330
Chapter 7 Tutorial
Signal Imperfections
7
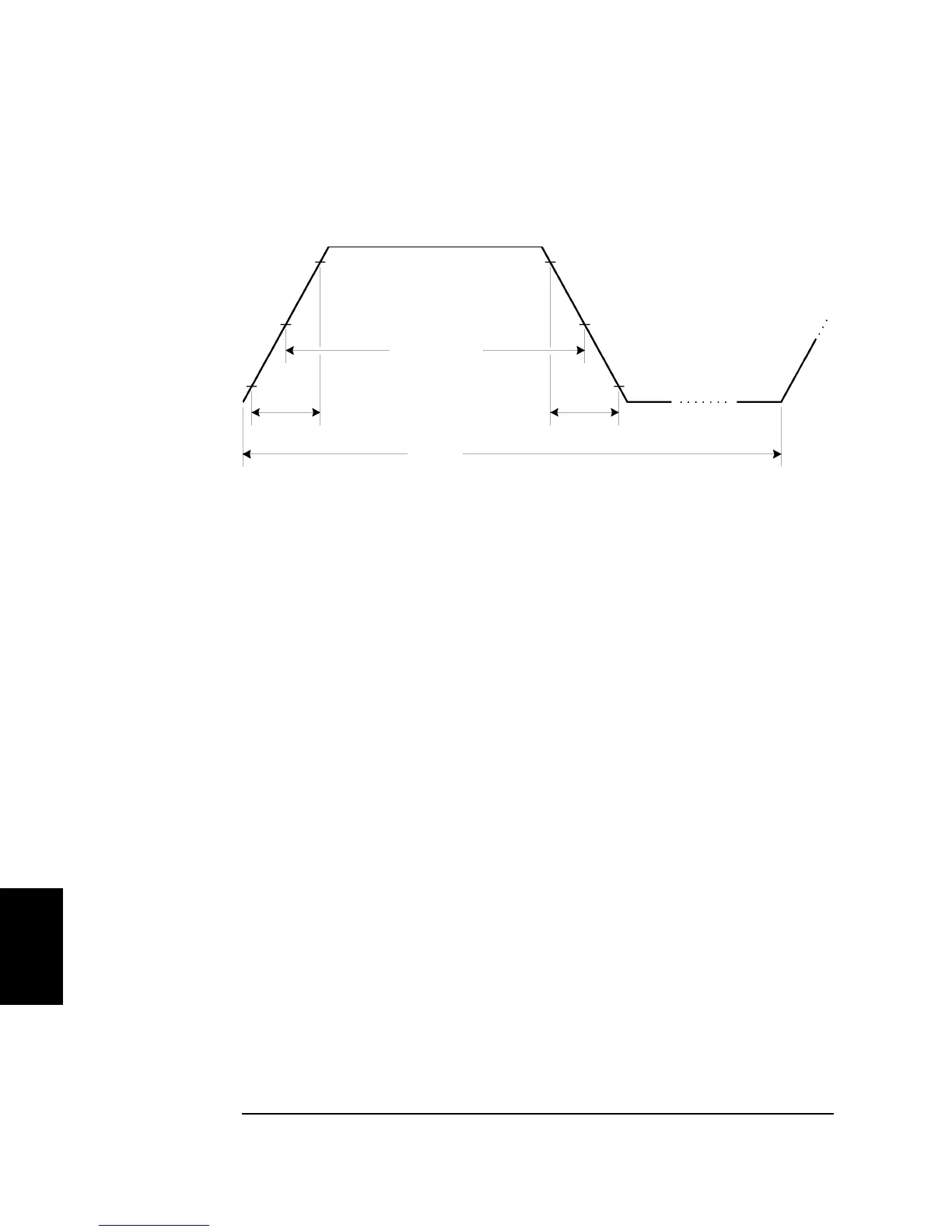
Pulse Waveform Parameters
Signal Imperfections
For sine waveforms, signal imperfections are easiest to describe and
observe in the frequency domain using a spectrum analyzer.
Any component of the output signal which has a different frequency
than the fundamental (or “carrier”) is considered to be spurious.
The signal imperfections can be categorized as harmonic, non-harmonic,
or phase noise and are specified in “decibels relative to the carrier level”
or “dBc”.
Harmonic Imperfections Harmonic components always appear at
multiples of the fundamental frequency and are created by non-linearities
in the waveform DAC and other elements of the signal path. At low
amplitudes, another possible source of harmonic distortion is due to the
current flowing through the cable
connected to the function generator’s
Sync
output connector. This current
can cause a small square-wave
voltage drop across the resistance of the
cable’s shield and some of this
voltage can be imposed on the main signal
. If this is a concern for your
application, you should
remove the cable or disable the
Sync
output
connector. If your application
requires that you
use the
Sync
output
connector, you can minimize the effect by terminating
the cable in a high
impedance load (rather than into a 50Ω load).
Rise Time Fall Time
10%
90%
0%
10%
90%
50%
Pulse Width
Period

 Loading...
Loading...