Behavior models used in CIP Motion
Rockwell Automation Publication MOTION-RM003I-EN-P - February 2018 57
Current State Event Conditions Next State
Running Shutdown
Shutdown
Running Major Fault
Major Faulted
Any State Connection Close
Initializing
Any State Connection Loss
Major Faulted
See also
State Behavior on page 61
Fault and Alarm Behavior on page 41
Exceptions on page 41
The Motor Attributes define the minimal set of required attributes to support
CIP Motion device interchangeability. This guarantees that there is sufficient
parametric data provided by the controller for any CIP Motion compliant device,
for example, a drive, to effectively control a given motor.
The Usage category for an attribute is based on the Motor Type. Where needed,
Required versus Optional is further differentiated by abbreviations for PM
(Permanent Magnet) and IM (Induction Motors). It is implied that these motor
attributes are applicable to all drive modes, F, P, V, and T, but not applicable for N
(No Control) axis configurations where there is no active motor control function.
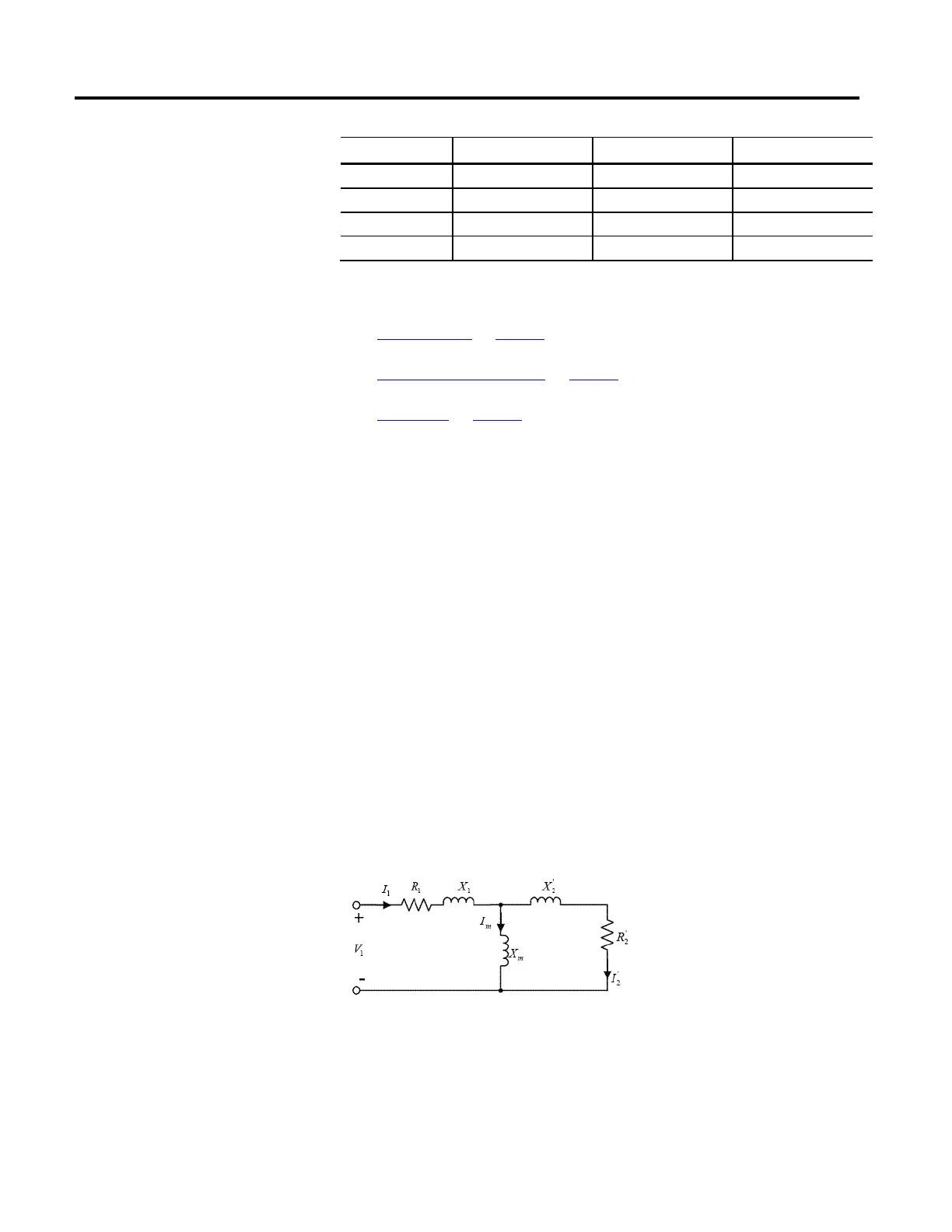
For induction motors, the Motion Control Axis leverages the IEEE recommended
phase-neutral equivalent circuit motor model based on "Wye" configuration.
Reactance values, X, are related to their corresponding Inductance values, L, by X
= ωL, where ω is the rated frequency of the motor. The prime notation, for
example, X
2
', R
2
', indicates that the actual rotor component values X
2
, and R
2
are
referenced to the stator side of the stator-to-rotor winding ratio.
IEEE per Phase Motor Model:
For permanent magnet motors, the Motion Control Axis assumes all motor
parameters are defined in the context of a phase-to-phase motor model.

 Loading...
Loading...











