60
CONNECTION OF THE POWER UNIT
4.2.6 Connection of the motor
4.2.6.1 Selection of the motor cable
The correct cabling as well as the motor cable plays an important part in case of low
power in connection with long motor cable lengths. Ferrite cores and low-capacitance
cables (phase/phase < 65 pF/m, phase/screen < 120 pF/m) at the output have the fol-
lowingeects:
• longer motor cable lengths
• less abrasion of the motor gearbox by leakage currents
• better EMC properties (reduction of the common-mode output currents to earth)
4.2.6.2 Cable-fed disturbances depending on the motor cable length at AC supply
The maximum motor cable length is depending on the capacity of the cable as well as
on the EMC emitted interference. The following data apply for operation under nominal
rating conditions.
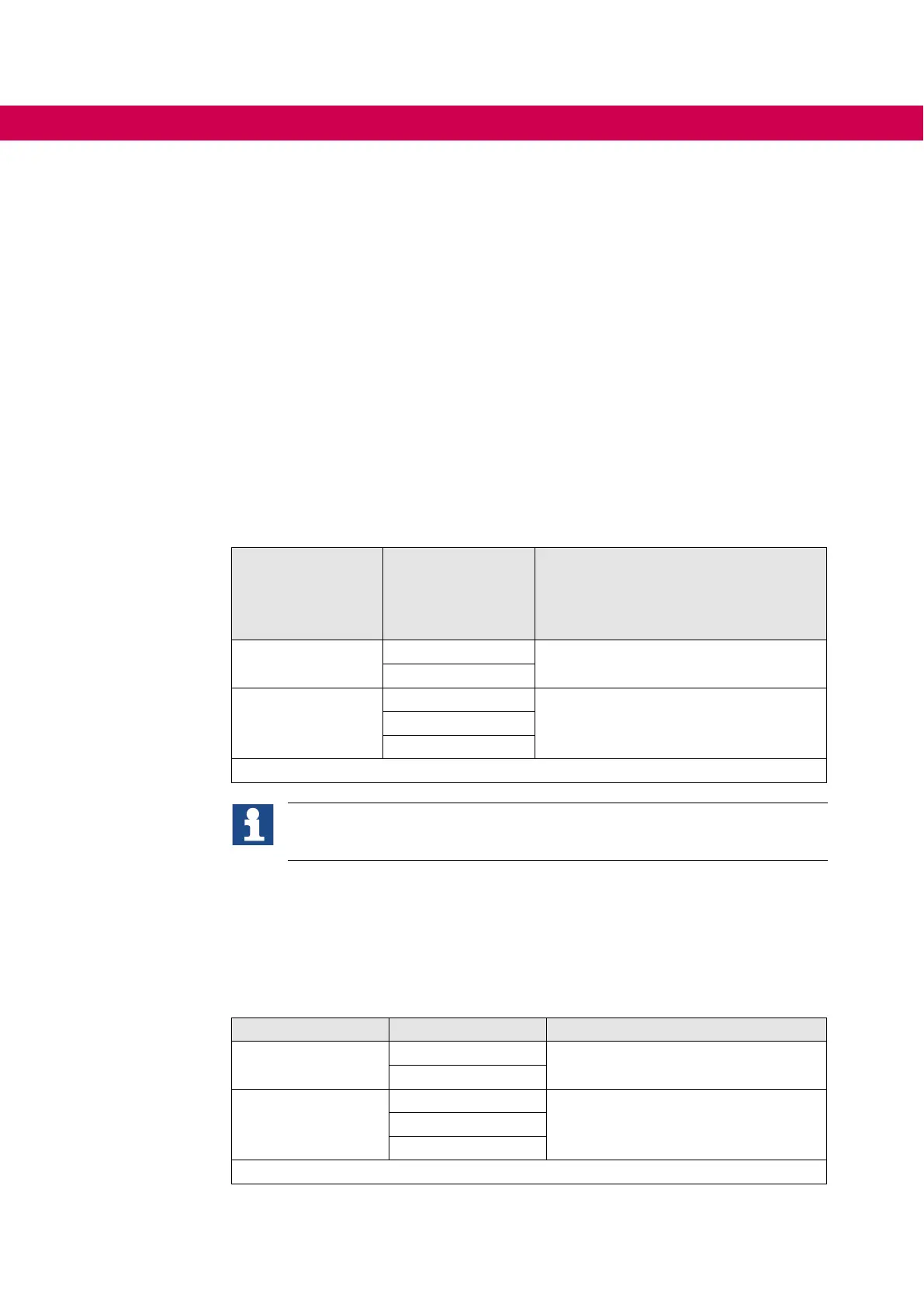
Voltage class Device size
Max. motor cable length (shielded)
in accordance with EN 61800-3
Category C2
Motor cable / m (low-capacitance)
230 V
1-phase
07
30
09
400 V
3-phase
07
5009
10
Table 38: Maximum motor cable length at AC supply
Theuseofmotorchokesorlterscansignicantlyincreasethecablelength.
KEBrecommendstheuseofmotorchokesorltersforalinelengthupto50m.
Motorchokesorltersareabsolutelynecessaryupto100m.
4.2.6.3 Motor cable length at operation with DC voltage
The maximum motor cable length at DC operation is basically dependent on the capaci-
tyofthemotorcable.TheinternallterisnotactiveatDCoperation.Externalmeasures
must be taken if necessary. The following data apply for operation under nominal rating
conditions.
Voltage class Device size Motor cable / m (low-capacitance)
230 V
1-phase
07
50
09
400 V
3-phase
07
5009
10
Table 39: Maximum motor cable length at DC operation

 Loading...
Loading...