Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-RM003N-EN-P - October 2011 677
Structured Text Programming Appendix C
Use Logical Operators
Logical operators let you check if multiple conditions are true or false. The result
of a logical operation is a BOOL value.
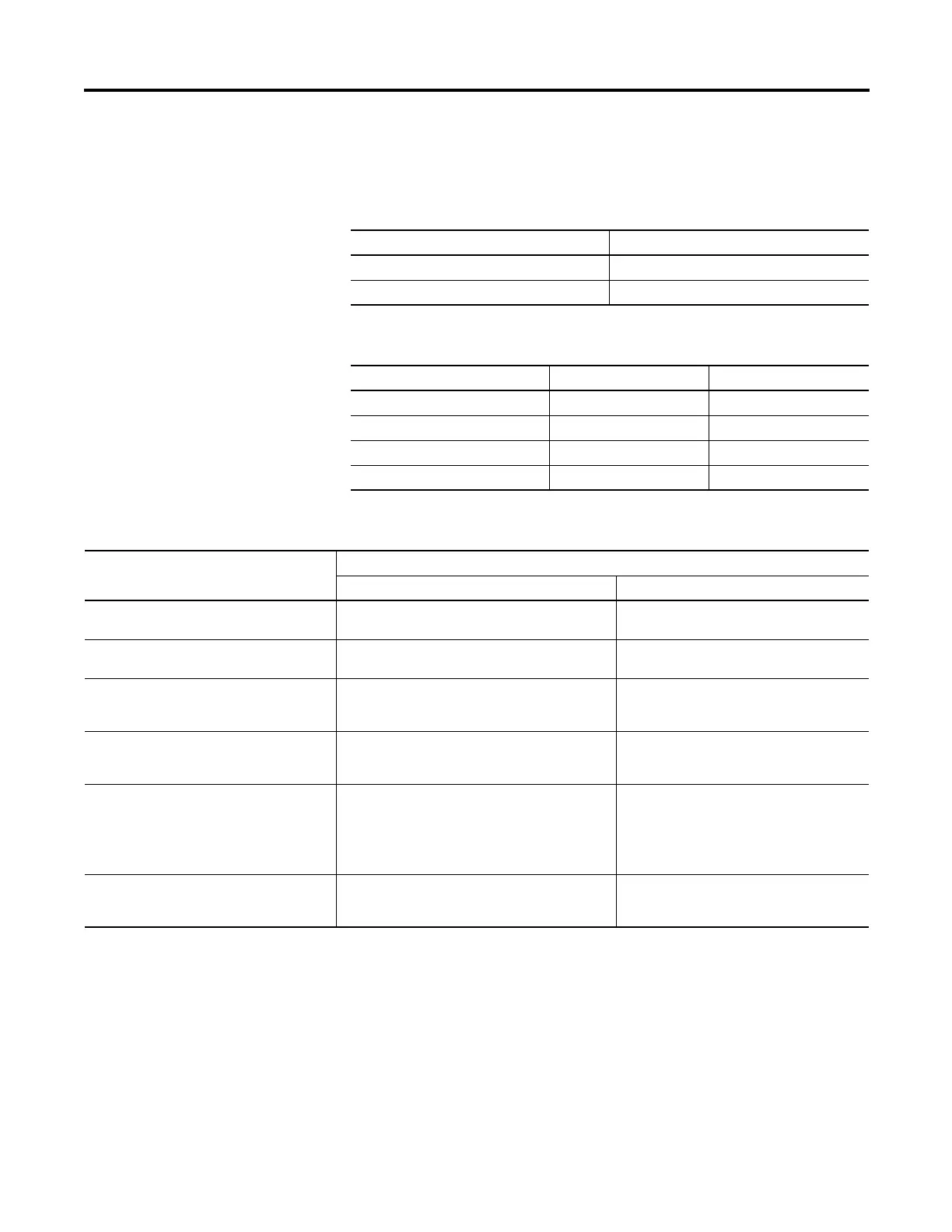
Use these logical operators.
The table shows some examples.
If the comparison is The result is
True 1
False 0
For Use this operator Data type
Logical AND &, AND BOOL
Logical OR OR BOOL
Logical exclusive OR XOR BOOL
Logical complement NOT BOOL
Use this format Example
For this situation Write
BOOLtag If photoeye is a BOOL tag and your specification
says: ‘If photoeye is on then…’
IF photoeye THEN...
NOT BOOLtag If photoeye is a BOOL tag and your specification
says: ‘If photoeye is off then…’
IF NOT photoeye THEN...
expression1 & expression2 If photoeye is a BOOL tag, temp is a DINT tag, and
your specification says: ‘If photoeye is on and temp is
less than 100⋅ then…’
IF photoeye & (temp<100) THEN...
expression1 OR expression2 If photoeye is a BOOL tag, temp is a DINT tag, and
your specification says: ‘If photoeye is on or temp is
less than 100⋅ then…’
IF photoeye OR (temp<100) THEN...
expression1 XOR expression2 If photoeye1 and photoeye2 are BOOL tags and your
specification says: ‘If:
·photoeye1 is on while photoeye 2 is off
·photoeye1 is off while photoeye 2 is on
then…’
IF photoeye1 XOR photoeye2 THEN...
BOOLtag := expression1 & expression2 If photoeye1 and photoeye2 are BOOL tags, open is a
BOOL tag, and your specification says: ‘If photoeye1
and photoeye2 are both on, set open to true’.
Open := photoeye1 & photoeye2;

 Loading...
Loading...











