4.8
Fuel Systems
Piston Valve Or Throttle Valve
The throttle valve controls the rate of engine air intake by
moving up and down inside the main bore. At small throttle
openings, air flow control is performed chiefly by the cutaway.
By controlling air flow the negative pressure over the needle
valve is regulated, in turn varying the fuel flow.
The throttle valves are numbered 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, etc., according to
the size of the cutaway in millimeters. The higher the number,
the leaner the gasoline/air mixture.
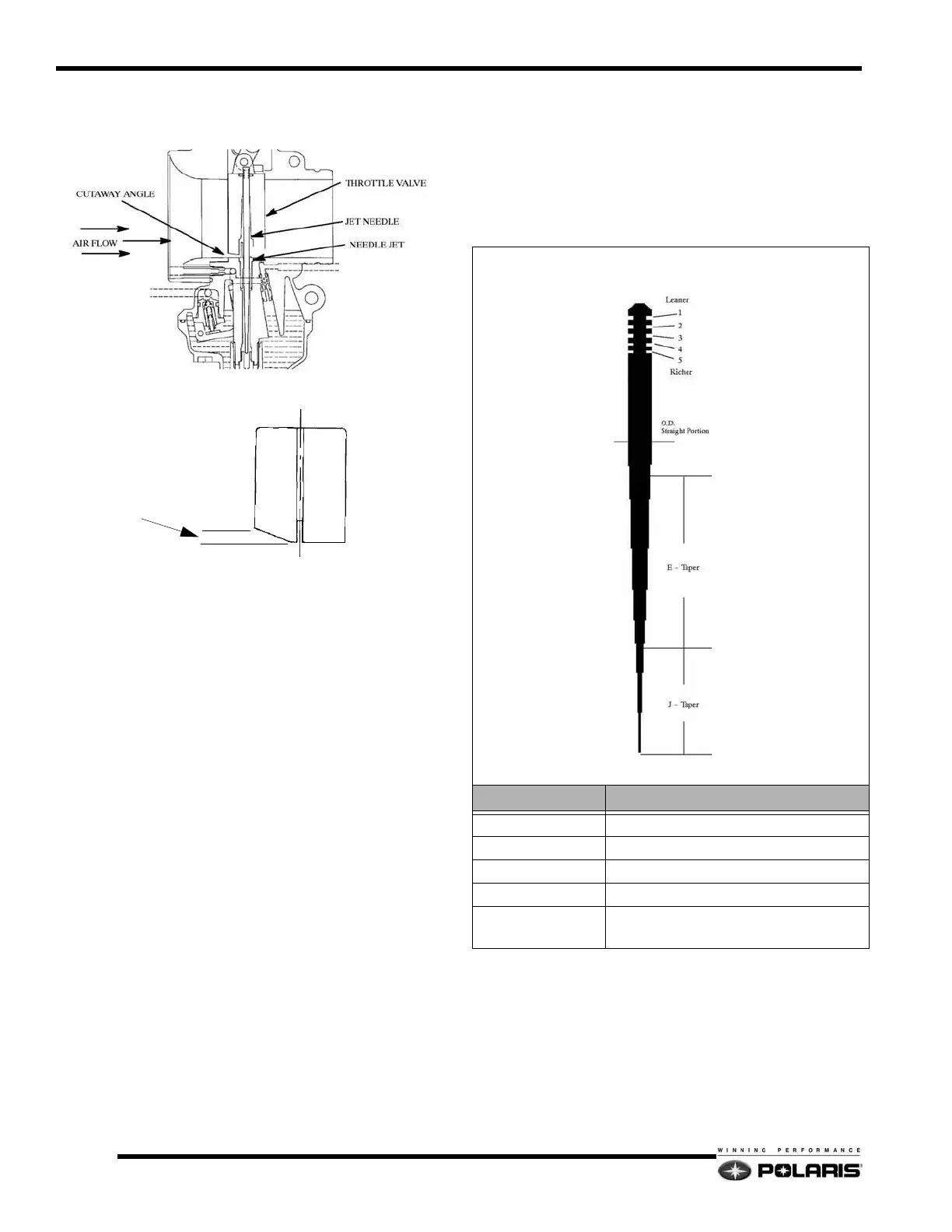
Jet Needle
The jet needle tapers off at one end and the clearance between
the jet needle and the needle jet increases as the throttle valve
opening gets wider. The air/fuel mixture ratio is controlled by
the height of the “E” ring inserted into one of the five slots
provided in the head of the jet needle.
This needle (example) is a 9DH01-57. The first number is the
approximate overall length in 10mm increments of the jet
needle. The 9 indicates the needle is approximately 90mm but
less that 100mm in length.
The letters on the jet needle indicate the angle of both tapers.
The first letter designates the taper angle of the top section
(closest to the grooves) and the second letter designates the
angle of the bottom taper. The taper angles are graduated in 15'
(15 minute) increments. The jet needle marked 9DH01-57
would have a top taper of 1_0' and a bottom taper of 2_0'.
The number following the letters on the jet needle is the serial
number and it varies with individual jet needles.
The last number, 57 indicates that the outside diameter is
2.57mm. The smaller the O.D., the richer the mixture.
Needle Jet
The needle jet works in conjunction with the jet needle.
intake side
9DH01-57
DESIGNATOR DESCRIPTION
9 Overall length in 10mm increments
D Taper of the top section of the needle
H taper of the bottom section of the needle
01 Serial number
-57
Outside diameter (O.D.) of the straight
portion

 Loading...
Loading...











