Chapter 2. Technology 43
Figure 2-32 shows the typical FlashCache deployment scenario:
Figure 2-32 IBM FlashCache Storage Accelerator deployment
The FlashCache Storage Accelerator also works in virtualized environment, transparently
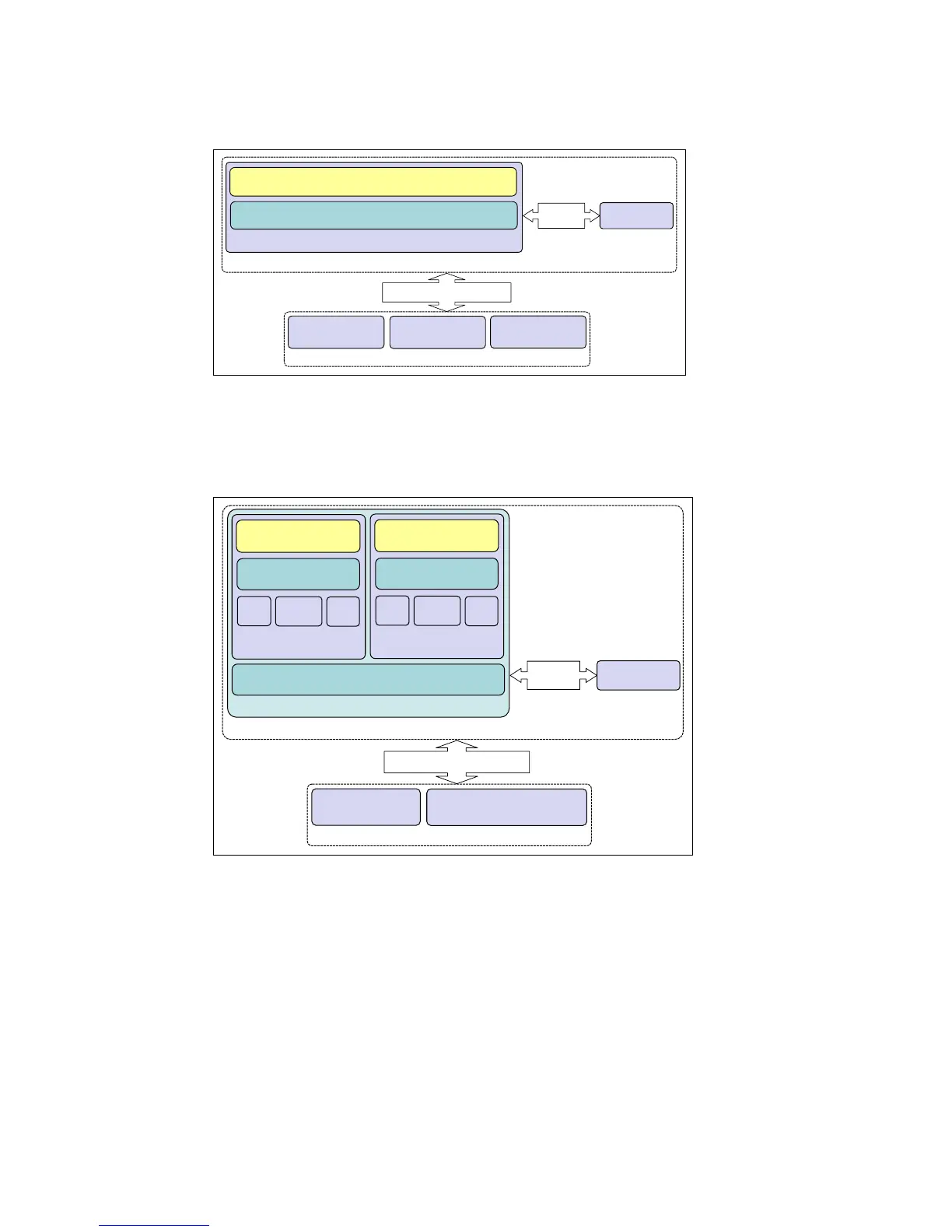
caching data of virtual machines. Figure 2-33 shows the typical FlashCache deployment
scenario for virtual environment.
Figure 2-33 BM FlashCache Storage Accelerator deployment in virtual environment
The FlashCache Storage Accelerator software intelligently caches the most actively read
application data. Cached data is read directly from flash cache instead of having to be read
from the slower primary storage. If the data is not available in cache, FlashCache Storage
Accelerator redirects the reads to primary storage and copies the data to cache to accelerate
subsequent reads.
For write operations, FlashCache Storage Accelerator employs “write-through” caching where
writes are written both to the FlashCache service in the host and to primary storage. A write is
considered complete only when the write to primary storage is acknowledged. Subsequent
reads of the data are quickly returned to the application from cache instead of from the slower
primary storage.
I/O
interface
IBM SSD
cache
Disks
Storage protocol
Volumes
Files
Primary data storage
Physical IBM server
Operating system (Windows Server or Linux Server)
FlashCache Storage Accelerator
Application
VMware vSphere ESXi hypervisor
I/O
interface
IBM SSD
cache
VMDK datastore
(VMDK file caching)
Storage protocol
VMDK datastore
(Disks, Volumes, Files caching)
Primary data storage
Physical IBM server
Virtual Machine
with guest OS (VMDK)
FlashCache software
(optional)
Application
FlashCache Storage Accelerator
Disks
Volumes
Files
Virtual Machine
with guest OS (VMDK)
FlashCache software
(optional)
Application
Disks
Volumes
Files
 Loading...
Loading...











