#reboot
Example
As an alternative to steps 2-4:
1. Execute the command:
export FIRMWARE_FLASH_NOW=1
2. Execute the command:
rpm -i firmware-intelligentprovisioning-ip-<version>.x86_64.rpm
About RAID arrays
RAID arrays can help increase system performance and reduce the risk of drive failure. You can create
RAID arrays with drives with different specifications, but performance will be based on the smallest drive
or lowest speed. For example, if you create an array with a 1 TB drive and a 2 TB drive, then the array
can store a maximum 1 TB of data. The extra storage on the larger drive is not available until you
reformat the drive.
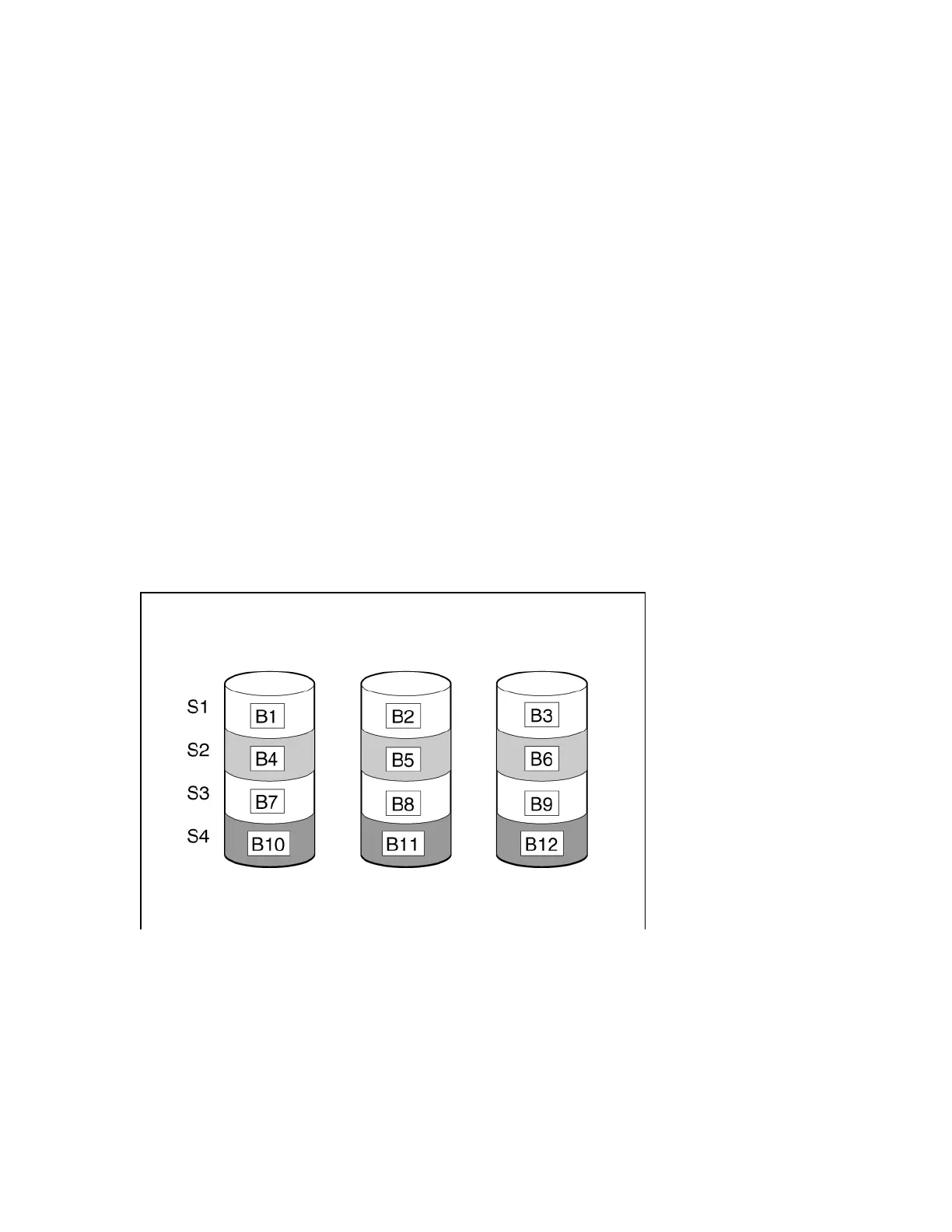
RAID 0
A RAID 0 configuration provides data striping, but there is no protection against data loss when a drive
fails. However, it is useful for rapid storage of large amounts of noncritical data (for printing or image
editing, for example) or when cost is the most important consideration. The minimum number of drives
required is one.
This method has the following benefits:
• Useful when performance and low cost are more important than data protection.
• Has the highest write performance of all RAID methods.
• Has the lowest cost per unit of stored data of all RAID methods.
• All drive capacity is used to store data (none allocated for fault tolerance).

 Loading...
Loading...











