162 Chapter 4
Basic Digital Operation
Using Waveform Scaling
Using Waveform Scaling
Waveform scaling is used to eliminate DAC over-range errors. The ESG provides two methods of waveform
scaling:
Runtime Scaling Available in the Dual ARB Player and the Multitone modulation format, this type of
scaling enables you to make real-time scaling adjustments of a currently playing
waveform.
Permanent Scaling Available in only the Dual ARB player, this type of scaling permanently scales the data
of a non-playing waveform file residing in volatile memory.
This section describes how DAC over-range errors occur and how you can use waveform scaling to
eliminate these errors effectively.
How DAC Over-Range Errors Occur
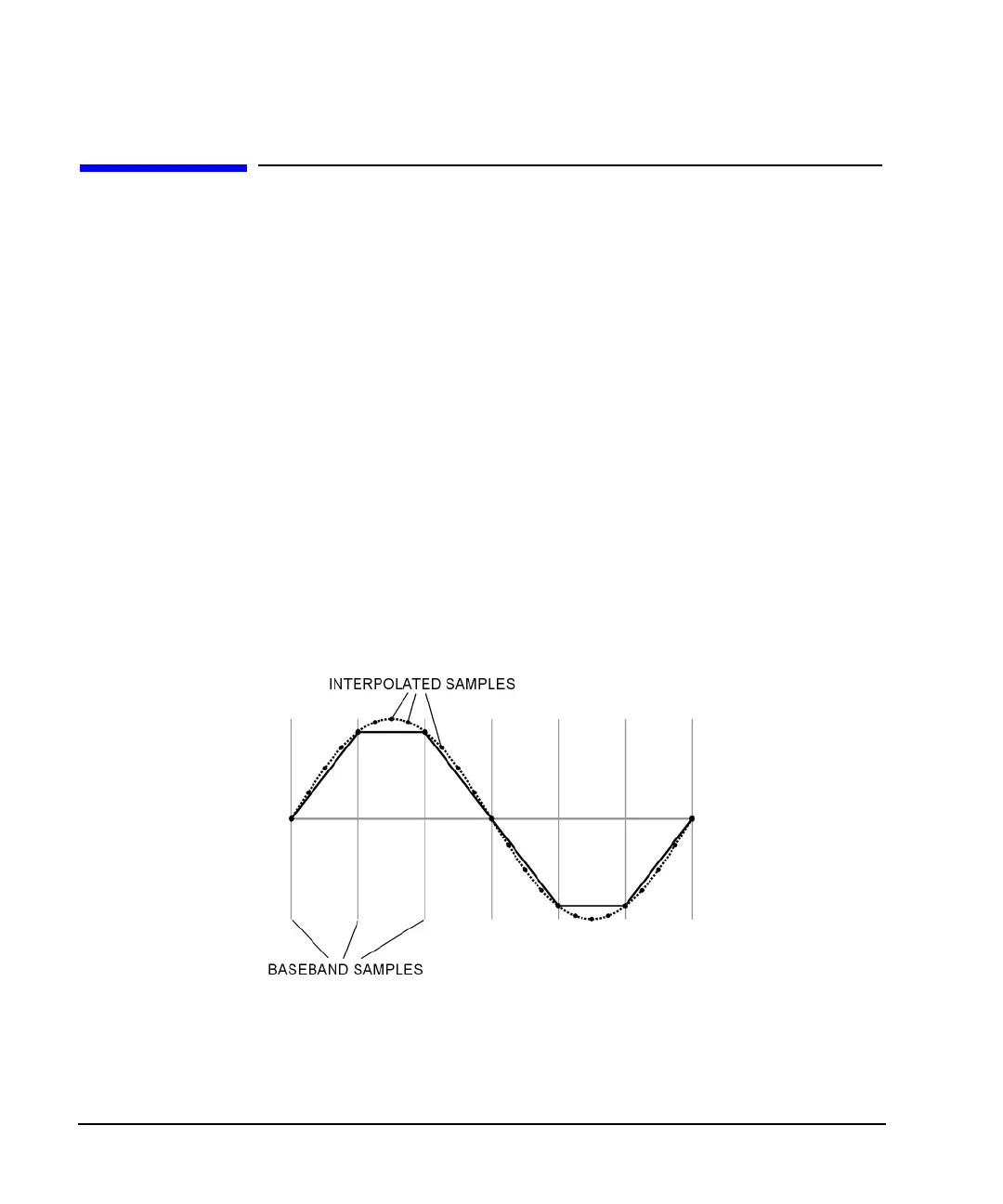
The ESG utilizes an interpolator filter in the conversion of the digital I and Q baseband waveforms into
analog waveforms. The clock rate of the interpolator is four times that of the baseband clock. The
interpolator therefore calculates sample points between the incoming baseband samples to equal the faster
clock rate and smooth out the waveform, giving it a more curve-like appearance (see Figure 4-24).
Figure 4-24 Waveform Interpolation
The interpolation filters in the DAC’s have overshoot. If a baseband waveform has a fast-rising edge, the
interpolator filter’s overshoot or frequency response becomes a component of the interpolated baseband
waveform. This response causes a ripple or ringing effect at the peak of the rising edge. If this ripple exceeds
(or overshoots) the upper limit of the DAC’s range, the interpolator calculates erroneous sample points and

 Loading...
Loading...