Chapter 6. Operating system installation 197
6.5 Booting from SAN
Boot from SAN (or SAN Boot) is a technique used when the node in the chassis has no local
disk drives. It uses an external storage system LUN to boot the operating system. Both the
operating system and data are on the SAN. This technique is commonly used to provide
higher availability and better utilization of the systems storage (where the operating system
is). Hot spare Nodes or “Rip-n-Replace” techniques can also be easily implemented by using
boot from SAN.
To successfully implement SAN Boot, the following conditions need to be met:
Storage system supports SAN Boot.
Operating system supports SAN Boot.
FC HBAs, or iSCSI initiators support SAN Boot.
Here are some useful guidelines for booting from SAN:
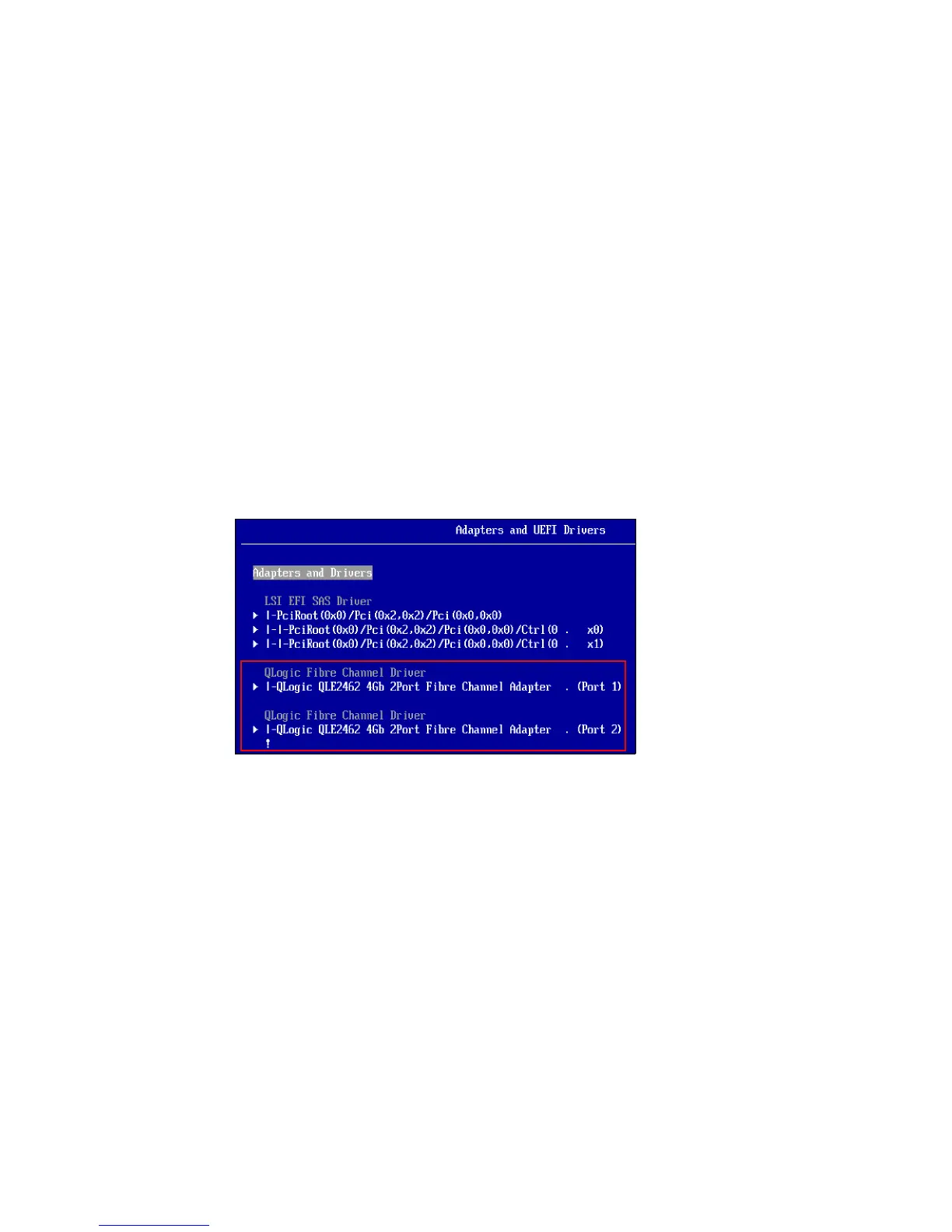
Check if UEFI recognizes the adapter. Select UEFI System Settings Adapters and
UEFI Drivers. The Adapters and UEFI Drivers panel displays, as shown in Figure 6-19.
You need to see Card - HBA. If not, reflash the UEFI, IMM, and Firmware of the HBA and
check again.
Figure 6-19 Adapters visible in UEFI
If you do not have internal drives, disable the onboard SAS RAID Controller by selecting
System Settings Devices and IO ports Enable/Disable Onboard Devices and
disabling the SAS Controller or Planar SAS.
Set the HBA as the first device in the Option ROM Execution Order by selecting System
Settings Devices and IO Ports Set Option ROM Execution Order.
For legacy operating systems only that do not support UEFI, set Legacy Only as the first
boot device.
Remove all devices, which might not host an OS, from the boot order. The optimal
minimum configuration is CD/DVD and Hard Disk 0. For legacy operating systems only,
set Legacy Only as the first boot device.
Enable the BIOS from your HBA.
Verify that your HBA can see a logical unit number (LUN) from your storage.
For Microsoft Windows installations, make sure that the LUN is accessible through only
one path, either Zoning or LUN masking.
After installation, remember to install the multipath driver
before you set more than one
path, if you have more than one path to the LUN.

 Loading...
Loading...











