duplication at the hosts addressing, that is, there is different MAC addresses to each
host. Figure 36 exemplifies the MAC table at a given LAN.
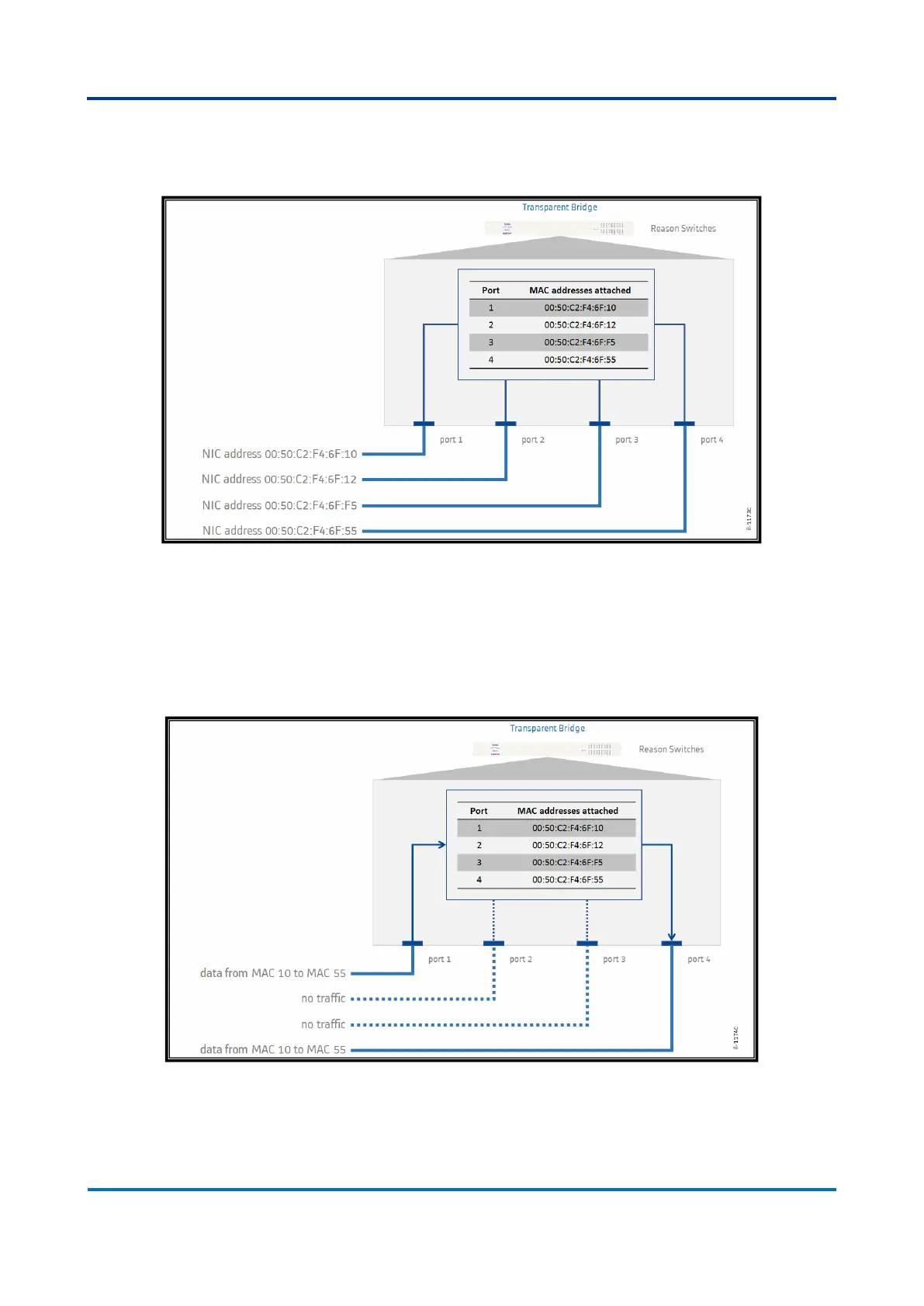
Figure 38: Address a table at a given Switch
As the switch knows where the hosts are, incoming data to a mapped host will be
redirected through the interface where the destination is attached, and no data will
be sent to other interfaces, as shown below. If there is incoming data to a host not
mapped as destination, the switch may flood the ports connected to other switching
equipment or drop the packets.
Figure 39: Forwarding traffic in an Ethernet switch
As networks are not static and hosts can be connected and disconnected any time,
the switch must inspect its own MAC table to update it. This is called aging of the
MAC table and it is performed by the switch verifying MAC addresses at the incoming
 Loading...
Loading...