Publication 1766-RM001A-EN-P - October 2008
272 File Instructions
Addressing Modes and File Types can be used as shown in the following
table:
BSL - Bit Shift Left
Instruction Type: output
The BSL instruction loads data into a bit array on a false-to-true rung
transition, one bit at a time. The data is shifted left through the array, then
unloaded, one bit at a time. The following figure shows the operation of
the BSL instruction.
TIP
The source and destination operands must be of the same file type, unless
they are bit (B) and integer (N).
FLL Instruction Valid Addressing Modes and File Types
For definitions of the terms used in this table see Using the Instruction Descriptions on page 92.
Parameter
Data Files Function Files
CS - Comms
IOS - I/O
DLS - Data Log
Address
Mode
(1)
Address Level
O
I
S
B
T, C, R
N
F
ST
L
MG, PD
RI/RIX
PLS
RTC
HSC
PTOX, PWMX
STI
EII
BHI
MMI
LCD
Immediate
Direct
Indirect
Bit
Word
Long Word
Element
Source •• •••• • • • • • •••
Destination •• •••• • •
• ••
Length
•
(1) See Important note about indirect addressing.
IMPORTANT
You cannot use indirect addressing with: S, MG, PD, RTC, HSC, PTOX,
PWMX, STI, EII, BHI, MMI, CS, IOS, and DLS files.
EN
DN
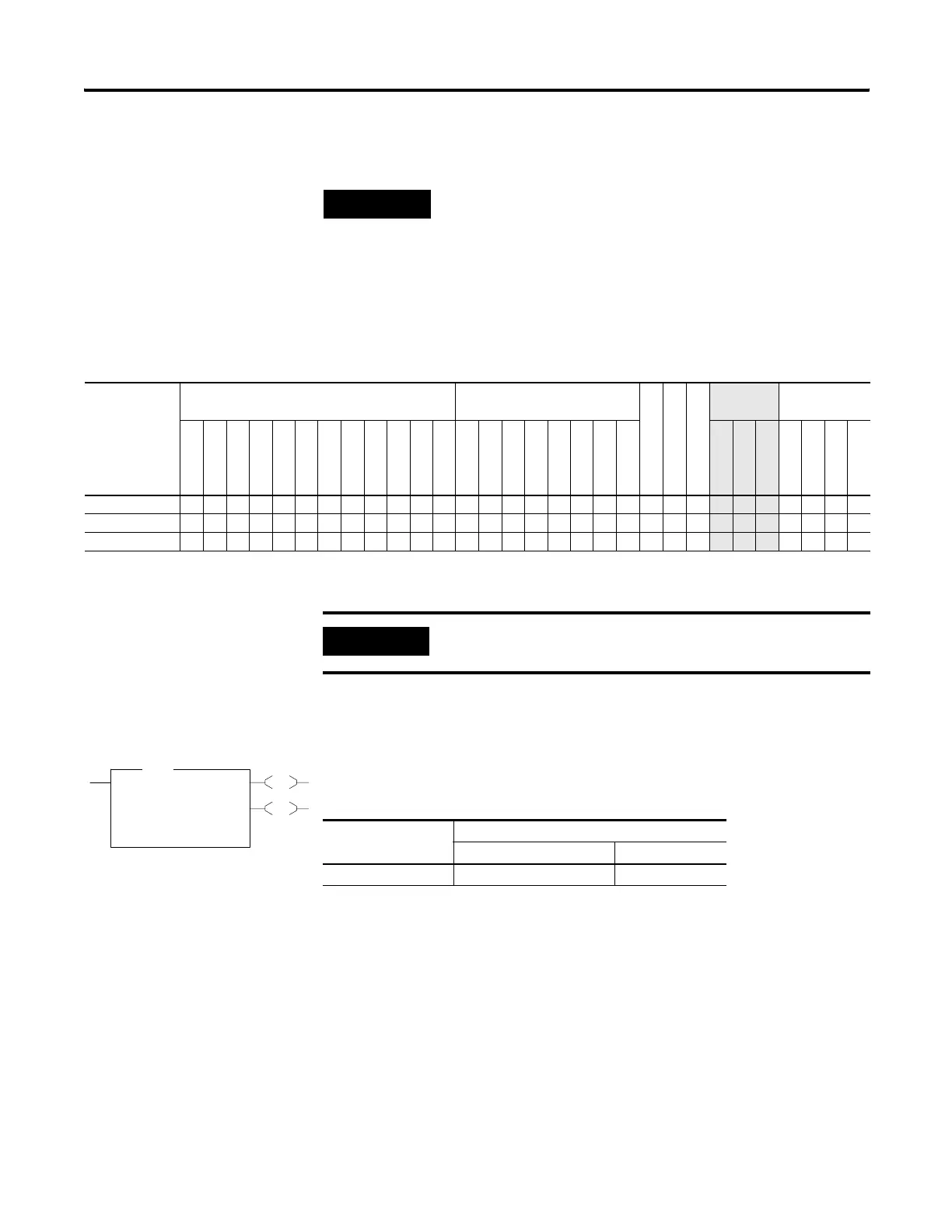
BSL
Bit Shift Left
File #B3:1
Control R6:0
Bit Address B32:0/0
Length 1<
BSL
Execution Time for the BSL Instruction
Controller When Rung Is:
True False
MicroLogix 1400 6.1018 µs 5.8258 µs
efesotomasyon.com - Allen Bradley,Rockwell,plc,servo,drive

 Loading...
Loading...