Stimulus-Response Measurements
Note
This application should only be performed using an HP 8590L or HP 85913 with
Option 010 or 011, or using an HP 85933, HP 85943, HP 85953, or HP 85963
with Option 010.
What Are Stimulus-Response Measurements?
Stimulus-response measurements require a source to stimulate a device under test (DUT), a
receiver to analyze the frequency-response characteristics of the DUT, and, for return-loss
measurements, a directional coupler. Characterization of a DUT can be made in terms of its
transmission or reflection parameters. Examples of transmission measurements include flatness
and rejection. A reflection measurement is return loss.
A spectrum analyzer combined with a tracking generator forms a stimulus-response
measurement system. With the tracking generator as the swept source and the spectrum
analyzer as the receiver, operation is analogous to a single-channel scalar network analyzer.
A narrow-band system has a wide dynamic measurement range, but the tracking generator’s
output frequency must be made to precisely track the spectrum analyzer input frequency. This
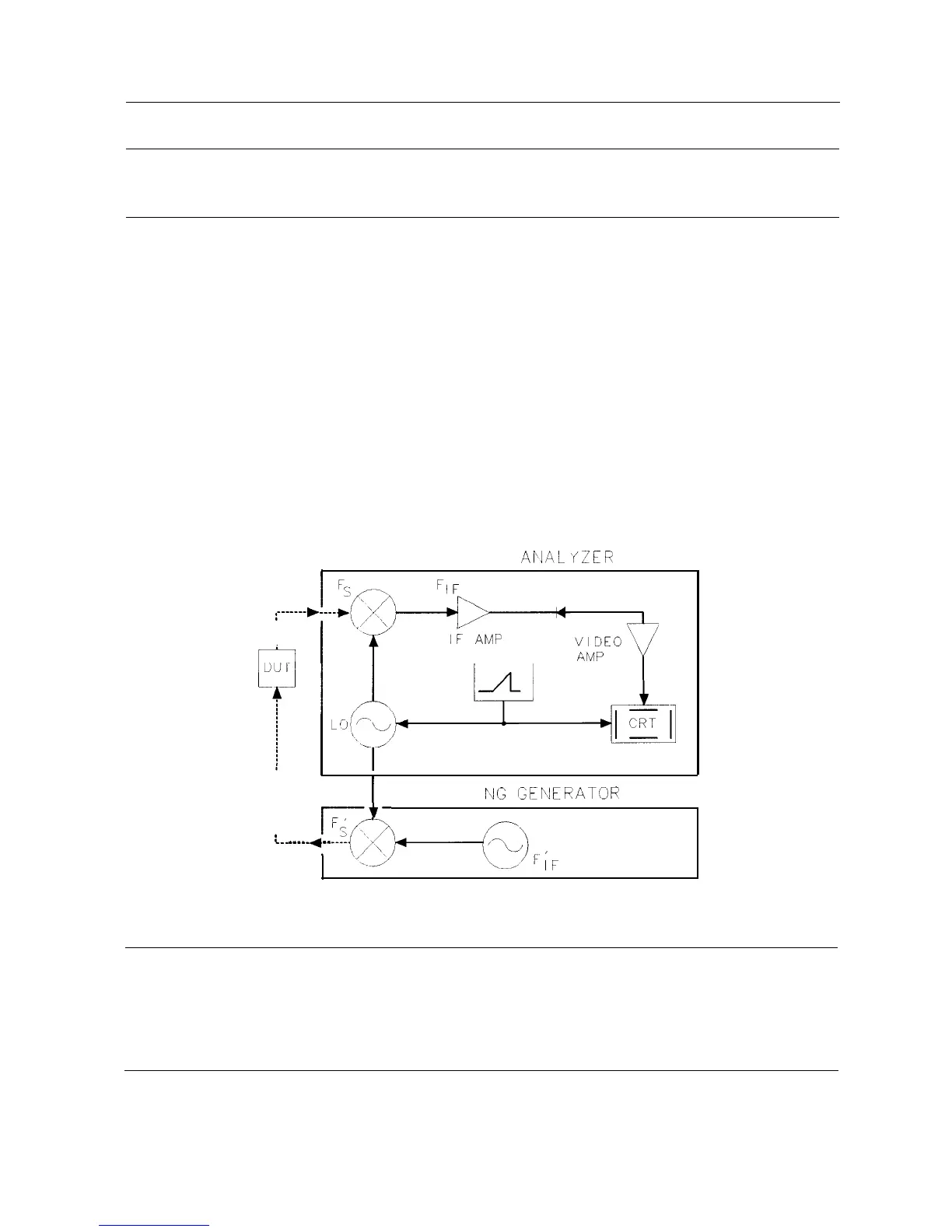
wide dynamic range will be illustrated in the following example. Figure 4-3 shows the block
diagram of a spectrum analyzer and tracking-generator system.
SPECTRUM
AI‘JAL
YZER
I
:‘---)
~-~~~2~~
I
T
\’
2-+-gg
Ii
AMP
-i
I
TRACK I
r\iG
GEI\IERATOR
v
L..
____
4
------
Fi\,;;~9-fgF.
;F
Figure 4-3.
Block Diagram of a Spectrum Analyzer/Tracking-Generator Measurement System
Note
The HP 85630A Transmission/Reflection Test Set with the HP 85714A Scalar
Measurement Personality is recommended for making transmission and
reflection measurements with your spectrum analyzer. The scalar measurement
personality provides simple menu-driven functions to make fast, accurate
scalar network analysis measurements with your spectrum analyzer and test
set.
Making Measurements 4-7

 Loading...
Loading...