Analog Outputs 2-19
Table 2.B Analog Output Scaling Ranges
Analog Output Configuration Examples
This section gives a few examples of valid analog output configurations and
describes the behavior of the output in each case.
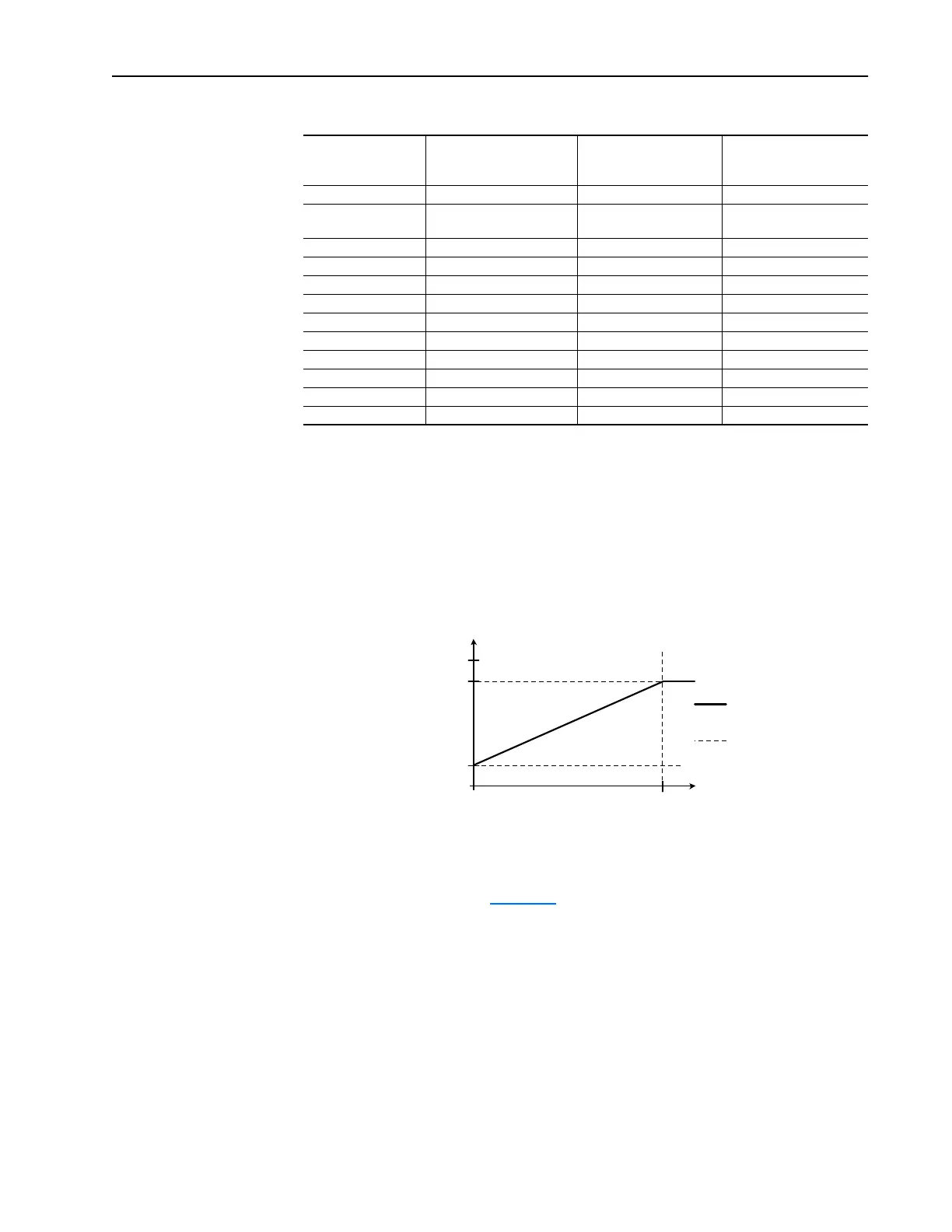
Example 1 -- Unsigned Output Quantity
• [Analog Out1 Sel] = “Output Current”
• [Analog Out1 Lo] = 1 volt
• [Analog Out1 Hi] = 9 volts
Note that analog output value never goes outside the range defined by
[Analog Out1 Lo] and [Analog Out1 Hi], even if output current is beyond
the range defined in
Table 2.B. This is true in all cases, including all the
following examples.
Example 2 -- Unsigned Output Quantity, Negative Slope
• [Analog Out1 Sel] = “Output Current”
• [Analog Out1 Lo] = 9 volts
• [Analog Out1 Hi] = 1 volts
This example shows that you can have [Analog Out1 Lo] greater than
[Analog Out1 Hi]. The result is a negative slope on the scaling from original
quantity to analog output voltage. Negative slope could also be applied to
any of the other examples in this section.
Quantity
[Analog Outx Lo]
Corresponds to:
(Absolute Value Disabled)
[Analog Outx Lo]
Corresponds to:
(Absolute Value Enabled)
[Analog Outx Hi]
Corresponds to:
Output Frequency -[Maximum Freq] 0 Hz [Maximum Freq]
Commanded
Frequency
-[Maximum Freq] 0 Hz [Maximum Freq]
Output Current 0 Amps 0 Amps 200% of drive rated current
Output Torque Current -200% of drive rated current 0 Amps 200% of drive rated current
Output Flux Current 0 Amps 0 Amps 200% of drive rated current
Output Power 0 kW 0 kW 200% of drive rated power
Output Voltage 0 V 0 V 120% of drive rated voltage
Dc Bus Voltage 0 V 0 V 200% of drive rated voltage
PI Reference -100% 0% 100%
PI Feedback -100% 0% 100%
PI Error -100% 0% 100%
PI Output -100% 0% 100%
10V
[Analog Out1 Hi]
[Analog Out1 Lo]
0V
0% 200%
Output Current
Analog
Output Voltage
Output Current vs.
Analog Output Voltage
Marker Lines

 Loading...
Loading...











