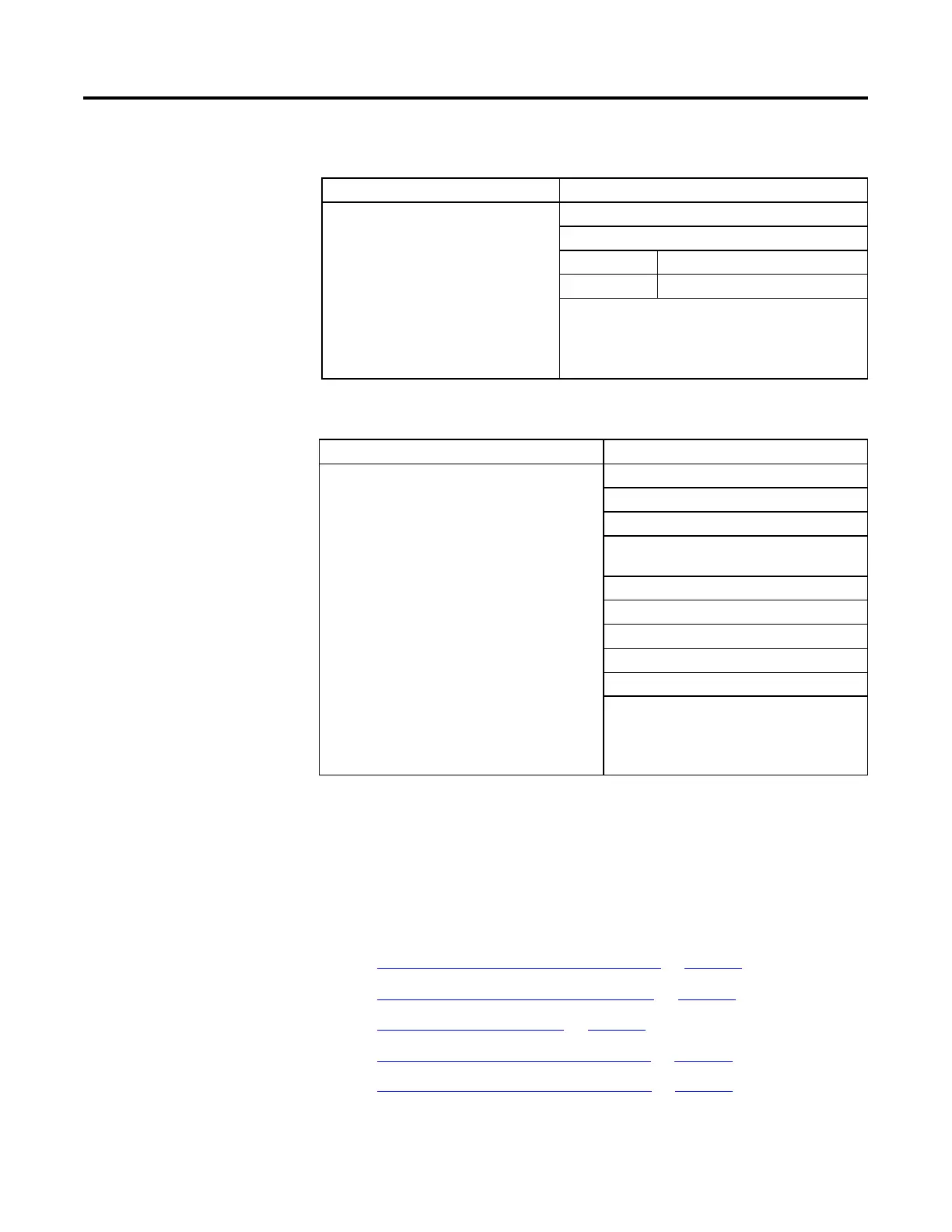
Example 1
If performing the following, Enter this structured text
The WHILE_DO loop evaluates its conditions first. If
the conditions are true, the controller then executes
the statements within the loop.
This differs from the REPEAT_UNTIL loop because the
REPEAT_UNTIL loop executes the statements in the
construct and then determines if the conditions are
true before executing the statements again. The
statements in a REPEAT_UNTIL loop are always
executed at least once. The statements in a
WHILE_DO loop might never be executed.
pos := 0;
While ((pos <= 100) & structarray[pos].value <> targetvalue)) do
pos := pos + 2;
String_tag.DATA[pos] := SINT_array[pos];
end_while;
Example 2
If performing the following, Enter this structured text
Move ASCII characters from a SINT array into a string tag. (In a
SINT array, each element holds one character.) Stop when you
reach the carriage return.
Initialize Element_number to 0.
Count the number of elements in SINT_array (array that
contains the ASCII characters) and store the result in
SINT_array_size (DINT tag).
If the character at SINT_array[element_number] = 13 (decimal
value of the carriage return), then stop.
Set String_tag[element_number] = the character at
SINT_array[element_number].
Add 1 to element_number. This lets the controller check the
next character in SINT_array.
Set the Length member of String_tag = element_number.
(This records the number of characters in String_tag so far.)
If element_number = SINT_array_size, then stop. (You are at
the end of the array and it does not contain a carriage return.)
element_number := 0;
SIZE(SINT_array, 0, SINT_array_size);
While SINT_array[element_number] <> 13 do
String_tag.DATA[element_number] :=
SINT_array[element_number];
element_number := element_number + 1;
String_tag.LEN := element_number;
If element_number = SINT_array_size then
exit;
end_if;
end_while;
Click a topic below for more information on issues that are unique to structured
text programming. Review this information to make sure you understand how
your structured text programming will execute.
See also
Structured Text Components: Assignments on page 510
Structured Text Components: Expressions on page 513
Structured Text Instructions on page 519
Structured Text Components: Constructs on page 520
Structured Text Components: Comments on page 509
Attributes
 Loading...
Loading...











