Start-Up
SINUMERIK 802S base line
4-27
Start-Up
MOVE, FILL AND FIND OPERATIONS
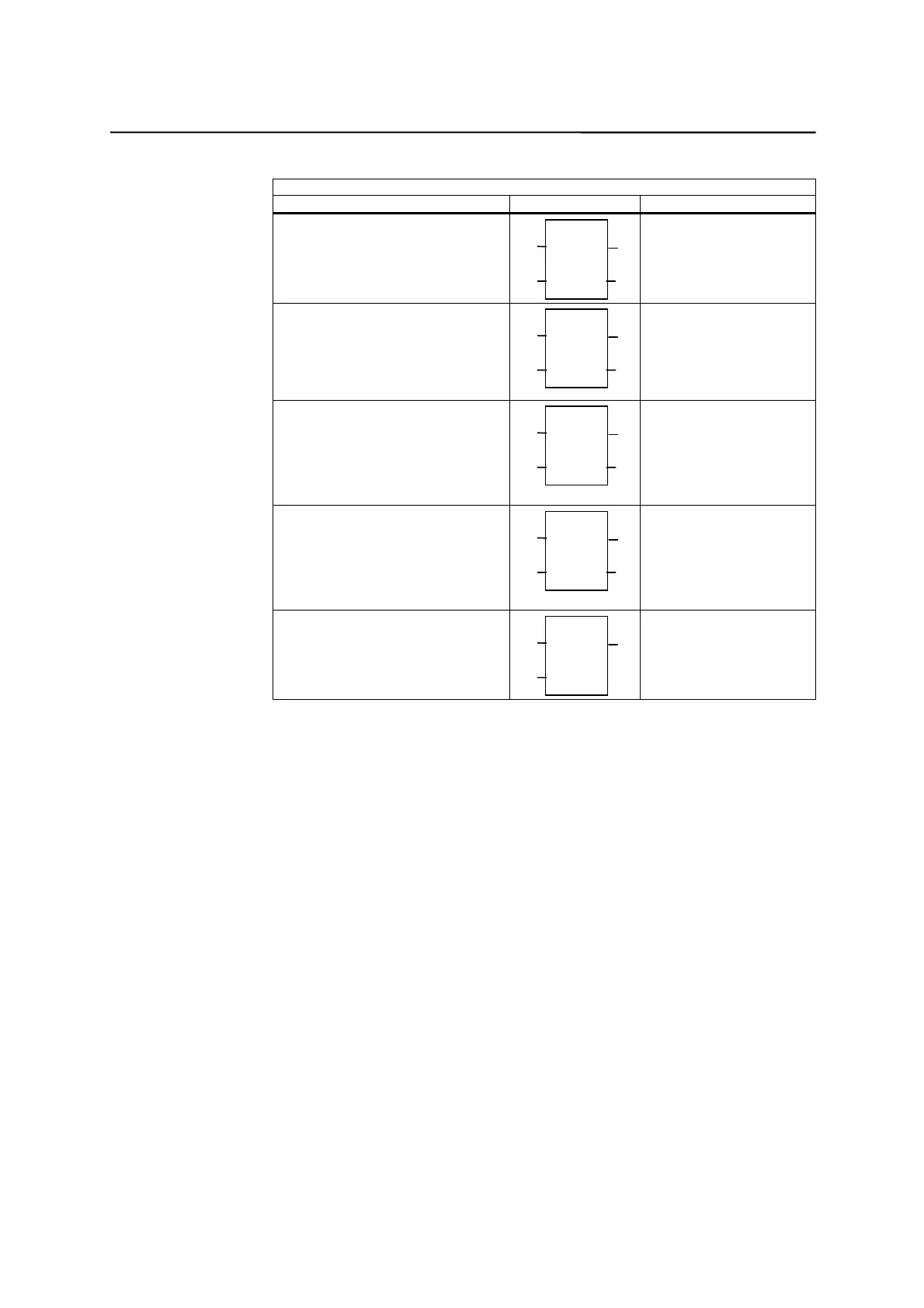
Instruction Ladder Symbol Valid Operands
Move Byte If EN = 1,
copy i to o.
MOV_B
IN
OUT
EN
ENO
Enable: EN
In: VB, IB, QB, MB, AC,
Constant, LB
Out: VB, IB, QB, MB, AC,
LB
Move Word If EN = 1,
copy i to o.
MOV_W
IN
OUT
EN
ENO
Enable: EN
In: VW, T, C, IW, QW,
MW, AC, Constant,
LW
Out: VW, T, C, IW, QW,
MW, AC, LW
Move DWord If EN = 1,
copy i to o.
MOV_DW
IN
OUT
EN
ENO
Enable: EN
In: VD, ID, QD, MD, AC,
Constant, LD
Out: VD, ID, QD, MD, AC,
LD
Move Real If EN = 1,
copy i to o.
MOV_R
IN
OUT
EN
ENO
Enable: EN
In: VD, ID, QD, MD,
AC, Constant, LD
Out: VD, ID, QD, MD, AC,
LD
Swap Bytes If EN = 1,
exchange MSB
and LSB of w.
SWAP
IN
EN
ENO
Enable: EN
In: VW, IW, QW, MW, T,
C, AC, LW
4.3.7 Program organization
Each programmer should divide the user program into several closed program
sections (subroutines). The S7-200 programming language allows the user to
create structured user programs. There are two program types - main
programs and subroutines. Eight program levels are possible.
A PLC cycle can be a multiple of the control-internal interpolation cycle (IPO
cycle). The machine manufacturer must set the PLC cycle according to his/her
own requirements (see machine data “PLC_IPO_TIME_RATIO”). The ratio
IPO/ PLC of 1:1 is the fastest possible cyclic processing.
Example:
The programmer programs a sequence control in the main program
using his own defined cycle counter. The sequence control defines all cyclic
signals in the subroutine (UP0); UP1/UP2 is called every two cycles, and UP 3
controls all signals in steps of three cycles.
 Loading...
Loading...











