2.4. Controller I/O
If the controlled equipment does not take a differential input, an alternative
solution can be made as shown above. This solution is not very good in terms of
noise, and can easily pick up disturbing signals from other machinery. Care must
be taken when the wiring is done, and it must be kept in mind that disturbing
signals induced into analog outputs may also be present on other analog I/O.
2.4.4 Analog Inputs
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
Common mode input voltage -33 - 33 V
Differential mode input voltage* -33 - 33 V
Differential input resistance - 220 - kohm
Common mode input resistance - 55 - kohm
Common mode rejection ratio 75 - - dB
The analog inputs can be set to four different voltage ranges, which are
implemented in different ways, and therefore can have different offset and gain
errors. The specified differential mode input voltage is only valid with a common
mode voltage of 0V. To make it clear how easy it is to use analog outputs, some
simple examples are shown.
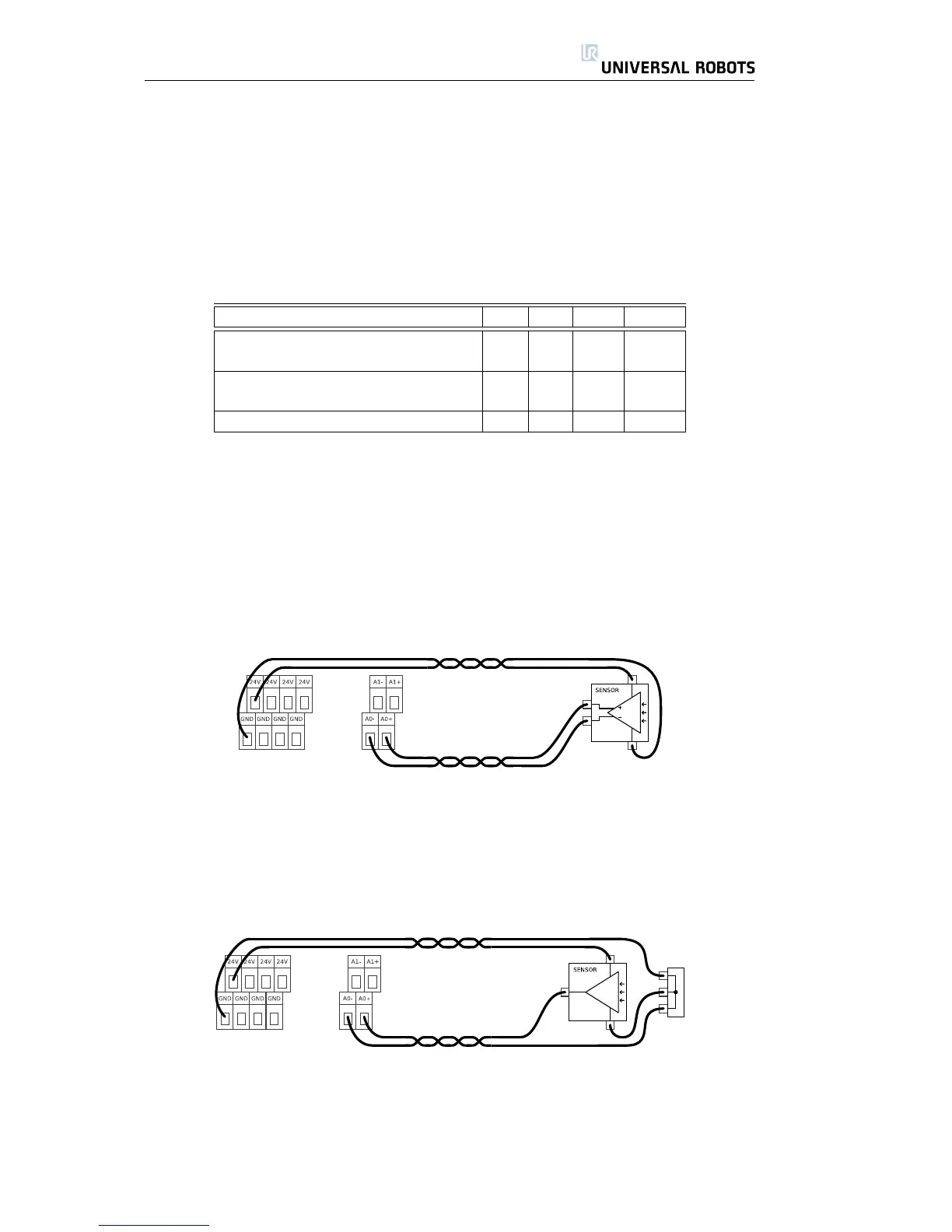
Using Analog Inputs, Differential Voltage Input
The simplest way to use analog inputs. The equipment shown, which could
be a sensor, has a differential voltage output.
Using Analog Inputs, Non-differential Voltage Input
If it is not possible to achieve a differential signal from the equipment used,
a solution could look something like the setup above. Unlike the non-differential
analog output example in subsection 2.4.3, this solution would be almost as
good as the differential solutions.
All Rights Reserved
25 UR10

 Loading...
Loading...











