41
9.4 DDNS
9.4.1 Overview
DDNS is short for Dynamic Domain Name Server. When the service runs, the DDNS client on the
router send its current WAN port IP address to the DDNS server, and then the server updates the
mapping relationship between the domain name and the IP address in the database to achieve
dynamic domain name resolution. You can enable this function to map the router's dynamically
changing WAN Port IP address (public network IP address) to a fixed domain name.
DDNS normally interworks with port forwarding, DMZ host and remote web-based management,
so that the internet users can access the internal server or the router’s web UI with a domain
name.
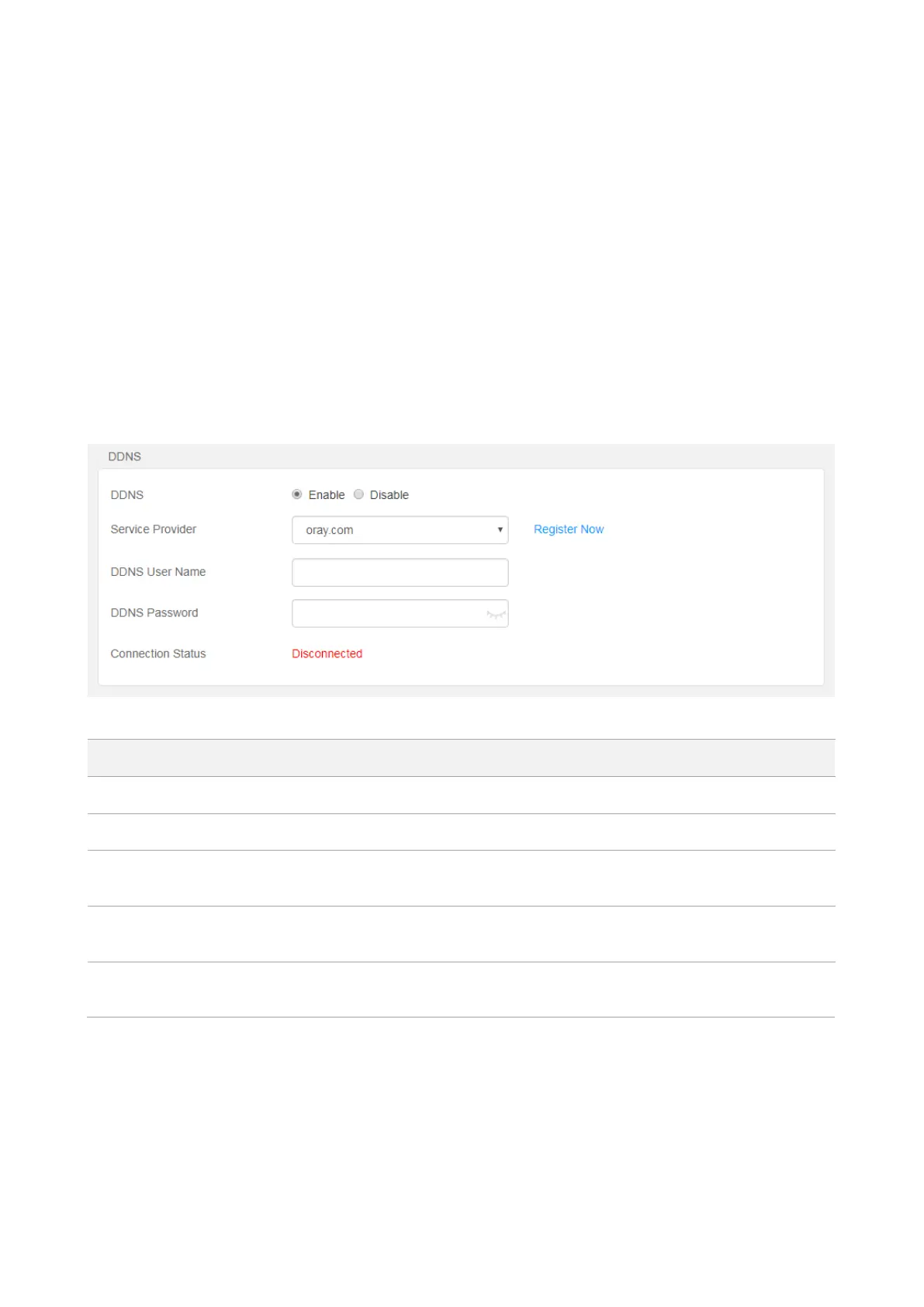
Choose Advanced, and move to DDNS module to access the configuration page. By default, it is
disabled. Select Enable, and the following page appears.
Parameter description:
It specifies whether to enable the DDNS function.
It specifies a DDNS service provider. The router supports oray.org and 88ip.cn.
It specifies the user name registered on a DDNS service provider's website for logging in
to the DDNS service.
It specifies the password registered on a DDNS service provider's website for logging in to
the DDNS service.
It specifies the current connection status of the DDNS service.
9.4.2 An example of configuring DDNS
Winnie uses F6 to set up network, and establishes a web server on LAN. She wants internet users
to access the resources on the server with a domain name. The port forwarding and DDNS
function can be enabled to fulfill the requirement.

 Loading...
Loading...