3. Instruction Set
API
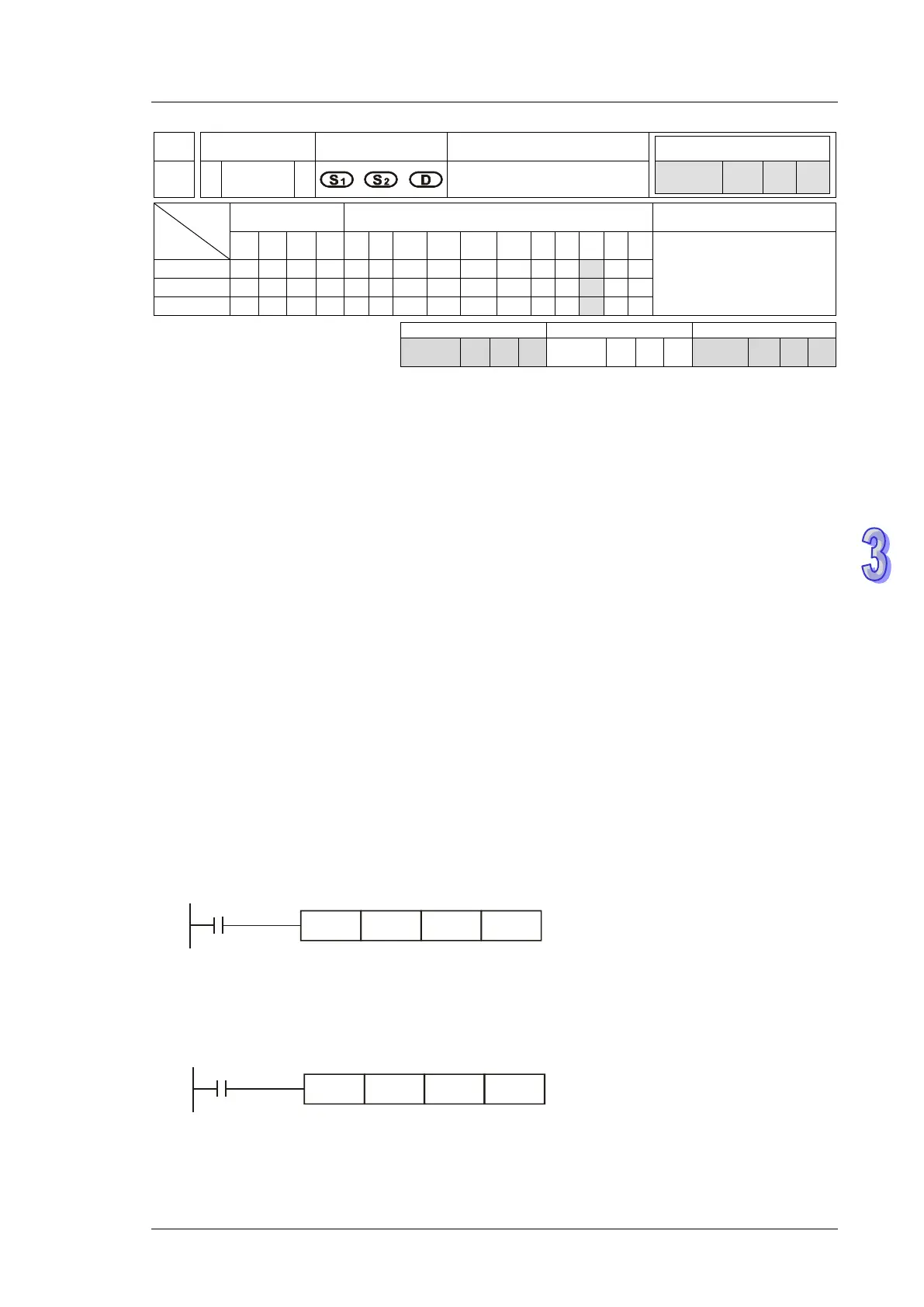
Mnemonic Operands Function
121 D
ESUB P
Floating point subtraction
Type
OP
Bit Devices Word devices Program Steps
X Y M S K H KnX
KnY
KnM
KnS
T C D E F
DESUB, DESUBP: 13
steps
SS2
SX2
SS2
SX2
SS2
SX2
Operands:
S
1
: Minuend S
2
: Subtrahend D: Subtraction result
Explanation:
1. S
1
− S
2
= D. The floating point value in S
2
is subtracted from the floating point value in S
1
and
the result is stored in D. The subtraction is conducted in binary floating point format.
2. If S
1
or S
2
is designated as constant K or H, the instruction will convert the constant into a binary
floating point value before the operation.
3. S
1
and S
2
can designate the same register. In this case, if the instruction is specified as
“continuous execution instruction” (generally DESUBP instruction) and the drive contact is ON,
the register will be subtracted once in every scan.
4. Flags: M1020 (Zero flag), M1021 (Borrow flag) and M1022 (Carry flag)
If absolute value of the result exceeds max. floating point value, carry flag M1022 = ON.
If absolute value of the result is less than min. floating point value, borrow flag M1021 = ON.
If the conversion result is 0, zero flag M1020 = ON.
Program Example 1:
When X0 = ON, binary floating point value (D1, D0) minuses binary floating point value (D3, D2) and
the result is stored in (D11, D10).
Program Example 2:
When X2 = ON, K1234 (automatically converted into binary floating point value) minuses binary
floating point (D1, D0) and the result is stored in (D11, D10).
 Loading...
Loading...