3. Instruction Set
API
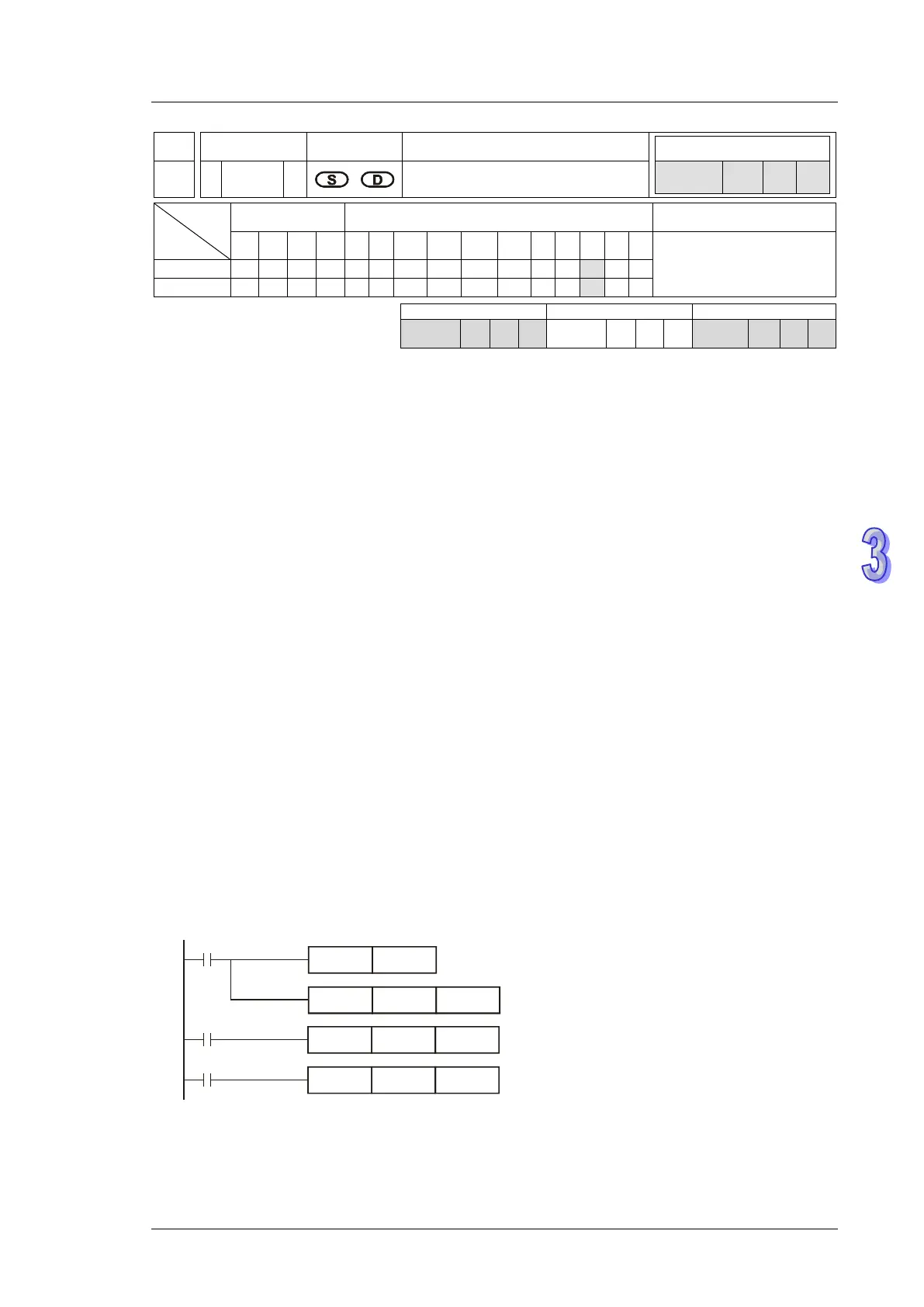
Mnemonic Operands Function
125 D
LN P
Float natural logarithm operation
Type
OP
Bit Devices Word devices Program Steps
X Y M S K H KnX
KnY
KnM
KnS
T C D E F
DLN, DLNP: 9 steps
SS2
SX2
SS2
SX2
SS2
SX2
Operands:
S: Source device D: Operation result
Explanations:
1. Perform natural logarithm (LN) operation on operand S:
LN[S +1, S ]=[ D +1, D ]
2. Only a positive number is valid for S. Register D has to be 32-bit format. Operation is conducted
in floating point value, so the value in S needs to be converted into floating value before natural
logarithm operation.
3. e
D
= S. The content of D = LN S, where the value in S is specified by users.
4. Flags: M1020 (Zero flag), M1021 (Borrow flag) and M1022 (Carry flag).
If absolute value of the result is larger than max. floating value, carry flag M1022 = ON.
If absolute value of the result is smaller than min. floating value, borrow flag M1021 = ON.
If the conversion result is 0, zero flag M1020 = ON
Program Example:
1. When M0 = ON, convert (D1, D0) to binary floating value and save the result in (D11, D10).
2. When M1= ON, perform natural logarithm operation with (D11, D10) as the antilogarithm. The
value is saved in register (D21, D20) in binary floating format.
3. When M2 = ON, convert the value in (D21, D20) into decimal floating point value and save the
result in (D31, D30). (At this time, D31 indicates powers of 10 for D30)
M0
RST M1081
M1
DLN D10 D20
M2
DEBCD D20 D30
DFLT D0 D10
 Loading...
Loading...